MAOB
-
Official Full Name
monoamine oxidase B -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the flavin monoamine oxidase family. It is a enzyme located in the;mitochondrial outer membrane. It catalyzes the oxidative deamination of biogenic and xenobiotic amines and plays an;important role in the metabolism of neuroactive and vasoactive amines in the central nervous sysytem and peripheral;tissues. This protein preferentially degrades benzylamine and phenylethylamine. -
Synonyms
MAOB;monoamine oxidase B;amine oxidase [flavin-containing] B;MAO-B;MAO, brain;MAO, platelet;tyramine oxidase;adrenalin oxidase;monoamine oxidase type B;MGC26382
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Mouse
- Bovine
- Guinea pig
- Insect cells
- Insect Cells
- Human
- E.Coli/Yeast
- Mammalian Cells
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Non
- His
- T7
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is MAOB Protein?
The MAOB protein, also known as monoamine oxidase B, is basically an enzyme that's living on the outer membrane of mitochondria in human cells. It's part of the flavin monoamine oxidase family and helps break down both biogenic amines, like neurotransmitters, and xenobiotic ones—those foreign to the body. This process, known as oxidative deamination, is crucial for managing neuroactive and vasoactive compounds in the central nervous system and various tissues throughout the body. The enzyme mostly goes after substances like benzylamine and phenethylamine, and it shares some functions with its cousin, monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A), especially in breaking down dopamine. In short, MAOB is pretty important for keeping things in balance within our nervous system.What is the Function of MAOB Protein?
Monoamine oxidase B, or MAOB, is this enzyme that hangs out on the outer membrane of mitochondria in your cells. It mainly breaks down various amines, both those naturally found in your body and some foreign ones. Specifically, it targets things like benzylamine and phenethylamine. It also helps break down dopamine, much like monoamine oxidase A (MAOA) does. This enzyme is essential for regulating certain chemicals in the nervous system and ensuring everything stays balanced.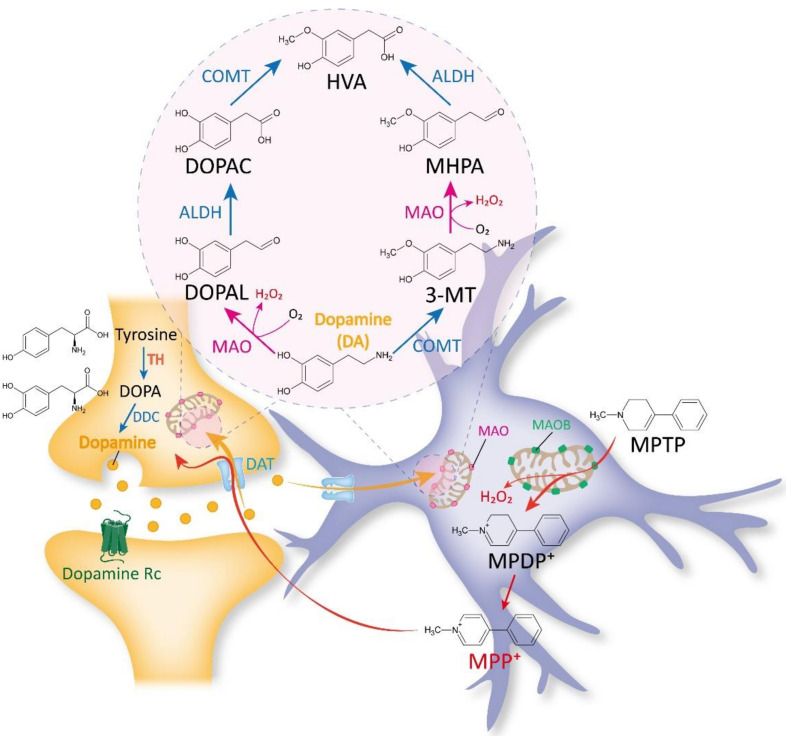
Fig1. The traditional view on MAOB as a DA- and MPTP-metabolizing enzyme. (Min-Ho Nam, 2022)
MAOB Related Signaling Pathway
Monoamine oxidase B (MAOB) is part of a larger neurochemical pathway involved in breaking down neurotransmitters such as dopamine. By degrading these neurotransmitters, MAOB influences various signaling pathways related to mood, movement, and other neurological functions. Its activity is particularly significant in neurological diseases like Parkinson’s, where altered dopamine levels play a crucial role. Inhibitors of MAOB are often used to manage symptoms by preventing dopamine breakdown, thereby affecting the signaling pathways that regulate motor control and mood.MAOB Related Diseases
