PTPN1
-
Official Full Name
protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 1 -
Overview
PTP1B is the prototypic member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family, which comprises at least 37 proteins. The family is characterized by a catalytic phosphatase domain of approximately 240 amino acids, and includes both transmembrane and cytosolic enzymes. The PTPs have high substrate specificity for phosphotyrosyl proteins. At the primary sequence level, PTPs share little similarity with the protein serine phosphatases, protein threonine phosphatases, or the acid and alkaline phosphatases. PTP1B is a negative regulator of insulin and leptin signal transduction and may be a potential therapeutic target for diabetes and obesity. Insulin also influences the expression of splice variants of PTP1B. -
Synonyms
PTPN1;protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 1;PTP1B;tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 1;protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B;protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B;protein tyrosine phosphatase, placental
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Chicken
- Zebrafish
- E.coli
- Sf9 Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- Insect Cells
- HEK293
- Non
- GST
- His
- Flag
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
Background
What is PTPN1 Protein?
PTPN1, also called PTP1B, is an enzyme from the protein tyrosine phosphatase family. It was discovered through its specific enzymatic functions and amino acid structure. PTP1B removes phosphate groups from tyrosine residues, using a conserved catalytic motif that's crucial for its action. It serves as a key inhibitor of insulin signaling by deactivating phosphotyrosine on the insulin receptor. Additionally, PTP1B affects the epidermal growth factor receptor and JAK2/TYK2 kinases, playing a part in regulating cell growth and how cells react to interferons. This protein is widely found in tissues like lymph nodes and the appendix. There are two forms of this gene, each encoding different versions of the protein.What is the Function of PTPN1 Protein?
PTPN1, or PTP1B, mainly functions by removing phosphate groups from the amino acid tyrosine on proteins, a process known as dephosphorylation. This action is crucial as it influences several cell signaling pathways. By deactivating parts of these pathways, PTP1B controls various functions like cell growth, metabolism, and how cells respond to hormones like insulin. In terms of insulin, PTP1B acts as a regulator that dampens the signal, playing a big role in managing blood sugar levels. Beyond insulin signaling, PTP1B also interacts with other important cellular proteins like the epidermal growth factor receptor and JAK kinases, impacting how cells grow and divide, and respond to other stimuli. In essence, PTP1B is a key regulator ensuring that cellular signals are fine-tuned for proper physiological responses.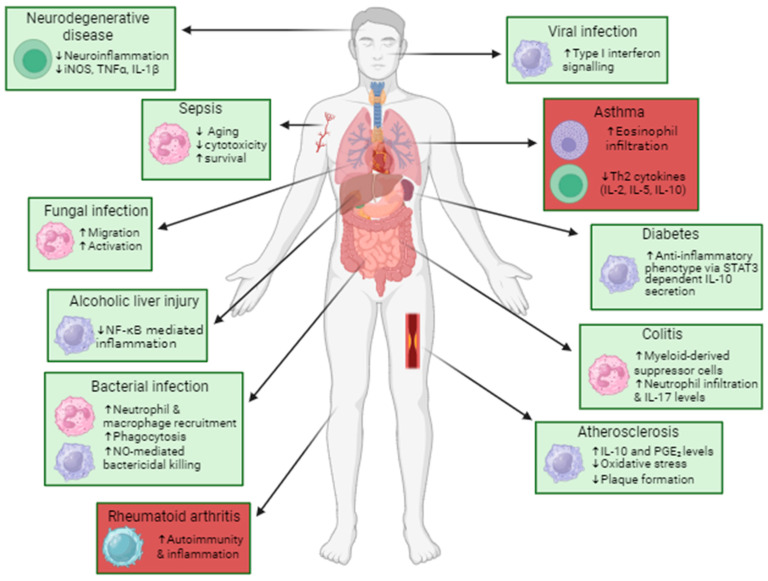
Fig1. Therapeutic potential of PTP1B inhibition in immune-mediated diseases. (Neve E Read, 2024)
PTPN1 Related Signaling Pathway
