LIPE
- Product List
- Overview
- Review / Q&A
-
Official Full Name
lipase, hormone-sensitive -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene has a long and a short form, generated by use of alternative translational start codons. The long form is expressed in steroidogenic tissues such as testis, where it converts cholesteryl esters to free cholesterol for steroid hormone production. The short form is expressed in adipose tissue, among others, where it hydrolyzes stored triglycerides to free fatty acids. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
LIPE;lipase, hormone-sensitive;HSL;LHS;hormone-sensitive lipase;hormone-sensitive lipase testicular isoform
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Human
- Rat
- HEK293
- Sf21 Cells
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Insect Cells
- His
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
- Flag
Background
What is LIPE Protein?
LIPE, also called hormone-sensitive lipase, is key in breaking down stored fats for energy, mainly found in fat tissues. It helps convert triglycerides into free fatty acids, ready for energy use. LIPE acts on various substrates, favoring diacylglycerols over others like triacylglycerols and monoacylglycerols, and targets specific bonds on molecules. Besides its role in fat, it aids in steroid hormone production by making cholesterol available. Found on chromosome 19, LIPE links to conditions like lipodystrophy and high blood pressure, and serves as a marker for obesity, playing a part in heart disease studies.What is the Function of LIPE Protein?
LIPE, or hormone-sensitive lipase, is a key enzyme in breaking down fat in our bodies. This enzyme mainly works in fat tissues, helping convert stored triglycerides into free fatty acids, providing energy on demand. LIPE targets different kinds of fat molecules but favors certain ones, making it quite versatile. Besides working in fat tissues, it plays a role in producing steroid hormones by freeing up cholesterol. LIPE has connections to certain health issues, like familial lipodystrophy and high blood pressure, and it's been studied as a marker for obesity and heart disease risks.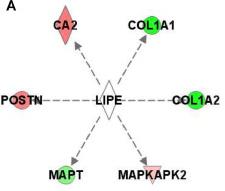
Fig1. Molecular interactions centered with potential regulators. (Byungwhi Kong, 2024)
LIPE Related Signaling Pathway
LIPE, or hormone-sensitive lipase, plays a central role in the breakdown of stored fats, primarily in fat tissues. It's regulated through several signaling pathways, particularly involving hormones like adrenaline and insulin. When adrenaline is high, it activates LIPE via a cascade that includes the cAMP pathway, leading to increased fat breakdown for energy. Conversely, insulin does the opposite by inhibiting LIPE, thus reducing fat breakdown and promoting storage. This balancing act ensures the body has energy when needed and stores it when surplus is available. Understanding LIPE's regulation is key to grasping how our body manages energy and stores fat, potentially impacting treatments for obesity and metabolic disorders.LIPE Related Diseases
LIPE, or hormone-sensitive lipase, is connected to several health conditions due to its role in fat metabolism. When LIPE isn't functioning properly, it can lead to familial partial lipodystrophy type 6, a disorder where fat distribution in the body becomes abnormal. This can cause insulin resistance, a key feature of type 2 diabetes, since fat metabolism is tightly linked to glucose handling. Additionally, issues with LIPE have been observed in some cases of hypertension and cardiovascular diseases, as the enzyme affects lipid levels and storage, influencing heart health. Because of these connections, LIPE is a focal point in research around metabolic health issues.Bioapplications of LIPE
LIPE, or hormone-sensitive lipase, has promising applications in biotech and medicine due to its role in fat metabolism. It's being explored for therapies targeting obesity, as manipulating LIPE activity could adjust fat breakdown. Additionally, in metabolic diseases like diabetes, understanding and modifying LIPE function offers a pathway to better glucose regulation, as it affects how fats and sugars are managed in the body. Researchers are also looking into LIPE's potential for treating cardiovascular issues, given its influence on lipid profiles. Its versatility makes LIPE a significant focus for developing treatments that address a range of metabolic disorders.Case Study
Case Study 1: Chen Y. et al. Sci Adv. 2025
Interferon regulatory factor-2 binding protein 2 (IRF2BP2) plays a key role in controlling fat breakdown in our bodies. When this protein is missing in fat cells, they break down more fat, but don't change how they handle sugar. On the flip side, having more of this protein slows down the fat breakdown. Experiments show that without IRF2BP2, certain genes that help in breaking down fat get more active. This causes more free fatty acids in the body, leading to fat tissue inflammation and problems with sugar metabolism. Thus, IRF2BP2 is crucial in managing how our bodies process fats, and it could be a target for treating metabolic disorders.-
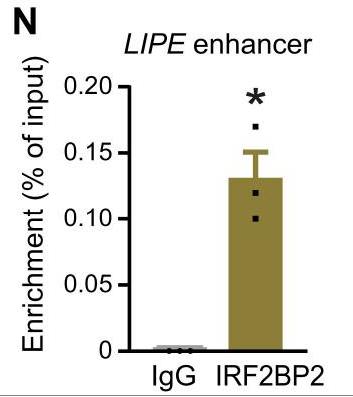 Fig1. ChIP-qPCR analysis for IRF2BP2 or IgG.
