Lypla1
-
Official Full Name
lysophospholipase I -
Overview
Lysophospholipases are enzymes that act on biological membranes to regulate the multifunctional lysophospholipids. The protein encoded by this gene hydrolyzes lysophosphatidylcholine in both monomeric and micellar forms. The use of alternate polyadenylation sites has been found for this gene. There are alternatively spliced transcript variants described for this gene but the full length nature is not known yet. -
Synonyms
LYPLA1;lysophospholipase I;acyl-protein thioesterase 1;Acyl protein thioesterase 1;APT 1;APT1;LPL1;LYPLA 1;LYSOPLA;LPL-I;lysoPLA I;lysophospholipase 1;acyl-protein thioesterase-1;lysophospholipid-specific lysophospholipase;APT-1;hAPT1
Recombinant Proteins
- Zebrafish
- Rhesus macaque
- Mouse
- Human
- Rat
- Mammalian Cells
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- T7
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- GST
Background
What is LYPLA1 Protein?
LYPLA1, short for lysophospholipase 1, is a protein you might not hear about every day, but it’s doing some important backstage work in your cells. It’s part of the team responsible for breaking down certain fats called lysophospholipids, which are crucial in building cell membranes and signaling. Imagine LYPLA1 as a maintenance crew member, ensuring that these fats are kept in check so that cells function smoothly. This protein not only helps maintain cell structure but also plays a role in sending signals within and between cells, kind of like making sure the cell's messaging system is working properly. Scientists are pretty interested in LYPLA1 because changes or malfunctions in its activity could be linked to different health issues, including metabolic disorders and certain neurological conditions. So, while it doesn’t get the spotlight, LYPLA1 is essential for keeping things running behind the scenes in the body.What is the Function of LYPLA1 Protein?
LYPLA1, or lysophospholipase 1, might not be famous, but it’s pretty important for keeping your cells in check. Its main gig is breaking down lysophospholipids, which are special fats involved in building cell membranes and sending signals around the body. Think of LYPLA1 as the cell’s handyman, making sure everything’s in the right place and the communication lines are clear. This helps the cell stay in shape and handle various tasks, like how our own network of systems needs constant upkeep. Plus, researchers are keeping a close eye on LYPLA1 because if it goes haywire, it might be connected to some health problems, like metabolic issues or certain brain disorders. So, even though it stays behind the scenes, LYPLA1 is crucial for keeping your cell’s operations running smoothly.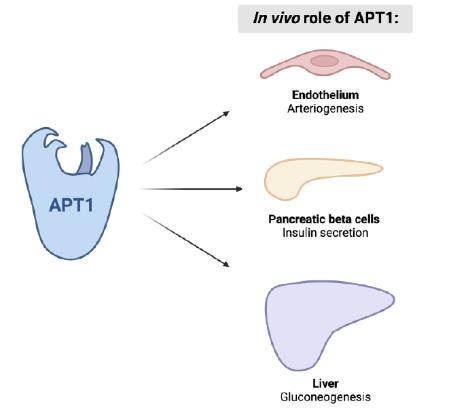
Fig1. APT1 as a mediator of metabolic signals. (Sarah L Speck, 2024)
LYPLA1 Related Signaling Pathway
LYPLA1, or lysophospholipase 1, operates in some pretty crucial signaling pathways in your body. Picture it as a key player in the cell’s communication team, making sure signals are sent and received properly to keep everything running smoothly. It works by processing lysophospholipids, fats involved in creating cell membranes and conveying messages between cells. When LYPLA1 does its job right, it helps regulate these signals, which can affect everything from how cells move to how they grow and divide. Scientists are interested in LYPLA1 because if it doesn’t work as it should, it might disrupt these pathways and lead to issues like metabolic disorders or even affect brain functions. So, while LYPLA1 might not be grabbing headlines, it’s essential for keeping those cellular conversations clear and effective.LYPLA1 Related Diseases