PTPN1, also known as PTP1B, is pivotal in several cellular signaling pathways. It plays a vital role by dephosphorylating tyrosine residues on proteins involved in signaling cascades. One of its primary functions is to act as a negative modulator of the insulin signaling pathway, which makes it crucial in controlling how the body manages glucose. By interacting with the insulin receptor, PTP1B ensures that the signaling is not excessively activated. Moreover, PTP1B is involved in regulating other pathways, such as those controlled by the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and the JAK/STAT pathway, both of which are important for cell growth and immune responses. Because it influences these key processes, PTP1B is an important target for drugs aimed at treating conditions like diabetes and cancer, where these signaling pathways may be dysregulated.PTPN1 Related Diseases
PTPN1, or PTP1B, is closely linked to several diseases, largely due to its role in regulating key signaling pathways. One of its most noted associations is with diabetes, particularly type 2 diabetes. By negatively regulating insulin signaling, PTP1B contributes to insulin resistance, making it a significant target for diabetes treatment research. Apart from diabetes, PTP1B has been implicated in obesity, as its expression can affect energy expenditure and fat storage. In the realm of cancer, PTP1B's role is twofold; it is involved in both promoting and suppressing tumor growth, depending on the cancer type and context. For instance, PTP1B can encourage cancer progression in breast and prostate cancers while acting differently in other tissues. Its diverse roles in these diseases make it an attractive target for developing drugs that could inhibit its activity to treat or manage these conditions more effectively.Bioapplications of PTPN1
The protein PTPN1, or PTP1B, finds promising bioapplications mainly due to its influence on major signaling pathways. In diabetes research, PTP1B is a popular target because it negatively regulates insulin signaling, offering pathways for improving insulin sensitivity and managing blood sugar levels. This makes it a potential drug target for developing diabetes therapies. In cancer treatment, PTP1B has a dual role. While it can support tumor growth in certain cancers, inhibiting it might halt cancer progression. Considering this, PTPN1 inhibitors are being explored as potential cancer therapies. Its regulatory effects on metabolic pathways also suggest PTPN1's involvement in obesity-related research, with hopes of developing treatments that can address metabolic syndromes more effectively. Hence, PTPN1 holds significant potential in therapeutic advancements for metabolic and cancer-related diseases.Case Study
Case Study 1: Liu R. et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022
Human protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) acts as a key player for downregulating crucial phosphorylation pathways like those of insulin and EGFR. It's becoming clear that PTP1B is quite involved in cancer development. Some genetic defects in PTP1B are found in cancers, especially B cell and Hodgkin's lymphomas. In this research, they looked into three PTP1B mutations in a type of lymphoma affecting key enzyme regions: WPD-loop (V184D), P-loop (R221G), and Q-loop (G259V). These mutations resulted in a notable drop in enzyme activity, affected protein stability, and altered how the enzyme's active site works. This highlights the importance of these loops in engaging with substrates and helping the reaction along.-
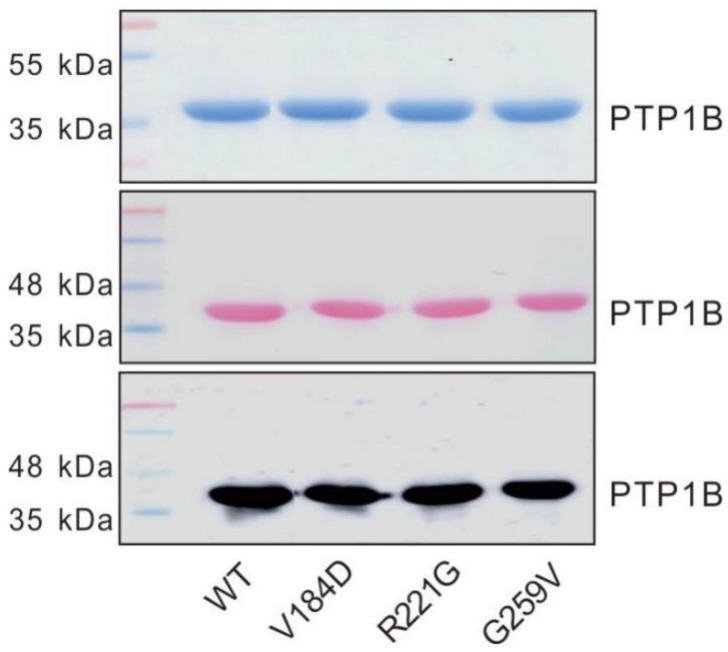 Fig1. Purification of the PTP1B proteins in the WT and mutants.
