NONO
-
Official Full Name
non-POU domain containing, octamer-binding -
Overview
This gene encodes an RNA-binding protein which plays various roles in the nucleus, including transcriptional regulation and RNA splicing. A rearrangement between this gene and the transcription factor E3 gene has been observed in papillary renal cell carcinoma. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. Pseudogenes exist on Chromosomes 2 and 16. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2009] -
Synonyms
NONO;non-POU domain containing, octamer-binding;P54;NMT55;NRB54;P54NRB;non-POU domain-containing octamer-binding protein;p54(nrb);55 kDa nuclear protein;54 kDa nuclear RNA- and DNA-binding protein;DNA-binding p52/p100 complex, 52 kDa subunit;non-POU domain-containing octamer (ATGCAAAT) binding protein
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Rhesus macaque
- Chicken
- Rat
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- His
- SUMO
- DDK
- Myc
- GST
- Non
- Flag
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is NONO protein?
NONO gene (non-POU domain containing octamer binding) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome X at locus Xq13. NONO protein is A versatile protein that is ubiquitous in eukaryotes and belongs to the nuclear poly(A)-binding protein (PABPN) related protein family. NONO proteins play a role in the nucleus and are involved in a variety of biological processes, including RNA processing, RNA stability, karyoplasmic transport, and X chromosome inactivation. NONO proteins interact with a variety of RNA-binding proteins and have regulatory effects on RNA polymerase II activity. In addition, NONO proteins have been linked to a number of diseases, such as certain types of cancer and neurological disorders. The NONO protein is consisted of 471 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 54.2 kDa.
What is the function of NONO protein?
NONO proteins can interact with transcription factors and participate in transcriptional regulation of genes. As a member of the splicing protein family, NONO is involved in the splicing process of mRNA. NONO proteins are involved in DNA unhelix and pairing processes, which may be involved in DNA replication and repair. NONO proteins are involved in regulating the retention of certain Rnas in the nucleus. NONO protein is involved in DNA damage repair mechanism. NONO protein is able to increase the stability of the intracellular epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and recruit CREB-binding protein (CBP) and its accompanying E1A-binding protein p300, which may be involved in cell signaling.
NONO Related Signaling Pathway
NONO participates in the CAMP-responsive signaling pathway, promoting gene transcription by shrinking the promoter region of RNA polymerase and downstream genes with CREB-responsive elements. NONO interacts with MSN to promote the nuclear localization of kinase PKCζ, thereby phosphorylating CREB and activating its downstream signaling pathway, which may have important implications in the treatment of triple-negative breast cancer. NONO interacts with TAZ, a core protein of the Hippo signaling pathway, and may influence cell growth and tumorigenesis. NONO protein, as a cofactor of transcription factors, is involved in gene transcriptional regulation, RNA splicing and DNA damage repair.
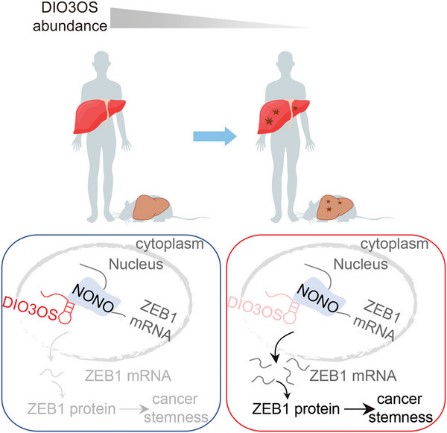
Fig1. Mechanism of action of DIO3OS in HCC stemness. (Ya-Rui Hou, 2023)
NONO Related Diseases
NONO protein is a protein that plays a role in a variety of cellular processes, including DNA repair, RNA splicing, and transcriptional regulation. NONO protein-related diseases include the following:
Neurodegenerative diseases: For example, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD), a proportion of cases of these two diseases are associated with mutations in NONO proteins.
Cancer: NONO protein is abnormally expressed in certain types of cancer, such as breast, lung, and liver cancers. Studies have shown that NONO proteins may be involved in the occurrence and development of cancer by regulating gene expression and cell proliferation.
Cardiovascular disease: NONO proteins also play an important role in heart development and function and may therefore be involved in the development of certain cardiovascular diseases.
Genetic disorders: Some rare genetic disorders, such as X-linked intellectual disability, may also be associated with abnormal functioning of NONO proteins.