LYPLA1, or lysophospholipase 1, may not be on the tip of everyone's tongue, but it can play a part in some pretty significant health issues. Since it’s involved in breaking down certain fats in cells, if anything goes wrong with LYPLA1, it can throw those cells out of whack. This imbalance might be linked to metabolic disorders, where the body’s ability to process fats and sugars gets messed up. There’s also some buzz around its potential connection to neurological conditions since those cellular signaling pathways play a big role in brain function. Researchers are delving into how irregular LYPLA1 activity could tie into neurodegenerative diseases or cognitive issues. Basically, while LYPLA1 doesn’t hog the spotlight, it’s crucial for keeping things balanced in the body, and when it’s out of sync, it could contribute to a range of health challenges.Bioapplications of LYPLA1
LYPLA1, also known as lysophospholipase 1, might not be widely known, but it's gaining attention for its bioapplication potential. This protein helps manage cell lipids, making it a hot topic for researchers exploring new medical uses. Since LYPLA1 is key in lipid metabolism, it's a promising target for developing drugs to treat metabolic disorders. Imagine a future where tweaking LYPLA1 activity helps manage conditions like obesity or diabetes. There's also buzz about its implications in neuroscience, considering its influence on cell signaling pathways that affect brain function. Scientists are examining whether LYPLA1 could be linked to neurodegenerative diseases, opening doors for novel treatment strategies. In essence, while LYPLA1 might be working behind the scenes, its potential applications in medicine could be a game-changer, offering insights and tools to tackle various health issues.Case Study
Case Study 1: Harris WT 3rd. et al. Proteins. 2024
Human APTs help proteins attach to and detach from cell membranes. In bacteria, a loop near a similar enzyme’s active site moves, influencing function. In humans, while the loop doesn't move, it has a similar sequence and plays a different role. Studying human APT1, which is linked to cancer and other key processes, this loop affects how the enzyme works, especially in binding and positioning materials. Changes to Trp71, a critical part of this loop, drastically reduce APT1's function and stability, marking it as a key site for possible drug targeting.-
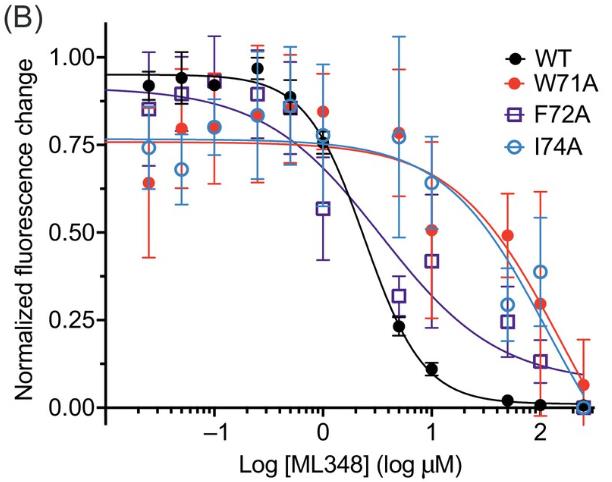 Fig1. Shifts in the intrinsic tryptophan fluorescence of APT1 in response to ligand binding.
Fig1. Shifts in the intrinsic tryptophan fluorescence of APT1 in response to ligand binding. -
 Fig2. Kinetic activity of APT1 Trp71 variants against C4 alkyl ester substrate.
Fig2. Kinetic activity of APT1 Trp71 variants against C4 alkyl ester substrate.
Case Study 2: Siegel G. et al. Nat Cell Biol. 2009
The microRNA pathway affects synapse growth and memory, but which microRNAs matter? Researchers have pinpointed some, like miR-138, that shape dendritic spines, crucial for memory. MiR-138, highly present in brain dendrites, limits spine size by controlling APT1, an enzyme affecting synaptic protein modifications. Reducing APT1 or changing Galpha(13) stops spine growth when miR-138 is blocked, showing miR-138's role in spine size control through APT1.-
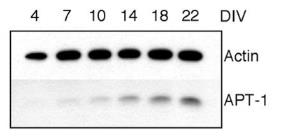 Fig3. APT1 protein expression is upregulated during the development of primary cortical neurons in culture.
Fig3. APT1 protein expression is upregulated during the development of primary cortical neurons in culture. -
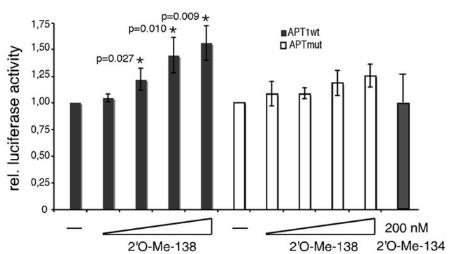 Fig4. Endogenous miR-138 inhibits APT1 luciferase reporter gene expression.
