LGALS8
-
Official Full Name
lectin, galactoside-binding, soluble, 8 -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of the galectin family. Galectins are beta-galactoside-binding animal lectins with conserved carbohydrate recognition domains. The galectins have been implicated in many essential functions including development, differentiation, cell-cell adhesion, cell-matrix interaction, growth regulation, apoptosis, and RNA splicing. This gene is widely expressed in tumoral tissues and seems to be involved in integrin-like cell interactions. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
LGALS8;lectin, galactoside-binding, soluble, 8;Gal-8;PCTA1;PCTA-1;Po66-CBP;galectin-8;galectin 8;galectin-8g;Po66 carbohydrate binding protein;po66 carbohydrate-binding protein;prostate carcinoma tumor antigen 1
Recombinant Proteins
- Rat
- Human
- Chicken
- Rhesus macaque
- Mouse
- Cattle
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Human
- HEK293
- GST
- Non
- His
- Avi
- Fc
- Flag
- DDK
- Myc
Background
What is LGALS8 Protein?
LGALS8, or galectin-8, is a protein that's quite handy around the body. It's part of the galectin family, known for sticking to certain sugars. This talent helps it manage how cells stick to each other and their environment, which is crucial for forming and fixing tissues. Galectin-8 also jumps into the immune system, acting like a guard that spots and reacts to potential threats. You can find it both inside and outside of cells, highlighting its various roles. It's been tied to health issues like cancer because of how it influences cell growth and communication. There’s still a lot to learn, but galectin-8 is definitely a big deal in keeping our cells in check and working smoothly.What is the Function of LGALS8 Protein?
The LGALS8 protein, also known as galectin-8, has quite a few roles up its sleeve. Primarily, it helps with cell adhesion, meaning it aids cells in sticking to each other and to their surroundings. This is crucial for things like building tissues and healing wounds. Additionally, galectin-8 is part of the body’s defense team. It helps spot invaders or problems, kicking off immune responses when needed. This protein also plays a part in communication inside cells, influencing how cells react and grow, which is why it’s caught the attention of researchers studying cancer. Its ability to bind with specific sugars means it’s involved in various cellular pathways, underscoring its importance in both maintaining normal processes and responding to challenges. In essence, galectin-8 is like a multitool for the body, essential for keeping things running smoothly.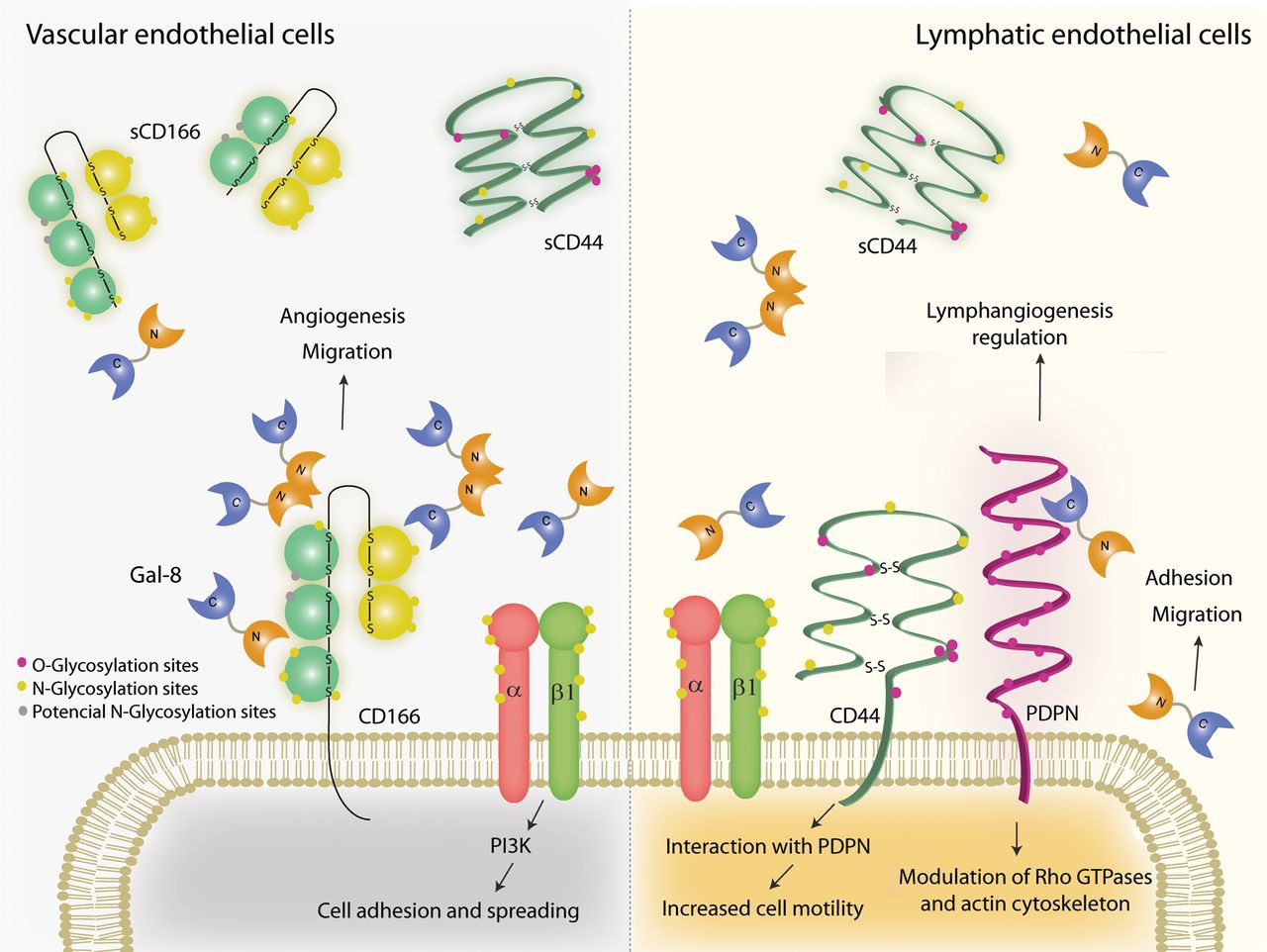
Fig1. Glycan-dependent interactions of gal-8 in endothelial cells and their microenvironment. (María F Troncoso, 2014)
LGALS8 Related Signaling Pathway
