RGN
-
Official Full Name
regucalcin (senescence marker protein-30) -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a highly conserved, calcium-binding protein, that is preferentially expressed in the liver and kidney. It may have an important role in calcium homeostasis. Studies in rat indicate that this protein may also play a role in aging, as it shows age-associated down-regulation. This gene is part of a gene cluster on chromosome Xp11.3-Xp11.23. Alternative splicing results in two transcript variants having different 5 UTRs, but encoding the same protein. -
Synonyms
RGN;regucalcin (senescence marker protein-30);regucalcin;RC;senescence marker protein 30;SMP30;Gluconolactonase;GNL;RGN_HUMAN;SMP 30;SMP-30;OTTHUMP00000023195;OTTHUMP00000023196;senescence marker protein-30
Recombinant Proteins
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Chicken
- Mammalian Cells
- E.coli
- Human
- HEK293
- Yeast
- His
- T7
- Non
- SUMO
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is RGN Protein?
RGN, or regucalcin, is a protein that plays a key role in calcium regulation within cells. Think of it as a sort of traffic controller, helping to direct various cellular processes by managing calcium levels. This protein is not only important for maintaining metabolic balance but is also involved in other crucial functions like DNA synthesis and cell proliferation. Research shows that it can have protective effects against cell stress by limiting excessive calcium entry, which is crucial since too much calcium can lead to problems like cell death. In fact, regucalcin's ability to manage internal calcium levels makes it a point of interest in studying conditions like cancer, where its functions may become disrupted, leading to cell growth issues. Scientists are paying close attention to regucalcin in hopes of unveiling more about its potential therapeutic impact on diseases.What is the Function of RGN Protein?
Regucalcin, often abbreviated as RGN, is a protein that plays a big role in keeping calcium levels balanced within cells. It's like a regulator, making sure everything stays in check, which is super important for cell functions like growth, DNA replication, and even preventing cell death. This protein helps control cell signaling pathways and can shield cells from stress by stopping too much calcium from entering. This is crucial because having excess calcium can lead to cellular problems or damage. RGN also takes part in metabolic processes, keeping things running smoothly. With its broad reach, RGN has become a key focus in diseases like diabetes, osteoporosis, and cancer, where its normal activity might be disrupted. Researchers are keen on exploring its full potential, as understanding how RGN works could open up new avenues for therapies or interventions in these and other diseases. This makes RGN a promising area of study in the quest to develop novel treatments.RGN Related Signaling Pathway
Regucalcin, or RGN, is involved in several signaling pathways that keep cells functioning smoothly. It plays a crucial role in managing calcium levels, making sure they don't go too high or too low, which is vital for cell growth, energy production, and gene activity. Beyond that, RGN also influences pathways that deal with oxidative stress and inflammation, helping cells avoid damage from things like reactive oxygen species. When these pathways go off track, it may lead to conditions like diabetes and cancer. Researchers are interested in RGN's potential for creating new treatments, as understanding how it works could make a big difference in managing these diseases.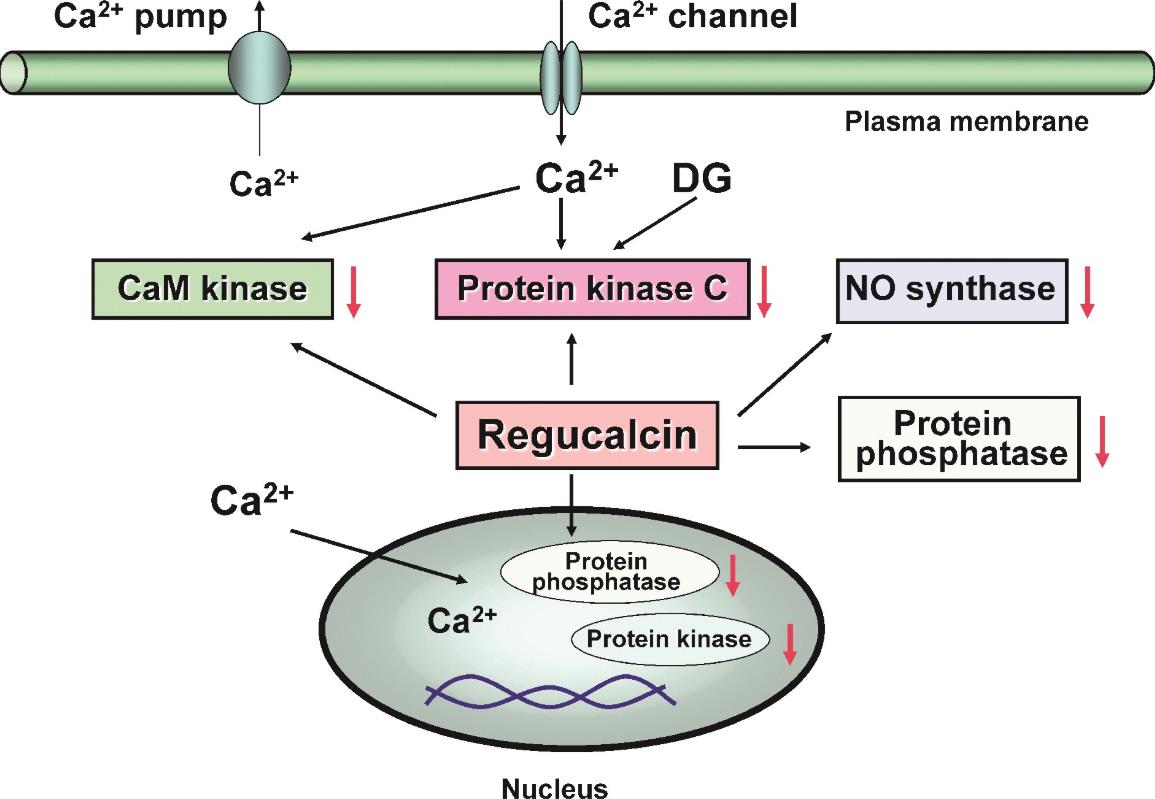
