NOTUM
-
Official Full Name
notum pectinacetylesterase homolog -
Synonyms
NOTUM;notum pectinacetylesterase homolog (Drosophila);protein notum homolog
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- His
- DDK
- Myc
- Non
- Flag
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is NOTUM protein?
NOTUM (notum, palmitoleoyl-protein carboxylesterase) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the chromosome 17 at locus 17q25. NOTUM is known to remove an essential palmitoleate group from Wnt proteins, which is crucial for the regulation of Wnt signaling. NOTUM has carboxylesterase activity and is involved in protein depalmitoleylation, acting on Wnt proteins to regulate their function. NOTUM is expressed in various tissues, including the liver and brain in mice, as shown by RNAscope technology. NOTUM is crucial for tooth dentin development in mice, and studies are investigating its effects on odontoblasts, which are cells responsible for the formation of dentin. The NOTUM protein is consisted of 496 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 55.7 kDa.
What is the function of NOTUM protein?
NOTUM has been shown to shape the Wingless morphogen gradient during development. NOTUM is involved in the regulation of intestinal stem cell function. It is produced by Paneth cells and can attenuate the regeneration of aged intestinal epithelium. NOTUM has been implicated in metabolic processes, with studies showing that it can promote thermogenic capacity and protect against diet-induced obesity and improve glucose homeostasis in mice. NOTUM's activity may influence the regenerative capacity of tissues, particularly in the context of aging, as it affects the Wnt signaling pathway which is known to play a role in tissue repair and stem cell maintenance.
NOTUM Related Signaling Pathway
NOTUM regulates Wnt activity by hydrolyzing the palmitoyl moiety from Wnt proteins, which is essential for their function. This action makes the Wnt proteins more hydrophilic and unable to bind to their cognate receptors, such as Frizzled receptors. NOTUM is tethered to the cell surface by binding to Glypican-like sulfated proteoglycans and functions as a Glypican-dependent Wnt inhibitor. This interaction is important for its role in regulating Wnt signaling. NOTUM induces the release of cell surface glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored proteins, such as Glypican-3, Cadherin-13, and uPAR, which can have broader implications for cell signaling and cell-cell interactions.
NOTUM Related Diseases
NOTUM is mentioned in the context of acute myeloid leukemia, suggesting a potential role in the development or progression of this type of cancer. NOTUM is also associated with glioma, a type of brain cancer, where it may play a role in the disease's pathology. NOTUM has been linked to osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weak and brittle bones, potentially through its effects on Wnt signaling, which is important for bone metabolism. NOTUM gene expression is increased in gastric cancer tissue, and its expression is correlated with lymph node metastasis, TNM staging, and prognosis, indicating its potential role in the disease's progression. NOTUM is overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma, a type of liver cancer, and is regulated transcriptionally by β-catenin/TCF, suggesting its involvement in the progression of this cancer.
