SMARCA4
-
Official Full Name
SWI/SNF related, matrix associated, actin dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily a, member 4 -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the SWI/SNF family of proteins and is similar to the brahma protein of Drosophila. Members of this family have helicase and ATPase activities and are thought to regulate transcription of certain genes by altering the chromatin structure around those genes. The encoded protein is part of the large ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complex SNF/SWI, which is required for transcriptional activation of genes normally repressed by chromatin. In addition, this protein can bind BRCA1, as well as regulate the expression of the tumorigenic protein CD44. Mutations in this gene cause rhabdoid tumor predisposition syndrome type 2. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2012] -
Synonyms
SMARCA4;SWI/SNF related, matrix associated, actin dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily a, member 4;BRG1;SNF2;SWI2;MRD16;RTPS2;BAF190;SNF2L4;SNF2LB;hSNF2b;BAF190A;transcription activator BRG1;SNF2-beta;SNF2-like 4;protein BRG-1;nuclear protein GRB1;brahma protein-like 1;BRM/SWI2-related gene 1;homeotic gene regulator;protein brahma homolog 1;BRG1-associated factor 190A;sucrose nonfermenting-like 4;ATP-dependent helicase SMARCA4;mitotic growth and transcription activator;global transcription activator homologous sequence
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Rat
- E.coli
- Insect Cells
- Sf9 Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- Insect cells
- Yeast
- HEK293
- GST
- Flag
- His
- Non
- Avi
- MBP
- Fc
Background
What is SMARCA4 protein?
SMARCA4 gene (SWI/SNF related, matrix associated, actin dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily a, member 4) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 19 at locus 19p13. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the SWI/SNF family of proteins. The encoded protein is part of the large ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complex SNF/SWI, which is required for transcriptional activation of genes normally repressed by chromatin. In addition, this protein can bind BRCA1, as well as regulate the expression of the tumorigenic protein CD44. The SMARCA4 protein is consisted of 1647 amino acids and SMARCA4 molecular weight is approximately 184.6 kDa.
What is the function of SMARCA4 protein?
The SMARCA4 protein, also known as SNF2L or BRG1, is a subunit that plays a catalytic role in the SWI/SNF complex, an ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complex. It regulates gene transcription, cell cycle, DNA replication, DNA repair, and stress response by using energy from ATP hydrolysis to restructure chromatin structure or alter chromosome structure. In cancer, the role of SMARCA4 is context-dependent, and it can act as a tumor suppressor or tumor promoter. Notably, the subunit of the SWI/SNF complex is mutated in more than 20% of human cancers and is one of the most common mutated chromatin modifying factors in the human body.
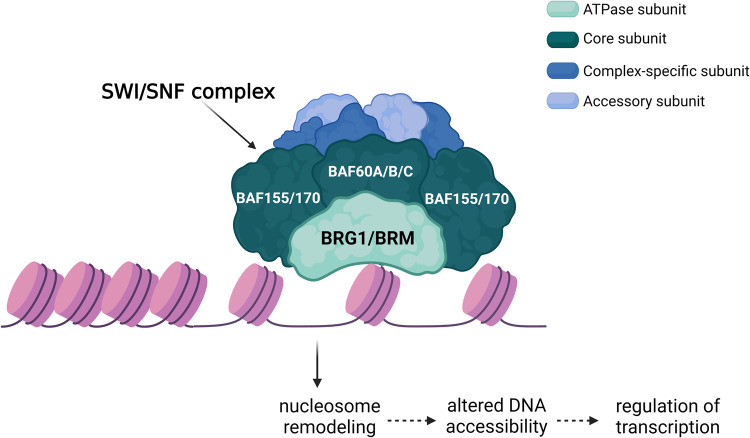
Fig1. The SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex regulates gene expression. (Sophie M Navickas, 2023)
SMARCA4 related signaling pathway
In terms of signaling pathways, the SWI/SNF complex functions mainly include the following: interacting with other transcription factors and co-activators or co-repressors, thereby affecting the transcriptional activity of specific genes. Involved in cell cycle regulation by influencing the expression of genes associated with cell proliferation and division. It plays a role in DNA damage repair and helps maintain genomic stability. It may interact with other important signaling pathways, such as Wnt and p53, and affect intracellular signaling and gene expression programs.