Fig1. Purification of the PTP1B proteins in the WT and mutants. -
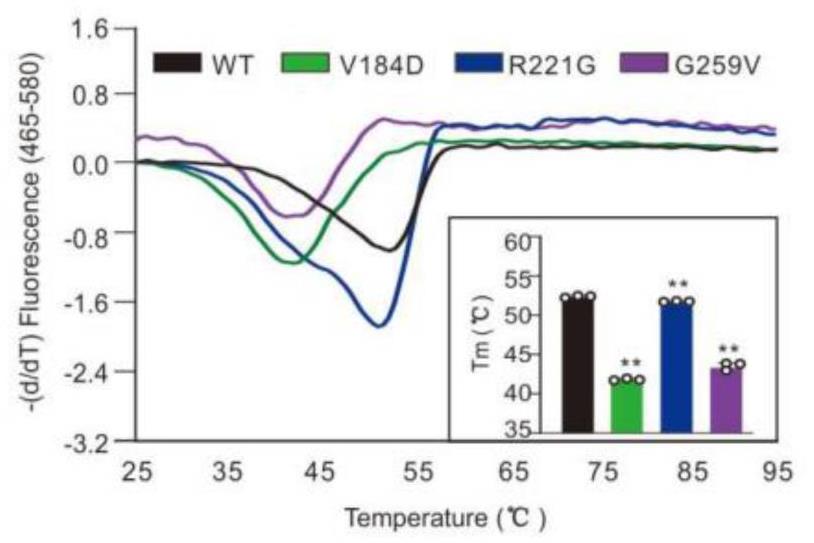 Fig2. Thermal shift assay of the PTP1B proteins (5 µM) in the presence of 10 X SYPRO in the WT and mutants.
Fig2. Thermal shift assay of the PTP1B proteins (5 µM) in the presence of 10 X SYPRO in the WT and mutants.
Case Study 2: Wang Q. et al. Bioengineered. 2021
Research has shown that protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) pushes tumor growth in cancers like breast, colon, and prostate. Surprisingly, it acts as a tumor suppressor in esophageal cancer and lymphoma, making it a complex player in cancer dynamics. While its role in malignant melanoma (MM) wasn't clear, our study explored it further. We checked PTP1B levels in normal and melanoma tissues and found higher expression in melanoma, which linked to worse patient outcomes. Lab tests showed that blocking PTP1B reduces, while boosting it increases, melanoma cell movement and invasion. PTP1B seems to aid melanoma spread by interacting with Src, a pivotal protein, helping its activation by dephosphorylating Src at a specific site. These findings highlight PTP1B's potential as a target for treatments against melanoma.-
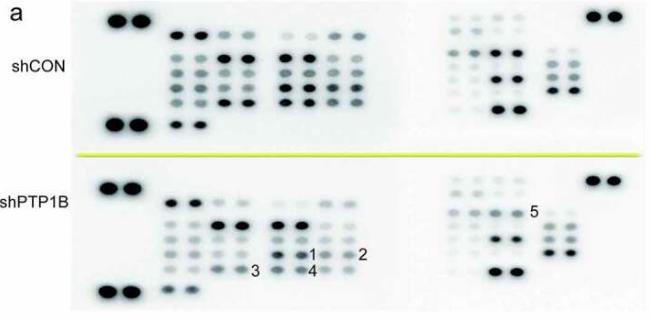 Fig3. Phosphorylation levels of proteins in A2058 cells with knockdown of PTP1B were detected in the Human Phospho-Kinase Array.
Fig3. Phosphorylation levels of proteins in A2058 cells with knockdown of PTP1B were detected in the Human Phospho-Kinase Array. -
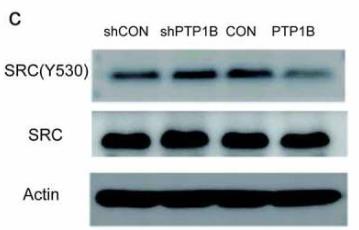 Fig4. The phosphorylation level of Src Tyr530 was detected in cells with knockdown or overexpression of PTP1B.