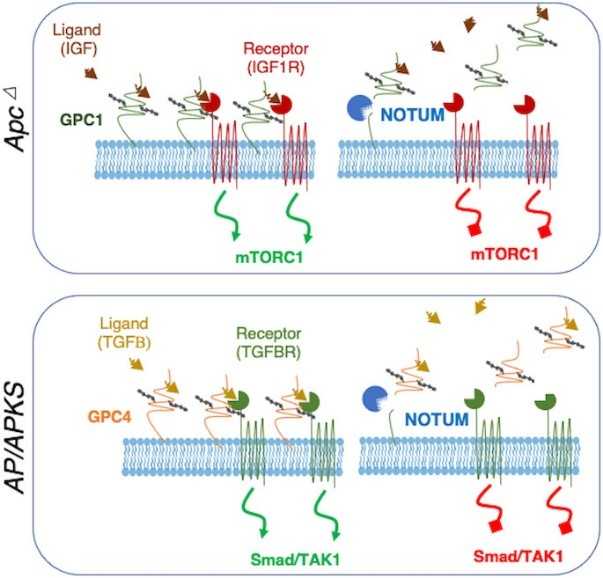
Fig1. Model for NOTUM tumour suppressive-to-oncogenic switch during the adenoma-adenocarcinoma transition. (Yuhua Tian, 2023)
Bioapplications of NOTUM
NOTUM is being explored as a therapeutic target, and small molecule inhibitors of NOTUM are being studied. These could potentially offer new treatments for diseases where Wnt signaling is dysregulated. Antibodies against NOTUM can be used in scientific applications such as Western Blot, Immunohistochemistry, and ELISA, which are crucial for the diagnosis and study of diseases associated with NOTUM dysregulation. NOTUM's involvement in shaping the Wingless morphogen gradient during development highlights its importance in understanding organogenesis and the formation of body structures.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Qingxuan Zhao, 2024
Notum is a secreted deacylase, which is crucial for tooth dentin development in mice. This study aimed to investigate the effect of NOTUM on the odontoblastic differentiation of human stem cells from the apical papilla (hSCAPs), to reveal the potential value of NOTUM in pulp-dentin complex regeneration. The expression pattern of NOTUM in human tooth germs and during in vitro odontoblastic differentiation of hSCAPs was evaluated by immunohistochemical staining, and quantitative polymerase chain reaction, respectively. To manipulate the extracellular NOTUM level, ABC99 or small interfering RNA was used to down-regulate it, while recombinant NOTUM protein was added to up-regulate it. The effects of changing NOTUM level on the odontoblastic differentiation of hSCAPs and its interaction with the WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway were studied using alkaline phosphatase staining, alizarin red staining, quantitative polymerase chain reaction, and western blot. During in vitro odontoblastic differentiation of hSCAPs, NOTUM expression initially increased, while the WNT/β-catenin pathway was activated. Downregulation of NOTUM hindered odontoblastic differentiation. Recombinant NOTUM protein had varying effects on odontoblastic differentiation depending on exposure duration. Continuous addition of the protein inhibited both odontoblastic differentiation and the WNT/β-catenin pathway. However, applying the protein solely in the first 3 days enhanced odontoblastic differentiation and up-regulated the WNT/β-catenin pathway.
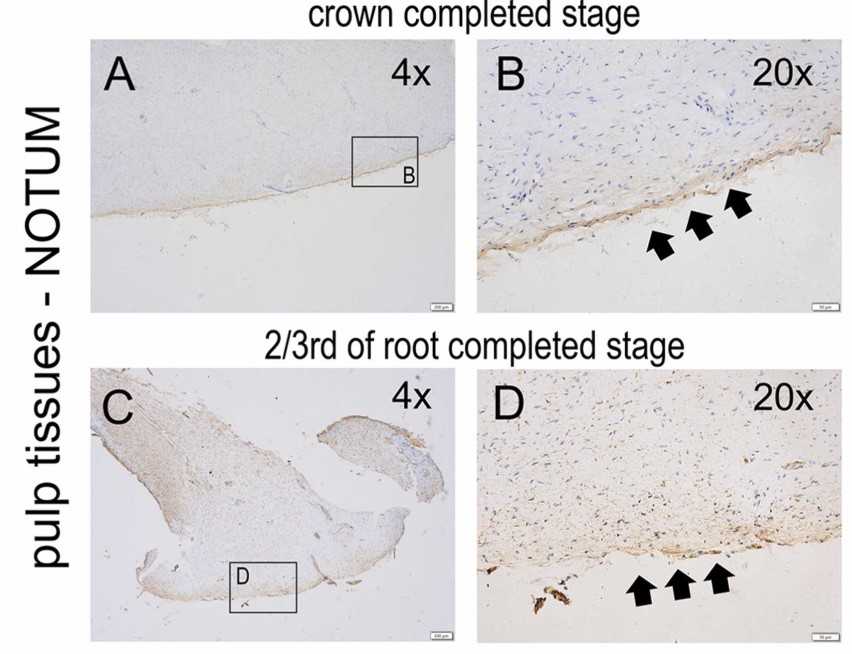
Fig1. Expression of NOTUM in human pulp tissues at different developmental stages.
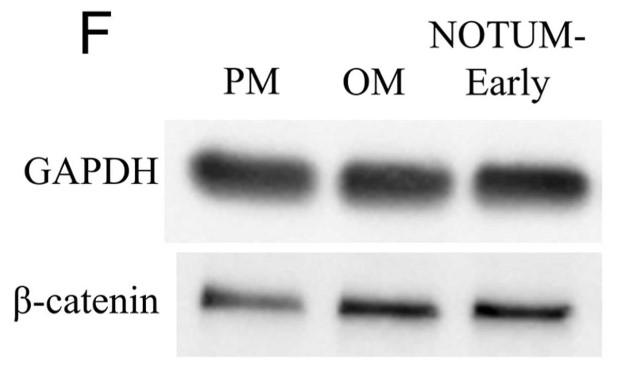
Fig2. Western blot and quantitative analysis of β-catenin after adding NOTUM protein.