SMARCA4 related diseases
The SMARCA4 protein has been implicated in a variety of diseases, particularly non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In NSCLC, mutations in SMARCA4 are associated with poor prognosis, and its loss of expression is associated with increased tumor aggressiveness and metastatic ability. The majority of NSCLC patients with SMARCA4 mutation are middle-aged men. Adenocarcinoma is a common pathological type, and patients with EGFR mutation have a better prognosis, while those with KRAS mutation have a worse prognosis. In addition, mutations in SMARCA4 also co-occur with other genes such as TP53 and ERBB2, which affect the prognosis of patients.
Bioapplications of SMARCA4
SMARCA4 proteins play an important role in a variety of biomedical applications, especially in the field of cancer therapy. In non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), mutations in SMARCA4 are associated with tumor aggressiveness and poor prognosis, suggesting that it may play a role as a tumor suppressor gene in lung cancer development. In addition, abnormal expression of SMARCA4 has also been associated with other types of cancer, including ovarian cancer, endometrial cancer, and certain rare tumors such as SmarCA4-deficient undifferentiated tumors. These tumors are often insensitive to conventional chemotherapy but may respond to immunotherapy, suggesting that the state of SMARCA4 may serve as a biomarker to predict tumor response to a specific treatment. Therefore, SMARCA4 not only has potential value in the diagnosis and prognostic evaluation of cancer, but may also be a target for the development of new therapeutic strategies.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Yuwen Zhu, 2023
Liver fibrosis, which can lead to end-stage diseases like hepatocellular carcinoma and cirrhosis, is driven by myofibroblasts originating from hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). This study explores how the Brahma-related gene 1 (BRG1), a product of the Smarca4 gene, controls the HSC-to-myofibroblast transition, which is crucial for fibrosis. The results showed that increased BRG1 expression during HSC maturation in cells, animal models, and human cirrhotic liver samples. Targeted disruption of BRG1 in HSCs reduced liver fibrosis across animal models, and its absence in myofibroblasts also improved the condition. RNA sequencing revealed IGFBP5 as a new BRG1 target; its overexpression counteracted BRG1 loss in myofibroblast activation, while its knockdown inhibited HSC transition and liver fibrosis in mice. IGFBP5 was shown to interact with Bat3, stabilizing the Bat3-TβR complex and maintaining TGF-β signaling.
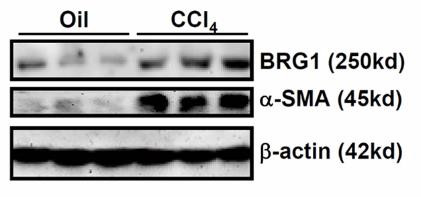
Fig1. Primary HSCs were isolated and gene expression was examined by Western blotting.
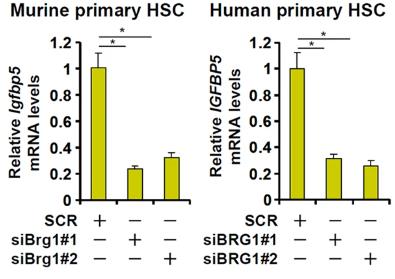
Fig2. Primary human/murine HSCs were transfected with siRNA targeting BRG1 or scrambled siRNA (SCR).
Case Study 2: Yinan Wang, 2021
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is a highly aggressive brain cancer with limited treatment options. This study reveals that BRG1, a component of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex, plays a key role in GBM malignancy. Although BRG1 is widely present in GBM tumors and associated with high expression in certain tumor regions, its knockout using CRISPR-Cas9 slightly affects cell growth but markedly reduces cell migration, invasion, and enhances the response to the chemotherapeutic drug temozolomide (TMZ). This suggests that targeting BRG1 could improve GBM treatment by increasing chemosensitivity and hindering tumor spread.
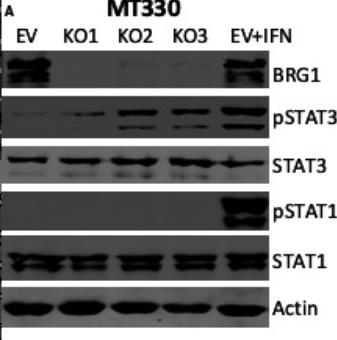
Fig3. The effect of BRG1-KO on the tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT3 in GBM cells.