Fig1. Regucalcin suppresses the activity of Ca2+ signaling-related enzymes in brain neuronal cells. (Masayoshi Yamaguchi, 2012)
RGN Related Diseases
Regucalcin (RGN) is connected to various health issues because of its important role in cellular activities, especially in maintaining calcium balance. When RGN levels or function go awry, it can lead to several diseases. For instance, in diabetes, improper calcium regulation and signaling disruptions are key factors, and RGN's regulatory role might be off balance. In cancer, low RGN expression has been observed, contributing to tumor growth and spread by failing to keep cell proliferation in check. It's also linked to osteoporosis since calcium plays a big role in bone health, and RGN helps modulate calcium within bone cells. Researchers are diving into how RGN's regulation — or misregulation — affects these diseases, as identifying RGN-related pathways might offer novel insights for treatment. As they continue to explore its broader impact, the hope is to leverage this knowledge into developing new strategies for managing or even preventing these conditions.Bioapplications of RGN
Regucalcin (RGN) is becoming a hot topic in bioapplications due to its diverse roles in cells. Researchers are excited about its potential in regenerative medicine, especially for bone healing and growth, thanks to its role in calcium regulation. This makes it particularly interesting for tackling osteoporosis. RGN's ability to manage oxidative stress and inflammation opens doors for treating chronic conditions like diabetes and heart diseases. There's also buzz around its potential in cancer therapy since it seems to help slow down tumor growth. By digging into how RGN influences these processes, scientists hope to unlock new medical treatments that can lead to better health results and offer fresh approaches to battling various diseases.Case Study
Case Study 1: Yamaguchi M. et al. Int J Oncol. 2019
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a common kidney cancer. Lower levels of regucalcin, a protein that regulates genes, might aid cancer growth. Here regucalcin was reduced in cancerous kidney tissues but higher in those who survived longer, based on data. By increasing regucalcin in RCC cells, researchers halted their growth by blocking key signals and boosting tumor suppressors like p53. This suggests that enhancing regucalcin could be a new treatment approach for RCC.-
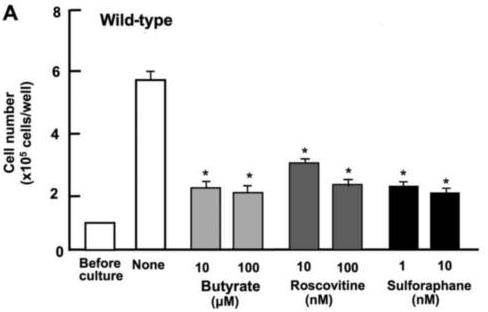 Fig1. Suppressive effects of regucalcin overexpression on the proliferation in A498 cells.
Fig1. Suppressive effects of regucalcin overexpression on the proliferation in A498 cells. -
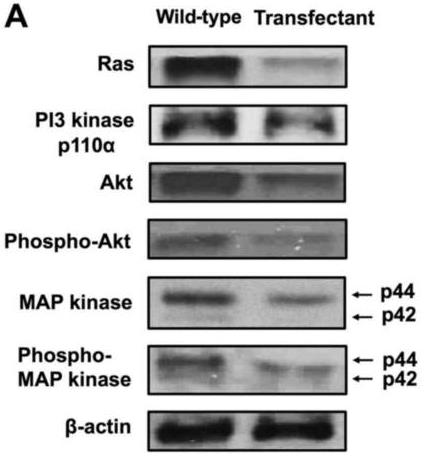 Fig2. Overexpression of regucalcin regulates various proteins implicated in cell signaling process and transcription activity in A498 cells in vitro.
Fig2. Overexpression of regucalcin regulates various proteins implicated in cell signaling process and transcription activity in A498 cells in vitro.