Fig4. The phosphorylation level of Src Tyr530 was detected in cells with knockdown or overexpression of PTP1B.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PTPN1-31256TH)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PTPN1-31256TH) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (PTPN1-1914H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (PTPN1-1914H)
Involved Pathway
PTPN1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PTPN1 participated on our site, such as Adherens junction,Insulin signaling pathway,Insulin resistance, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PTPN1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Adherens junction | FER,PVRL1,TGFBR1B,FYN,PVRL1B,SMAD3A,LEF1,TGFBR2,EGFRA,PTPRB |
| Insulin signaling pathway | RPS6,PYGMA,PIK3R2,AKT3A,FLOT1B,PPARGC1A,INPPL1A,PIK3CB,MAP2K2A,PPP1CA |
| Insulin resistance | RPS6KA6,PPP1CAA,CREB1A,RPS6KA3B,GSK3AA,STAT3,RPS6KB1B,PIK3R5,RPS6KA1,NR1H2 |
-
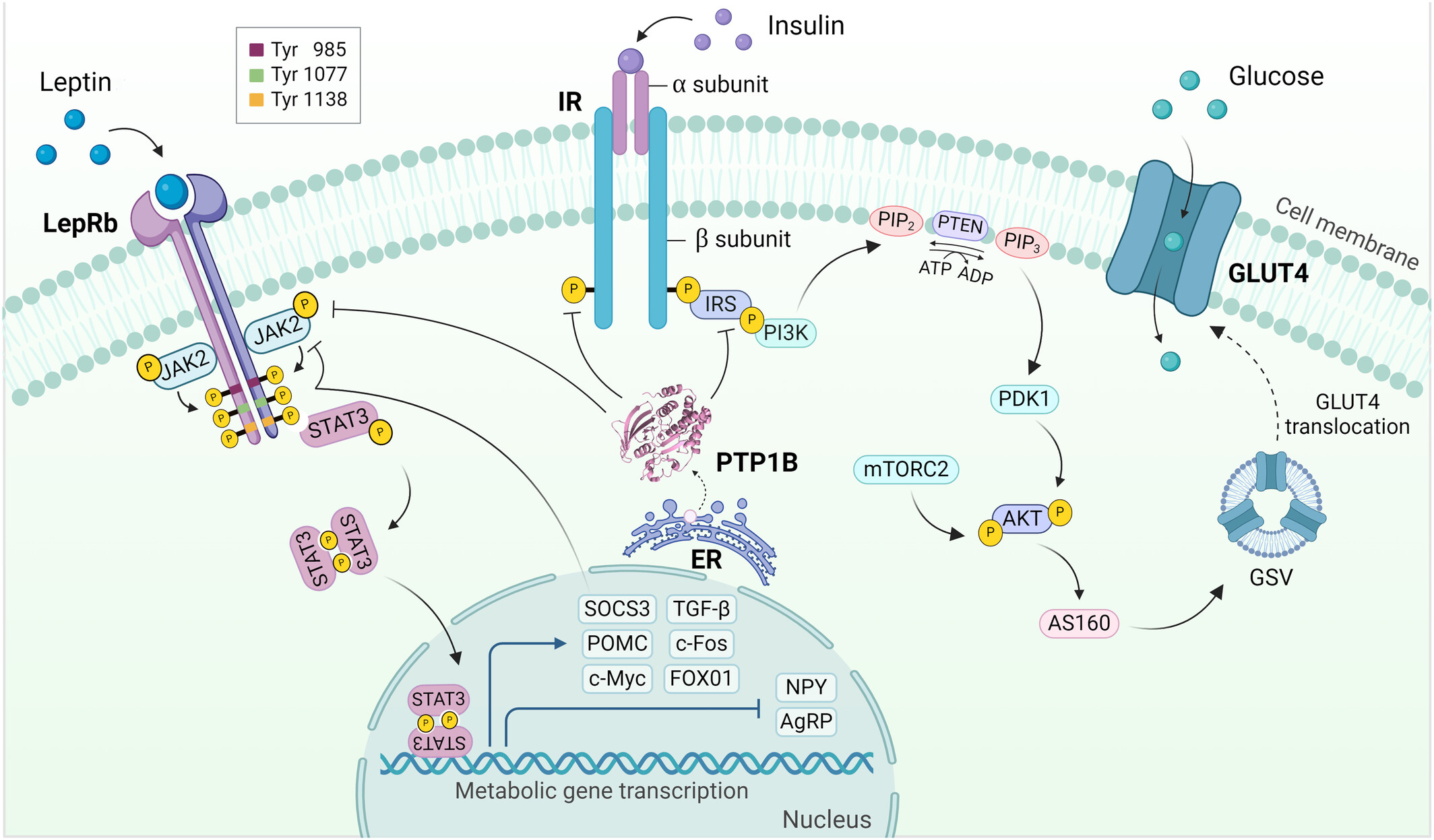 Fig1. Main physiological functions and signaling pathways modulated by PTP1B. (Andrea Coronell-Tovar, 2024)
Fig1. Main physiological functions and signaling pathways modulated by PTP1B. (Andrea Coronell-Tovar, 2024) -
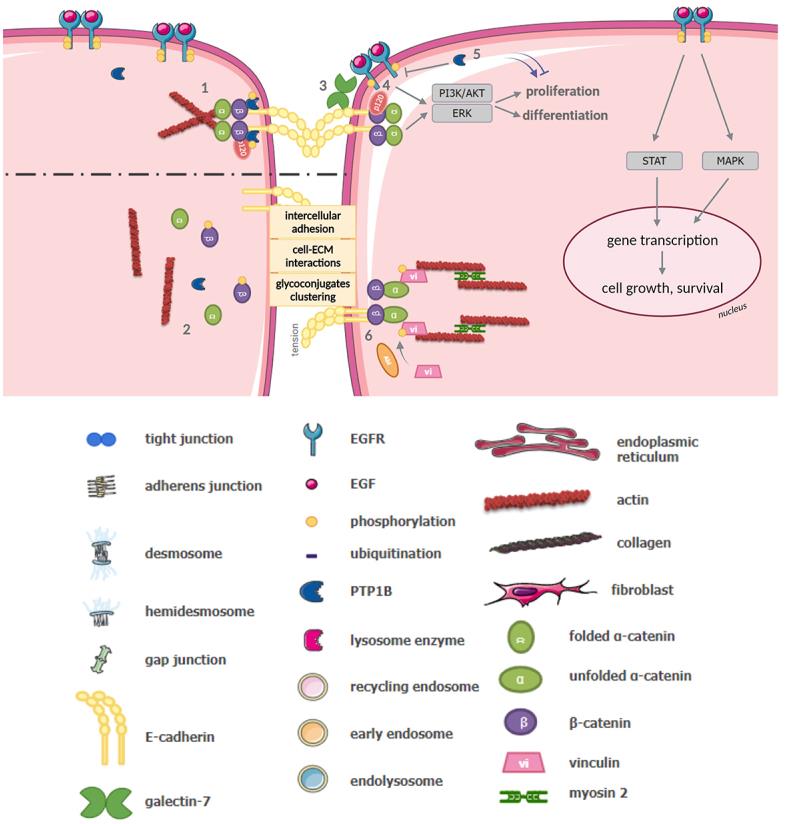 Fig2. Overview of EGFR, E-Cadherin and PTP1B interactions, and their roles in the maintenance of AJ and intracellular signaling. (Tessa Arnaud, 2023)