LGALS8, known as galectin-8, plays a key role in several important signaling pathways within cells. It’s involved in the mTORC1 pathway, which helps control cell growth and energy use. By influencing how cells sense nutrients, galectin-8 impacts cell growth and division. It also participates in pathways related to how cells stick to and move around their environment—crucial for forming tissues and healing wounds. By interacting with molecules on the cell surface, it helps manage these cell movements and attachments. These roles make galectin-8 vital for keeping cellular activities in check and are why it’s a focus in research, especially concerning conditions like cancer where these processes can malfunction.LGALS8 Related Diseases
LGALS8, or galectin-8, is associated with several diseases, particularly cancer. In cancer, it influences how tumor cells grow and spread, helping them move to new areas in the body. This makes galectin-8 a prime target for treatments aiming to stop metastasis. It's also connected to autoimmune diseases, where the immune system wrongly attacks the body's own cells. Galectin-8 helps regulate immune responses, so when it goes awry, it could play a part in conditions like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis. Researchers are investigating how modifying galectin-8's actions could lead to innovative treatments for these diseases, making it a focal point in medical research.Bioapplications of LGALS8
LGALS8, or galectin-8, is gaining attention for its diverse bioapplications. In cancer treatment, it's crucial because it influences how cancer cells grow and spread. Scientists are looking into ways to target galectin-8 to prevent tumors from advancing and metastasizing. It’s equally interesting in autoimmune disease research, as it helps regulate the immune response. By adjusting its function, there’s potential for new treatments for conditions like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body. Additionally, galectin-8's role in cell adhesion and signaling makes it valuable for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Understanding and modifying galectin-8 could lead to advancements in medical therapies and biotech innovations, placing it at the forefront of cutting-edge research.Case Study
Case Study 1: Roy M. et al. Life Sci Alliance. 2024
In overactive human osteoclasts, an LGALS8 splice change reduced the long version of galectin-8, which usually handles cell interactions. Blocking galectin-8 showed it helps in bone resorption and mTORC1 signaling, with the short version being key in bone breakdown. Using LC-MS/MS, 22 proteins were common to both isoforms, but nine, tied to cell adhesion and lysosomes, were unique to the short isoform. Galectin-8 interacted with secretory vesicle proteins like CLCN3, CLCN7, LAMP1, and LAMP2 in osteoclasts.-
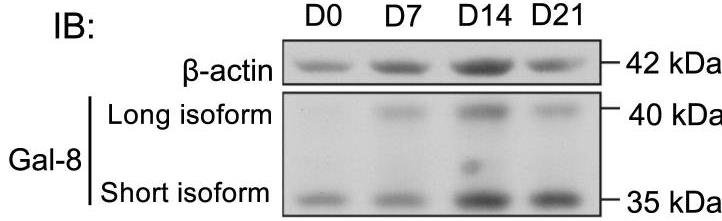 Fig1. Time-dependent expression of galectin-8 during osteoclast differentiation.