Fig1. ChIP-qPCR analysis for IRF2BP2 or IgG. -
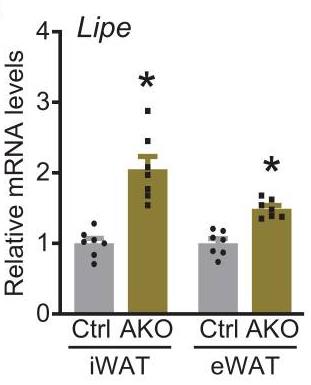 Fig2. Relative Lipe mRNA levels in iWAT and eWAT.
Fig2. Relative Lipe mRNA levels in iWAT and eWAT.
Case Study 2: Adom MA. et al. Neurobiol Dis. 2024
Poor lipid metabolism is linked to Parkinson's and dementia because it shifts α-synuclein (αS) into harmful forms. Too many αS monomers combine with fatty acids, leading to aggregation. By lowering monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) through hormone-sensitive lipase (LIPE) reduction, nerve health improved in male mice with Parkinson’s traits while females showed less benefit. Reducing LIPE lowered MUFA release, minimizing αS aggregation interactions. This suggests LIPE as a promising target for treating Parkinson's and related diseases by focusing on fatty acid processing.-
 Fig3. Automated gait scans of mice paw pattern on a horizontal treadmill (Cleversys) record to quantify step abnormalities.
Fig3. Automated gait scans of mice paw pattern on a horizontal treadmill (Cleversys) record to quantify step abnormalities. -
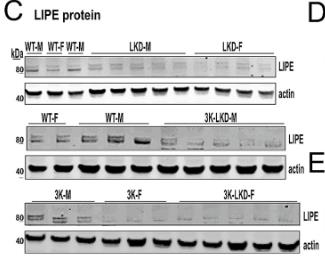 Fig4. WB shows the predicted short isoforms (80 and 83KDa) of the LIPE protein in WT, 3K and expected reduced level in LKD, 3K-LKD mouse brain cortex.
Fig4. WB shows the predicted short isoforms (80 and 83KDa) of the LIPE protein in WT, 3K and expected reduced level in LKD, 3K-LKD mouse brain cortex.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (LIPE-017H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (LIPE-017H) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (LIPE-6019H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (LIPE-6019H)
Involved Pathway
LIPE involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways LIPE participated on our site, such as cAMP signaling pathway,AMPK signaling pathway,Insulin signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with LIPE were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| cAMP signaling pathway | GRIN2D,GRIA1,SOX9,HHIP,GRIN2B,MAPK1,ATP1A1,ATP2B4,RAC2,GRIA3 |
| Aldosterone synthesis and secretion | STAR,GNA11,CAMK4,AGTR1B,KCNK9,CALML5,ATF2,NETO2,HSD3B1,CYP21A2 |