Case Study 2: Elsawy H. et al. Saudi J Med Med Sci. 2022
Deoxynivalenol (DON) is a toxic compound known for harming cells by causing inflammation and making reactive oxygen species go wild. Enter Ruscogenin (RGN), a natural compound with strong anti-inflammatory effects. This study checked how RGN could help protect cells from the damage DON causes, particularly through the Nrf2 pathway and regulated by PI3K/AKT. Using HepG2 cells, researchers found that RGN helped shield these cells from DON's harmful effects. It reduced inflammation markers like TNF-α and COX-2 and cut down on reactive oxygen species. RGN also boosted antioxidant defenses by increasing Nrf2 and other protective proteins and engaged the PI3K/AKT pathway. Plus, it helped prevent cell death by altering levels of certain proteins.-
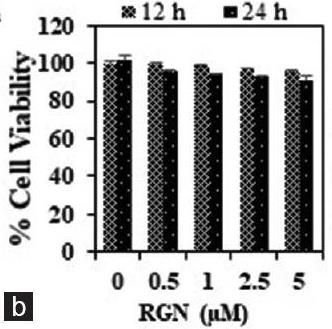 Fig3. Cell viability effect of RGN on HepG2.
Fig3. Cell viability effect of RGN on HepG2. -
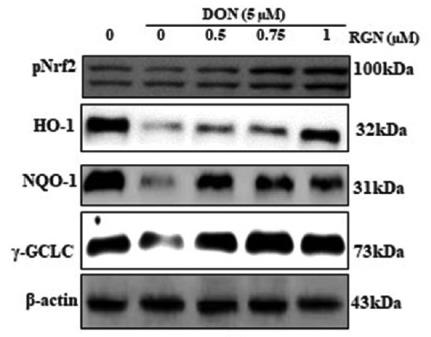 Fig4. RGN induces Nrf2 expression in DON-treated HepG2 cells.
Fig4. RGN induces Nrf2 expression in DON-treated HepG2 cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (RGN-6687H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (RGN-6687H) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (Rgn-8051M)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (Rgn-8051M)
Involved Pathway
RGN involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways RGN participated on our site, such as Pentose phosphate pathway,Ascorbate and aldarate metabolism,Metabolic pathways, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with RGN were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Pentose phosphate pathway | G6PD,ALDOAB,TKTL2,ALDOC,PFKP,PRPS1A,PGM1,DERA,TKTL1,PFKM |
| Ascorbate and aldarate metabolism | UGT5G1,UGT1A7C,UGT2A3,ALDH2.2,ALDH9A1,ALDH1B1,UGT1A7,UGT1A6,UGT1A1,UGT1A9 |
| Metabolic pathways | Cel,OGDHA,ALDH4A1,GALC,ATP6V0A1B,MAOB,CYP8B1,PEMT,QDPR,BCO1L |
| Degradation of aromatic compounds | ADH5,AKR1A1B,AKR1A1A,AKR1A1 |
| Carbon metabolism | GAPDH,PDHA1,ALDOCA,CPS1,GPT2,HADHAA,DLAT,ALDOCB,PDHA2,MDH1 |
-
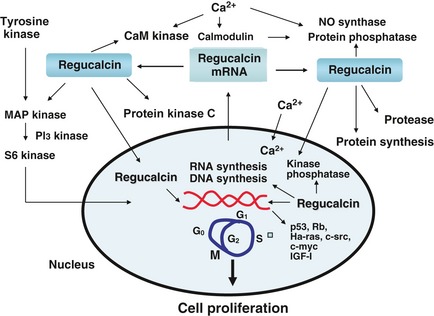 Fig1. Regucalcin suppresses promotion of cell proliferation
Fig1. Regucalcin suppresses promotion of cell proliferation -
 it is expressed via signalling factors that stimulate cell proliferation and translocation to the nucleus by mechanisms mediated through protein kinase C. (M Yamaguchi, 2013)
it is expressed via signalling factors that stimulate cell proliferation and translocation to the nucleus by mechanisms mediated through protein kinase C. (M Yamaguchi, 2013)
Protein Function
RGN has several biochemical functions, for example, calcium ion binding,enzyme regulator activity,gluconolactonase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by RGN itself. We selected most functions RGN had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with RGN. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| enzyme regulator activity | EIF2B1,PPP1R7,BRCC3,DPM2,APOC3,CPN2,PSMD3,DCP1B,RAB3GAP2,GCLM |
| zinc ion binding | TRAF5,RARB,LMCD1,ADH8B,RARAA,SP140,RNF43,PARP1,ZNF346,GFI1 |
| calcium ion binding | SYT7,PLCB1,LRP2A,CIB4,CDHR3,CALR3B,MAN1C1,EFCAB2,LDLRB,S100B |
Interacting Protein
RGN has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with RGN here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of RGN.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