Bioapplications of NONO
As a multifunctional nuclear protein, NONO plays a role in gene expression regulation, RNA processing, DNA repair and other biological processes, and is an important tool to study these basic biological mechanisms. Functional abnormalities of NONO proteins are associated with disease, and drug development targeting NONO proteins may help treat related diseases, especially in the field of cancer therapy. The change of NONO protein expression level may be used as a biomarker for some diseases, which is helpful for early diagnosis and treatment monitoring of diseases.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Zi-Yi Yang, 2024
Gallbladder cancer (GBC) is a highly malignant and rapidly progressing tumor of the human biliary system, and there is an urgent need to develop new therapeutic targets and modalities. Non-POU domain-containing octamer-binding protein (NONO) is an RNA-binding protein involved in the regulation of transcription, mRNA splicing, and DNA repair. Here, researchers found that NONO was highly expressed in GBC and promoted tumor cells growth. The dysregulation of RNA splicing is a molecular feature of almost all tumor types. Accordingly, mRNA-seq and RIP-seq analysis showed that NONO promoted exon6 skipping in DLG1, forming two isomers (DLG1-FL and DLG1-S). Furthermore, lower Percent-Spliced-In (PSI) values of DLG1 were detected in tumor tissue relative to the paraneoplastic tissue, and were associated with poor patient prognosis. Moreover, DLG1-S and DLG1-FL act as tumor promoters and tumor suppressors, respectively, by regulating the YAP1/JUN pathway. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most common and abundant RNA modification involved in alternative splicing processes. Researchers identified an m6A reader, IGF2BP3, which synergizes with NONO to promote exon6 skipping in DLG1 in an m6A-dependent manner. Furthermore, IP/MS results showed that RBM14 was bound to NONO and interfered with NONO-mediated exon6 skipping of DLG1. In addition, IGF2BP3 disrupted the binding of RBM14 to NONO.
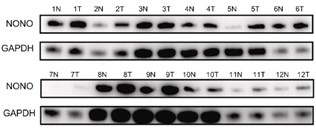
Fig1. Western blot analysis of the NONO protein levels in GBC tumor tissues and adjacent non-tumor tissues.
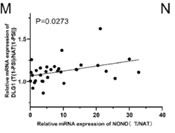
Fig2. Correlation analysis of DLG1-S/DLG1-FL ratio and NONO expression.
Case Study 2: Nuoqing Weng, 2024
As an immune checkpoint protein expressed by diverse cancer cells, programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) facilitates immune evasion by interacting with programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) on T cells. Despite the clinical benefits observed in various cancer types, strategies targeting PD-1/PD-L1 have demonstrated limited efficacy in gastric cancer (GC). Furthermore, the regulation of PD-L1, especially at post-translational modification levels, remains largely unknown. In this study, by perfoming pull-down assay, researchers have identified that IKAROS family zinc finger 4 (IKZF4) and Non-POU domain-containing octamer-binding (NONO) synergistically regulate and enhance the expression of RAB11 family-interacting protein 3 (RAB11FIP3) in GC. The IKZF4/NONO-RAB11FIP3 axis facilitates the endosomal recycling of PD-L1, particularly on the cell membrane of GC cells. Moreover, overexpression of RAB11FIP3 mitigates the hypo-expression of PD-L1 protein resulting from IKZF4 or NONO deletion.
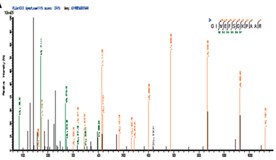
Fig3. Mass spectrometry analysis of the above band identified NONO as the interaction protein of IKZF4.
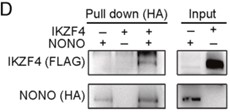
Fig4. Pull-down assays were conducted to confirm the direct binding activity between IKZF4 and NONO.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (NONO-1688H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (NONO-2496HB)
Involved Pathway
NONO involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways NONO participated on our site, such as Circadian rhythm pathway,mRNA processing, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with NONO were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| mRNA processing | Ankar,MCTS2,SF3B2,CELF4,SRSF10,WBP4,HNRPL,HNRNPAB,PPM1G,PRPF4BB |
| Circadian rhythm pathway | TIMELESS,DEC1,CHEK1 |
Protein Function
NONO has several biochemical functions, for example, RNA polymerase II distal enhancer sequence-specific DNA binding,chromatin binding,core promoter binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by NONO itself. We selected most functions NONO had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with NONO. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| RNA polymerase II distal enhancer sequence-specific DNA binding | NFKB1,RUVBL2,RXRB,ESRRB,ZBTB16,SFPQ,NR2F6,BACH1,MSC,ARX |
| nucleotide binding | RAP1AB,TUBA2,SBK1,AKT3A,NLK1,RBM17,MAT2AB,EIF3BA,HNRNPA2B1,RBM12B1 |
| identical protein binding | LEPR,ATL2,MYBPC3,TTC32,VIL1,HOOK3,LYZ,SNX1,ATXN3,DYNLT3 |
| poly(A) RNA binding | TFAM,PCBP3,RPL8,CCT4,SRSF9,SAMSN1,RPL35A,NOC2L,WDR46,LRPPRC |
| transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding | GATA1,ATF3,HDAC1,PSPC1,DDIT3,SOX12,ZNF658,CREB3L3,PITX2,POU5F1 |
| core promoter binding | E2F3,DHX36,XBP1,REST,GADD45A,E2F1,FOXP3,TFAP2C,ELK1,HDAC1 |
| chromatin binding | MSH6,PPARG,RELB,RUNX2,UBE2T,MSGN1,KLHDC3,TCF7,PHF13,NCAPD3 |
| protein binding | SARM1,SNTB1,THRAA,SEC31A,ZNF155,SIL1,CLPP,IL1R1,ATP6V1E1,PRICKLE1 |
Interacting Protein
NONO has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with NONO here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of NONO.
PSPC1;PIN1;RNF43
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