Fig2. Overview of EGFR, E-Cadherin and PTP1B interactions, and their roles in the maintenance of AJ and intracellular signaling. (Tessa Arnaud, 2023)
Protein Function
PTPN1 has several biochemical functions, for example, enzyme binding,ephrin receptor binding,insulin receptor binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PTPN1 itself. We selected most functions PTPN1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PTPN1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| insulin receptor binding | DOK4,IRS4,FRS2,IGF2,DOK2,SNX4,DOK1,IGF1,DOK7,DOK5 |
| receptor tyrosine kinase binding | ELMO2,GNB2L1,SHC4,LRP4,TRP53,GAS6,PTPN11,ZFP259,NRG3,NRG1 |
| protein phosphatase 2A binding | PPP2R4,ENSA,MASTL,RPS6KB1,PPME1,TP53,HMGCR,SMG5,STRN,GRIN3A |
| enzyme binding | PEX7,PAWR,NR5A1,Il6ra,PRKDC,STC2,APOA5,GSTM7,CDK19,PIAS3 |
| zinc ion binding | TRIM35-30,TRIM35-31,CNBP,RNF150A,TRIM35-27,ADAM30,POLR1A,GTF2B,TMEM163,PHF2 |
| protein binding | CCNL2,SOX4,WAC,FAM107A,PIK3R3,SOX17,TMEM173,SAE1,CTTN,PDCL3 |
| protein kinase binding | LIMS1,CCNYL1,FGR,AP2A1,FBXO7,KIF20A,TBC1D14,PTPRK,RHOD,CDKN2C |
| poly(A) RNA binding | SURF6,GFM1,G3BP2,KIF1C,C1orf53,EIF2S2,PFN1,WBP11,POLR2B,PES1 |
| protein tyrosine phosphatase activity | MTMR7A,PTPN11B,DUSP21,PTPRU,DUSP10,PTPRK,PTPRC,DUSP4,PTPN9,MTMR4 |
Interacting Protein
PTPN1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PTPN1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PTPN1.
INSR
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References