Monoamine oxidase B (MAOB) relates to a few health issues, notably Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. In these conditions, MAOB levels tend to be too high in the brain. Normally, MAOB helps break down neurotransmitters, but its regular action creates reactive oxygen species that can harm cells. As people get older, MAOB levels can go up, which might be partly why there’s a natural decline in brain function and a greater chance of developing neurological problems. Interestingly, some genetic variations of the MAOB gene have been linked to negative emotions and may be a factor in depression. Additionally, increased MAOB activity is suspected to contribute to stress-related heart damage. In Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, higher MAOB levels are connected to the buildup of amyloid-beta plaques in the brain. Some studies suggest that shutting down MAOB with certain drugs can slow disease progress and even reduce these plaques.Bioapplications of MAOB
MAOB, or monoamine oxidase B, is involved in several practical applications, especially in medicine. It's commonly targeted in treatments for neurodegenerative disorders like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s. By using drugs that inhibit MAOB, it's possible to boost dopamine levels in the brain, which can help improve symptoms related to movement and mood for Parkinson's patients. Additionally, understanding how MAOB works is crucial for research on aging and mood disorders since it affects neurotransmitter balance and the production of reactive oxygen species.Case Study
Case Study 1: Pu T. et al. Sci Adv. 2024
In prostate cancer, stromal cells play a key role in tumor growth. This study found that high levels of the enzyme MAOB in prostate cancer stroma are linked to worse outcomes. By altering MAOB levels in prostate stromal fibroblasts, researchers showed that MAOB boosts cancer cell growth and invasion, both in lab tests and in mice. MAOB changes the stroma to support tumors by increasing reactive oxygen species and remodeling the matrix. It also activates CXCL12, which enhances cancer signaling. Blocking MAOB slowed tumor growth in mice, suggesting it as a target for new prostate cancer treatments.-
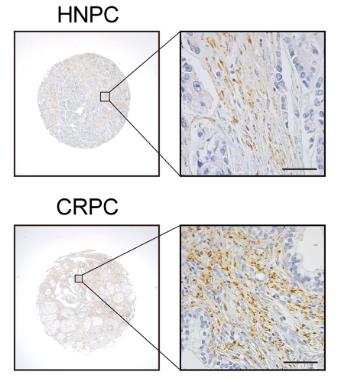 Fig1. Representative images and quantitation of MAOB IHC staining.
Fig1. Representative images and quantitation of MAOB IHC staining. -
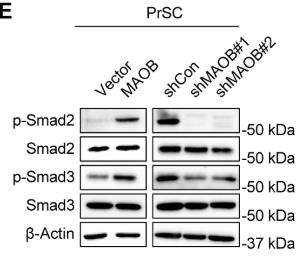 Fig2. Western blot of p-Smad2 and p-Smad3 in control and MAOB-manipulated PrSC cells.
Fig2. Western blot of p-Smad2 and p-Smad3 in control and MAOB-manipulated PrSC cells.
Case Study 2: Qi Y. et al. Head Neck. 2024
Monoamine oxidase B (MAOB) plays a role in processing amines. This study explored its impact on head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Bioinformatics indicated MAOB might be downregulated in HNSCC. This was confirmed in lab tests and animal models. Reduced MAOB levels were found in HNSCC tissues and cells, with changes noted as the cancer progresses. When MAOB was overexpressed, it reduced cancer cell malignancy, an effect partially reversed by selegiline.-
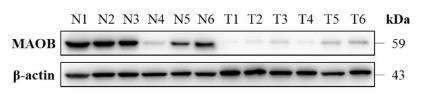 Fig3. MAOB protein abundance was assessed using western blot in HNSCC tissues.
Fig3. MAOB protein abundance was assessed using western blot in HNSCC tissues. -
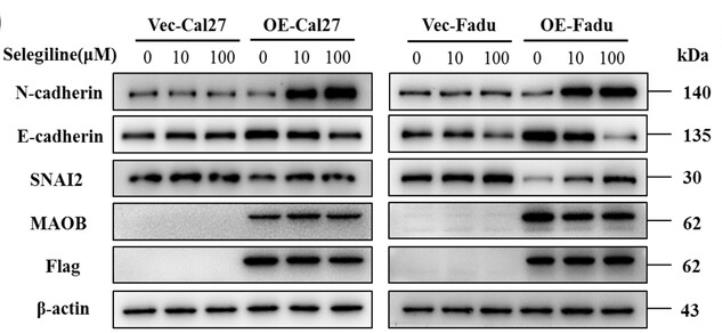 Fig4. Following Slg treatment, the abundances of N-cadherin, E-cadherin, SNAI2, MAOB, and Flag were determined using western blot.