Fig4. Endogenous miR-138 inhibits APT1 luciferase reporter gene expression.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (LYPLA1-7904M)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (LYPLA1-7904M) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (LYPLA1-0171H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (LYPLA1-0171H)
Involved Pathway
Lypla1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Lypla1 participated on our site, such as Choline metabolism in cancer,Glycerophospholipid metabolism,Metabolism, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Lypla1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Metabolism | ARL2,CETP,LOC100686744,SLC25A2,CYB5A,SLC35D1A,COX7C,DPYS,SLC5A4,CYP2U1 |
| eNOS activation | DDAH1,DDAH2,CYGB2,CYGB1,CYGB,ZDHHC21 |
| Choline metabolism in cancer | MAPK1,SLC44A2,PLA2G4F,PIK3CG,RALGDS,EGF,MAP2K1,AKT1,WASF3,DGKD |
| eNOS activation and regulation | CYGB2,GCHFR,NOSIP,DDAH2,CYGB1,DDAH1,ZDHHC21,NOSTRIN,SPRB,CYGB |
| Glycerophospholipid metabolism | ACHE,AGPAT5,PPAP2D,PLA2G10,PLD2,AGPAT9L,PLA2G1B,AGPAT4,PTDSS1A,LPCAT3 |
| Metabolism of nitric oxide | NOSIP,CYGB1,SPRB,DDAH2,ZDHHC21,CYGB,NOSTRIN,DDAH1,GCHFR,CYGB2 |
-
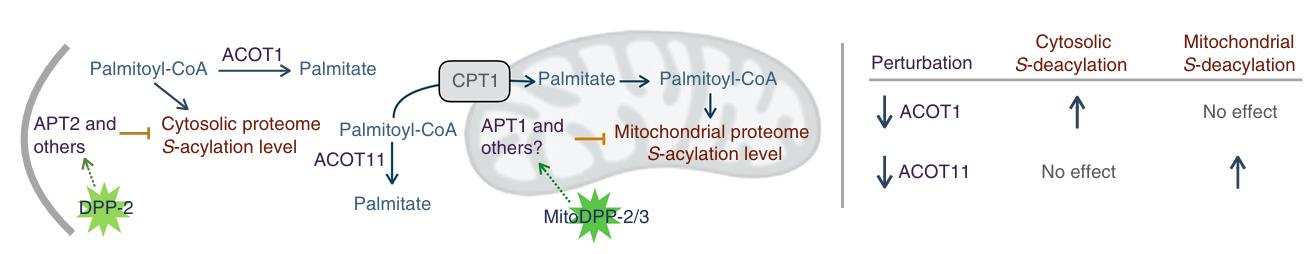 Fig1. Of the identified APTs, APT1 localizes predominantly to mitochondria, whereas APT2 is found in the cytosol. (Rahul S Kathayat, 2018)
Fig1. Of the identified APTs, APT1 localizes predominantly to mitochondria, whereas APT2 is found in the cytosol. (Rahul S Kathayat, 2018) -
 Fig2. A working model of FA uptake by CD36-mediated caveolar endocytosis. (Jian-Wei Hao, 2020)
Fig2. A working model of FA uptake by CD36-mediated caveolar endocytosis. (Jian-Wei Hao, 2020)
Protein Function
Lypla1 has several biochemical functions, for example, lipase activity,lysophospholipase activity,palmitoyl-(protein) hydrolase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Lypla1 itself. We selected most functions Lypla1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Lypla1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| lysophospholipase activity | PLA2G4A,PNPLA7,Cel,PNPLA6,ENPP2,LYPLAL1,PNPLA8,PNPLA7A,MGLL,PLA2G4AA |
| palmitoyl-(protein) hydrolase activity | LYPLAL1,LYPLA2,PPT1,PPT2 |
| lipase activity | DAGLB,ABHD2B,C2orf43,NOTUM1A,GOLT1A,PNPLA7,LIPM,CELL,CES1C,AADAC |
Interacting Protein
Lypla1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Lypla1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Lypla1.
VHL;IKBKE;NS;VCAM1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Aerts, I; Martin, JJ; et al. The expression of ecto-nucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 1 (E-NPP1) is correlated with astrocytic tumor grade. CLINICAL NEUROLOGY AND NEUROSURGERY 113:224-229(2011).
- Dennis, J; White, MA; et al. Phosphodiesterase-I alpha/autotaxin's MORFO domain regulates oligodendroglial process network formation and focal adhesion organization. MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE 37:412-424(2008).