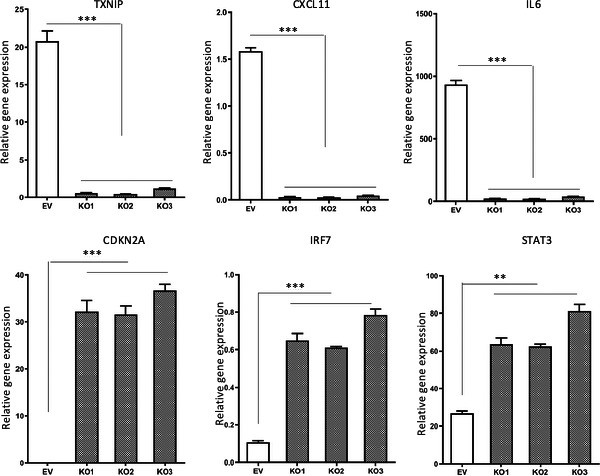
Fig4. The effects of BRG1-KO on expression of STAT3 target genes.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (SMARCA4-2861H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (SMARCA4-5521H)
Involved Pathway
SMARCA4 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways SMARCA4 participated on our site, such as Chromatin modifying enzymes,Chromatin organization,Direct p53 effectors, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with SMARCA4 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Prostate Cancer | ACTL6B,MAP2K1,GRB2,Ar,INS1,ARID1A,CASP9,CPN1,Pdgfa&Pdgfb,PIK3CA |
| Direct p53 effectors | PRDM1,FOXA1,PCBP4,EPHA2,PLK3,NDRG1,CTSD,CD82,DUSP1,TRIAP1 |
| RMTs methylate histone arginines | SMARCC1B,ARID1A,SMARCC1,PBRM1L,SMARCB1A,PRMT6,PRMT7,SMARCC2,SMARCA2,ARID2 |
| Glucocorticoid receptor regulatory network | KRT17,CSN2,EGR1,NR1I3,SMARCC2,KRT5,KRT14,BGLAP,SMARCD1,POU2F1 |
| Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex | BCL9,TLE1,TLE3,PYGO1,H3F3B.1,CDC73,RBBP5,H3F3D,PYGO2,BCL9L |
| Chromatin organization | PAX3A,DPY30,SUZ12,SMYD2,C3orf75,ARID4A,SETD3,JADE1,MSL2B,CHD4 |
| Chromatin modifying enzymes | SMARCE1,MTA1,ATXN7L3,MSL2,SMARCD3,ING5B,PRDM16,KAT7,SAP30,C20orf20 |
| Integrated Breast Cancer Pathway | ERAL1,PLK3,CCNB1IP1,DHTKD1,DAG1,SELK,GRN,LGALS13,AHR,USP16 |
Protein Function
SMARCA4 has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,DNA polymerase binding,DNA-dependent ATPase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by SMARCA4 itself. We selected most functions SMARCA4 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with SMARCA4. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| transcription corepressor activity | LOXL2,WTIP,HOMEZ,TAF9B,ZHX1,NAB2,SUFU,MXD4,RUNX1T1,CBFA2T2 |
| transcription factor binding | MECP2,KCTD1,GPX3,ARNT,CEBPA,SORBS3,MED12L,FOXC1,NKX3,LEF1 |
| Tat protein binding | NPM1,ACTB,TRIM32,DLL1,MDFIC,GABARAPL1,SMARCB1 |
| RNA polymerase II transcription coactivator activity | PHF17,POU3F2,MEF2A,NEUROD1,MED12L,CITED2,SOX4,SOX12,PRRX1,CREBBP |
| transcription coactivator activity | TAF7,LPIN2,CCNE1,PER2,SMARCA2,NEUROD1,EP300,CD3D,CALCOCO1,KMT2E |
| contributes_to RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific DNA binding | RBBP4,HDAC1,ACTL6A,ACTB,GATAD2B,SMARCC2,SMARCC1,SMARCB1,HDAC2,MTA2 |
| androgen receptor binding | PRPF6,KDM4C,WIPI1,EP300,CALR,PIAS1,PIAS2,CDK7,NSD1,CCNE1 |
| contributes_to RNA polymerase II distal enhancer sequence-specific DNA binding | HDAC1,RBBP4,SMARCB1,ACTB,GATAD2B,SMARCE1,MTA2,MBD3,SMARCC2,SMARCC1 |
| lysine-acetylated histone binding | TAF1,BRDT,TAF1L,PSME4B,CARM1,BRD2,BAZ1B,BRD4,BRD9,PSME4 |
Interacting Protein
SMARCA4 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with SMARCA4 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of SMARCA4.
ARID1A
Resources
Research Area
Tumor SuppressorsSWI/SNF Family
Neural Stem Cell Transcription Factors
Epigenetics and EMT
Neural Stem Cell Markers
Related Services
Related Products
References