Fig4. Following Slg treatment, the abundances of N-cadherin, E-cadherin, SNAI2, MAOB, and Flag were determined using western blot.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (MAOB-7976M)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (MAOB-7976M) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (Maob-1757R)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (Maob-1757R)
Involved Pathway
MAOB involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways MAOB participated on our site, such as Glycine, serine and threonine metabolism,Arginine and proline metabolism,Histidine metabolism, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with MAOB were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Tyrosine metabolism | ADH1,TPO,AOX4,FAH,AOX2P,HPDA,GOT1,ADH2-1,COMTB,HPDB |
| Glycine, serine and threonine metabolism | SDSL,GCSHA,SHMT1,GRHPRA,GRHPRB,MAOA,GNMT,LSM1,GCSHB,DAO1 |
| Phenylalanine metabolism | GOT2A,HPDB,GOT2,MIF,HPD,ALDH3A1,TAT,AOC2,MAOA,GOT1 |
| Metabolic pathways | PIGC,AKR1B8,B3GNT5A,GPAT2,G6PDX,ADH4,MAT2AL,NDUFB4,HGSNAT,TRIT1 |
| Histidine metabolism | ALDH9A1B,ALDH7A1,ALDH3A2A,AMDHD1,UROC1,CNDP1,ALDH2.1,HAL,ABP1,ALDH2.2 |
| Drug metabolism - cytochrome P | ALDH3B2,UGT2B7,GSTM6,UGT5G1,UGT1A4,GSTT2,GSTA1,GSTP1,GSTAL,MGST1.2 |
| Alcoholism | GNB1,HIST1H2AM,MAOA,GM14479,HIST1H2AH,GRIN2B,GNG10,HIST2H2BB,HIST2H3C1,GNGT1 |
| Cocaine addiction | PRKACG,GNAS,GRM3,GNAI3,GRIN2D,CREB3L2,SLC18A1,GRIN2A,FOSB,NFKB1 |
| Arginine and proline metabolism | MAOA,CKMA,SAT2B,P4HA3,GATM,ALDH2.2,CKMT2,P4HA2,Ckmm,SRM |
-
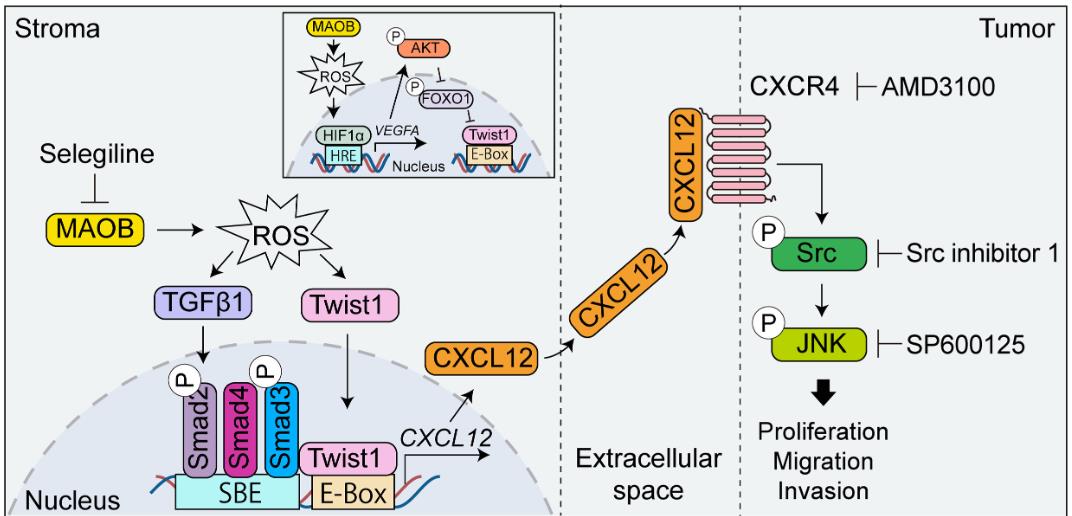 Fig1. Schematic depicting stromal-derived MAOB activation of paracrine CXCL12-CXCR4/Src/JNK signaling. (Tianjie Pu, 2024)
Fig1. Schematic depicting stromal-derived MAOB activation of paracrine CXCL12-CXCR4/Src/JNK signaling. (Tianjie Pu, 2024) -