Fig1. Time-dependent expression of galectin-8 during osteoclast differentiation. -
 Fig2. Galectin-8 splicing profile determined as the ratio of the long isoform to total galectin-8.
Fig2. Galectin-8 splicing profile determined as the ratio of the long isoform to total galectin-8.
Case Study 2: Liu D. et al. Neuro Oncol. 2024
Glioma stem cells drive relapse and resistance in glioblastoma, with hypoxia supporting stem cell renewal and autophagy managing cell balance. Galectin-8 (Gal-8) plays a critical role under hypoxia, enhancing autophagy in GSCs. High Gal-8 levels in GBM predict poor patient outcomes. Inhibiting Gal-8 in mouse models slows tumor growth and extends survival, affecting mTORC1 and promoting cell growth.-
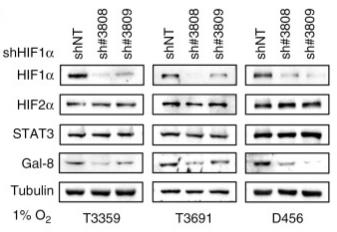 Fig3. Western blot analysis of Gal-8, HIF1α, HIF2α, and STAT3 expression.
Fig3. Western blot analysis of Gal-8, HIF1α, HIF2α, and STAT3 expression. -
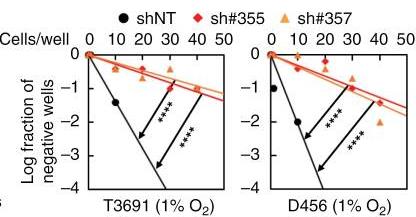 Fig4. In vitro limiting dilution assay of GSCs with Gal-8 knockdown under hypoxia.
Fig4. In vitro limiting dilution assay of GSCs with Gal-8 knockdown under hypoxia.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (LGALS8-428H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (LGALS8-428H) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (LGALS8-429M)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (LGALS8-429M)
Involved Pathway
LGALS8 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways LGALS8 participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with LGALS8 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
-
 Fig1. Dual role of Gal-8 on the adaptive immune response. (María V Tribulatti, 2020)
Fig1. Dual role of Gal-8 on the adaptive immune response. (María V Tribulatti, 2020) -
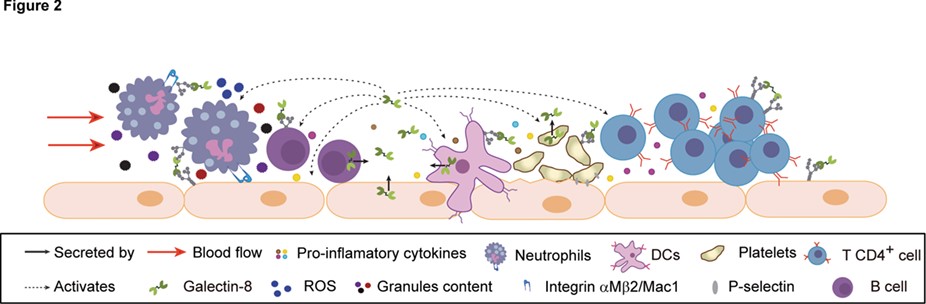 Fig2. Participation of Gal-8 in the inflammatory process. (María V Tribulatti, 2020)
Fig2. Participation of Gal-8 in the inflammatory process. (María V Tribulatti, 2020)
Protein Function
LGALS8 has several biochemical functions, for example, carbohydrate binding,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by LGALS8 itself. We selected most functions LGALS8 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with LGALS8. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| carbohydrate binding | GALNT3,CLEC10A,CLEC5A,FREM1,Mgl2,KLRB1B,CLEC4D,Reg2,PRPS1,CDIPT |
| protein binding | HIST1H2AL,TOM1,KCNN4,RUFY4,RPL14,FGFBP1,VASH1,BTF3L4,TFAP4,RHBDD1 |
Interacting Protein
LGALS8 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with LGALS8 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of LGALS8.
CALCOCO2;TGIF1;APEH;TRIM23
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