| Insulin signaling pathway | PPP1CBL,PDE3B,INS,AKT2L,PRKAG3,TRIP10A,PIK3CB,PPP1R3C,PRKACB,PPP1R3A |
| AMPK signaling pathway | ADIPOR1,EEF2K,LEPR,MAP3K7,PIK3R1,ACACB,GYS1,PFKFB3,IRS1,PPP2R3A |
| Regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes | AQP7,INS,NPY,ABHD5,PRKG1,AKT2,INS1,PIK3CG,TSHB,PTGER3 |
-
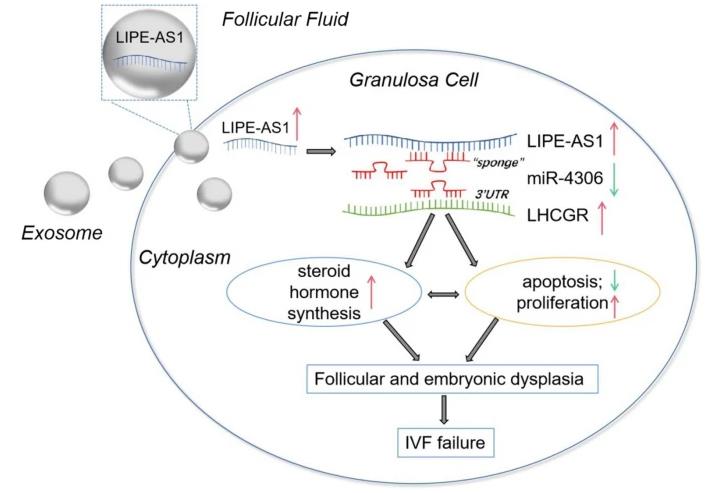 Fig1. The mechanism diagram. FF-derived exosomal LIPE-AS1 binds to miR-4306 to promote LHCGR expression. (Li Yu, 2024)
Fig1. The mechanism diagram. FF-derived exosomal LIPE-AS1 binds to miR-4306 to promote LHCGR expression. (Li Yu, 2024) -
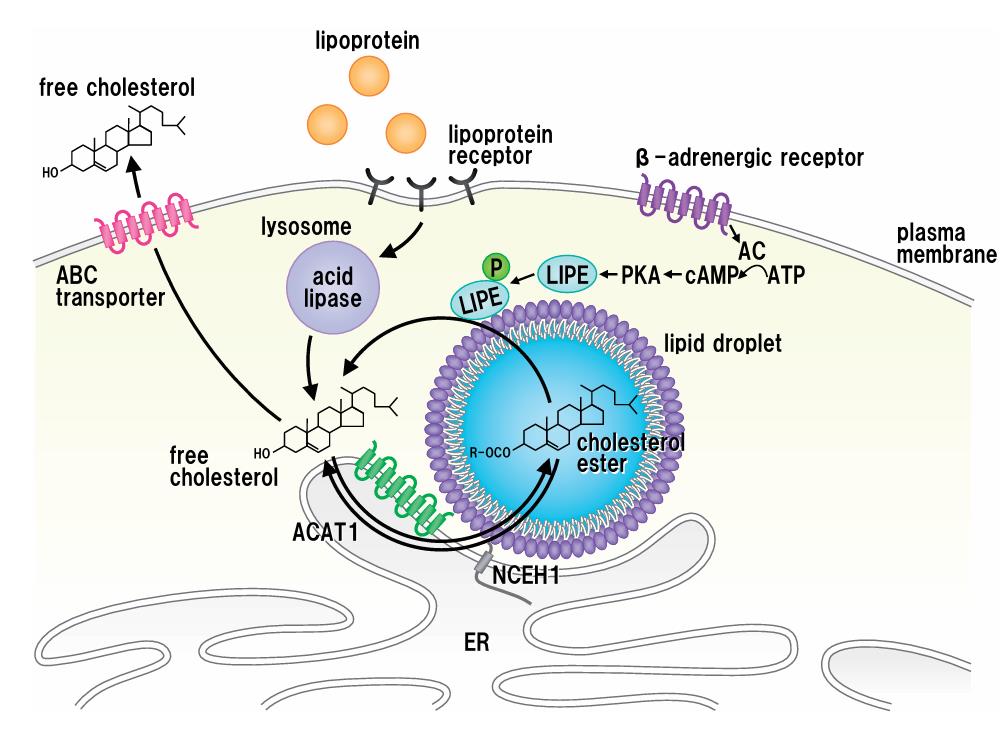 Fig2. Schematic representation of macrophage cholesterol ester homeostasis. (Motohiro Sekiya, 2011)
Fig2. Schematic representation of macrophage cholesterol ester homeostasis. (Motohiro Sekiya, 2011)
Protein Function
LIPE has several biochemical functions, for example, hormone-sensitive lipase activity,protein binding,protein kinase binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by LIPE itself. We selected most functions LIPE had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with LIPE. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | NOL3,CTLA2B,STRADA,DPM3,PDZD3,CRHBP,SMO,RAB1B,ZNF239,MKRN3 |
| protein kinase binding | RAD9,GSK3B,DAXX,ILK,MEF2A,MAP3K12,CCNK,TCTN2,E2F1,GCET2 |
| triglyceride lipase activity | CES3,Cel,CES1D,AADAC,PNPLA3,PNPLA4,PNLIPRP1,PNLIPRP2,LIPC,CES5A |
Interacting Protein
LIPE has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with LIPE here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of LIPE.
NSFL1C
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Faylon, MP; Koltes, DE; et al. Regulation of lipid droplet-associated proteins following growth hormone administration and feed restriction in lactating Holstein cows. JOURNAL OF DAIRY SCIENCE 97:2847-2855(2014).
- McDonough, PM; Maciejewski-Lenoir, D; et al. Differential Phosphorylation of Perilipin 1A at the Initiation of Lipolysis Revealed by Novel Monoclonal Antibodies and High Content Analysis. PLOS ONE 8:-(2013).