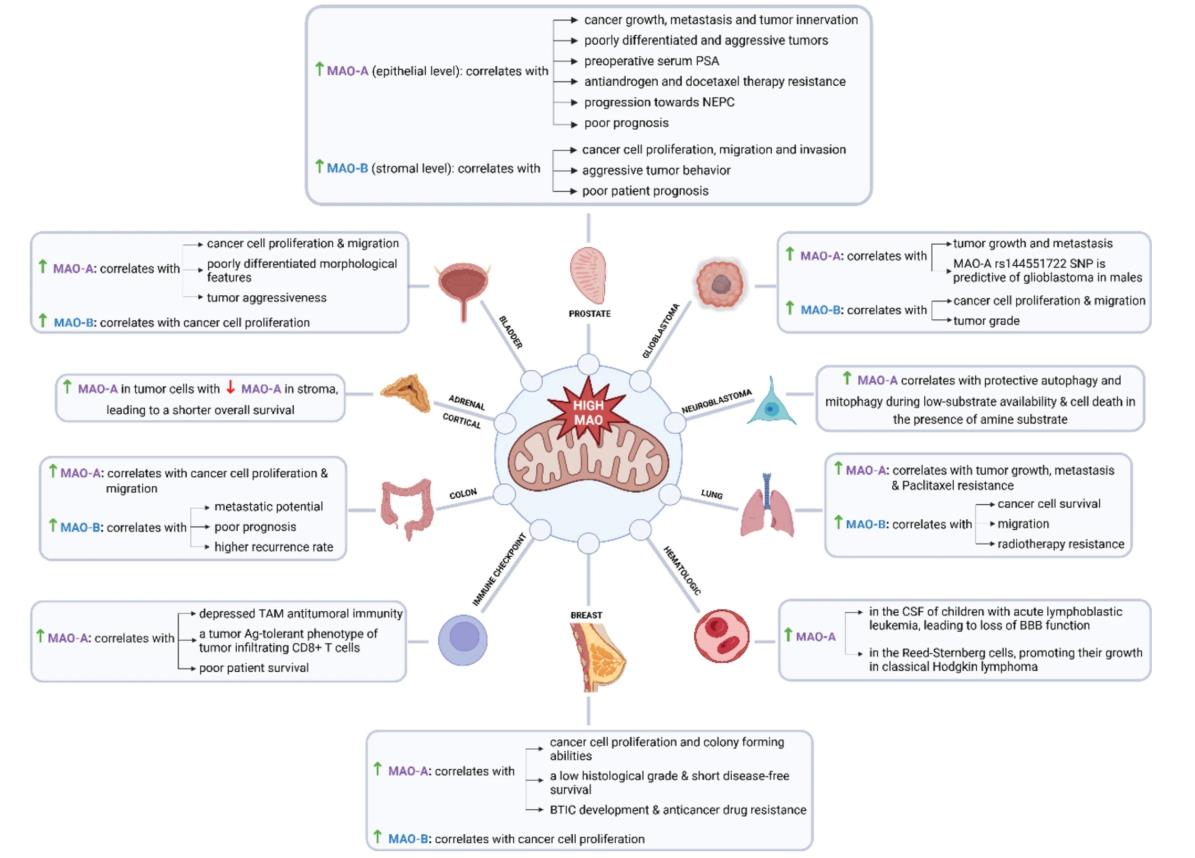 Fig2. Cancer-promoting effects of MAO upregulation. (Iasmina M Hâncu, 2024)
Fig2. Cancer-promoting effects of MAO upregulation. (Iasmina M Hâncu, 2024)
Protein Function
MAOB has several biochemical functions, for example, electron carrier activity,flavin adenine dinucleotide binding,primary amine oxidase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by MAOB itself. We selected most functions MAOB had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with MAOB. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| primary amine oxidase activity | AOC2,AOC1,VCAM1,MAOA,AOC3,ABP1 |
| flavin adenine dinucleotide binding | GCDHB,NOS2,AIFM2,GCDH,MTO1,DUS3L,AIFM4,KDM1A,XDH,ACAD11 |
| protein homodimerization activity | APOE,PGCP,NPPC,HNF1B,CR2,SYT10,RAP1GAP,CHMP4C,ATG7,NR4A3 |
| electron carrier activity | TXNRD1,SDHC,COX7A2A,CYCSB,AOX1,GLRX5,FDX1,GLDC,AKR1B1,ETFA |
Interacting Protein
MAOB has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with MAOB here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of MAOB.
Dlg4;kynuramine;deprenyl/selegiline;NFYB;SRPK1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Vitalis, T; Alvarez, C; et al. Developmental expression pattern of monoamine oxidases in sensory organs and neural crest derivatives. JOURNAL OF COMPARATIVE NEUROLOGY 464:392-403(2003).
- Bradley, M; Soderhall, C; et al. The Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome gene as a candidate gene for atopic dermatitis. ACTA DERMATO-VENEREOLOGICA 81:340-342(2001).
- Cutler, NR; Sramek, JJ; et al. Review of the next generation of Alzheimer's disease therapeutics: Challenges for drug development. PROGRESS IN NEURO-PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY & BIOLOGICAL PSYCHIATRY 25:27-57(2001).
Reviews
Everything went smoothly with the proteins, no issues that I can report in using them.