Case Study 2: Panpan Yang, 2022
Notum, which belongs to the α/β hydrolase family, is a deacylated extracellular protein that regulates the Wnt signaling pathway. Studies have found that Notum participates in the progression of colorectal cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma, but its role in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is currently unclear. This study aimed to explore the role of Notum in regulating OSCC and further reveal the underlying mechanisms. Various approaches including bioinformatics analysis, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and immunohistochemical staining were used to detect the expression of Notum in OSCC cells and tissues. Cell counting kit-8 assay, clone formation assay, wound healing assay, transwell assay and in-gel zymography assay were explored to evaluate the regulation of Notum in OSCC proliferation and migration. The results showed that Notum was highly expressed in OSCC tissues and cells, and Notum promoted the proliferation and migration of OSCC cells while it inhibited their apoptosis. Furthermore, signaling pathway analysis showed that Notum led to potential pro-survival of OSCC through crosstalk between sonic hedgehog (Shh) and Wnt/β-catenin signaling via phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta.
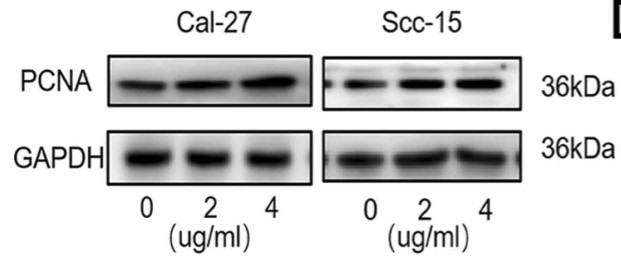
Fig3. Western blot analysis of PCNA, GAPDH in OSCC cells with a different dose Notum human recombinant protein.
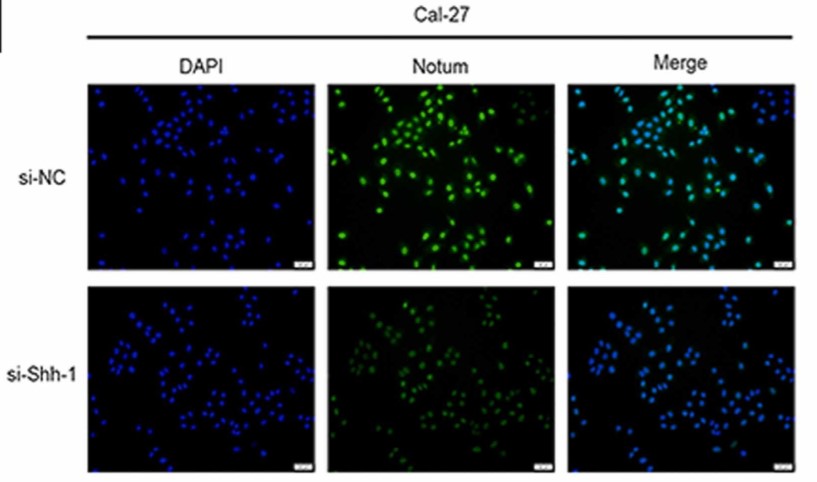
Fig4. Cell immunofluorescence analysis of Notum expression in Shh knockdown Cal-27 cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (NOTUM-1624H)
Involved Pathway
NOTUM involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways NOTUM participated on our site, such as Hedgehog ligand biogenesis,Release of Hh-Np from the secreting cell,Signal Transduction, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with NOTUM were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Signaling by Hedgehog | WDR19,DZIP1,IFT88,SPOPL,CDC73,TTC21B,SPOP,EVC,EVC2,IFT122 |
| Hedgehog ligand biogenesis | NOTUM1A,OS9,SCUBE2,DISP2,HHAT,GPC5A,DERL2 |
| Release of Hh-Np from the secreting cell | NOTUM1A,SCUBE2,DISP2 |
| Signal Transduction | PROKR2,ABI1A,NMU,METAP2,CCDC88C,PYGO1,CXCR7B,TNKS,ARHGAP11A,BCL9L |
Protein Function
NOTUM has several biochemical functions, for example, palmitoleyl hydrolase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by NOTUM itself. We selected most functions NOTUM had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with NOTUM. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| palmitoleyl hydrolase activity | NOTUM1A,NOTUM1B |
Interacting Protein
NOTUM has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with NOTUM here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of NOTUM.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Xu, B; Li, XW; et al. Evaluation of Ga-68-Labeled MG7 Antibody: A Targeted Probe for PET/CT Imaging of Gastric Cancer. SCIENTIFIC REPORTS 5:-(2015).
- Hong, H; Yan, YJ; et al. PET of Follicle-Stimulating Hormone Receptor: Broad Applicability to Cancer Imaging. MOLECULAR PHARMACEUTICS 12:403-410(2015).


