ICOSLG
-
Official Full Name
inducible T-cell co-stimulator ligand -
Overview
Human B7-H2, also called B7RP-1, B7h, LICOS, and GL50, is a member of the growing B7 family of immune costimulatory proteins. Other family members include B7-1, B7-2, B7-H1 (PD-L1);, PD-L2, and B7-H3. B7 proteins are members of the immunoglobulin (Ig); su -
Synonyms
ICOSLG;inducible T-cell co-stimulator ligand;ICOSL;ICOS ligand;B7 homolog 2;B7 homologue 2;B7 H2;B7 related protein 1;B7H2;B7RP 1;B7RP1;CD275;GL50;ICOS L;KIAA0653;B7-like protein Gl50;B7-related protein 1;transmembrane protein B7-H2 ICOS ligand;B7-H2;LICOS;B7RP-1;ICOS-L
Recombinant Proteins
- Cynomolgus
- Human
- Rat
- Monkey
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Chicken
- HEK293
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- CHO
- Human Cells
- His
- Fc
- Avi
- hIgG4
- Flag
- Non
- T7
- DDK
- Myc
- mFc
Background
What is ICOSLG protein?
ICOSLG gene (inducible T cell costimulator ligand) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 21 at locus 21q22. ICOSLG belongs to the B7 family of molecules. It acts as a ligand for T cell-specific surface receptors ICOS and is involved in activation and regulation of a variety of immune cells. ICOSLG is localized to cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein particles and cell membranes, suggesting that it may play a critical role in transport and signaling within cells. The ICOSLG gene is expressed in a variety of cell types, including immune and non-immune cells, and its protein expression levels may vary in different cells and tissues. ICOSLG has been linked to a variety of diseases, including certain cancers and immune deficiency disorders. The ICOSLG protein is consisted of 302 amino acids and ICOSLG molecular weight is approximately 33.3 kDa.
What is the function of ICOSLG protein?
ICOSLG acts as a ligand for T cell-specific surface receptors ICOS, providing co-stimulatory signals that promote T cell proliferation and cytokine secretion. ICOSLG also induces the proliferation and differentiation of B cells into plasma cells, which may play a role in regulating local tissue response to inflammation and in regulating secondary immune responses by co-stimulating memory T cell function. ICOSLG plays a key role in the immune response of T helper cells and is involved in the ICOS signaling pathway, which is critical in the activation and differentiation of T cells. Specific miRNAs, such as miR-331-3p, can act as negative regulators of ICOSLG and inhibit malignant phenotypes of gastric cancer cells by decreasing the expression of ICOSLG.
ICOSLG Related Signaling Pathway
ICOSLG acts as a co-stimulatory factor that binds to the ICOS receptor on the surface of T cells, providing the necessary second signal to promote T cell activation, proliferation, and differentiation, while promoting antibody production of B cells. In the germinal center, ICOSLG promotes B cell proliferation and antibody class switching by interacting with T follicular helper cells (TFH), as well as the production of high-affinity antibodies. ICOSLG activation can affect the production of cytokines, such as regulating Th1 and Th2 balance through the ICOS/ICOSLG signaling pathway, affecting cytokine secretion.
ICOSLG Related Diseases
Due to its important role in immune regulation, ICOSLG has been linked to a variety of diseases, such as autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Up-regulated ICOSLG expression in some cancers may promote the proliferation, migration, and invasion of tumor cells, and is associated with tumor progression and poor prognosis. ICOSLG plays a role in regulating the immune response to pathogens, and abnormalities in ICOSLG may influence the body's resistance to infection. It can also be involved in transplant rejection, allergic disease and chronic inflammation.
Bioapplications of ICOSLG
As an immune checkpoint molecule, ICOSLG may promote tumor escape in the tumor microenvironment. Inhibitors targeting ICOSLG are being developed to enhance the immune response of T cells to tumors. The role of ICOSLG in modulating immune responses to pathogens may influence vaccine design and treatment strategies for infectious diseases. The expression and function of ICOSLG may influence immune tolerance and rejection after transplantation, which provides a potential intervention target for organ transplantation. The expression level of ICOSLG may serve as a biomarker of disease status and contribute to the diagnosis and prognosis assessment of disease.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Edurne Rujas, 2020
The inducible co-stimulator (ICOS) is a member of the CD28/B7 superfamily, and delivers a positive co-stimulatory signal to activated T cells upon binding to its ligand (ICOS-L). Here, researchers describe the molecular interactions of the ICOS/ICOS-L immune complex at 3.3 Å resolution. A central FDPPPF motif and residues within the CC' loop of ICOS are responsible for the specificity of the interaction with ICOS-L, with a distinct receptor binding orientation in comparison to other family members. Furthermore, the structure and binding data reveal that the ICOS N110 N-linked glycan participates in ICOS-L binding. In addition, researchers report crystal structures of ICOS and ICOS-L in complex with monoclonal antibodies under clinical evaluation in immunotherapy.
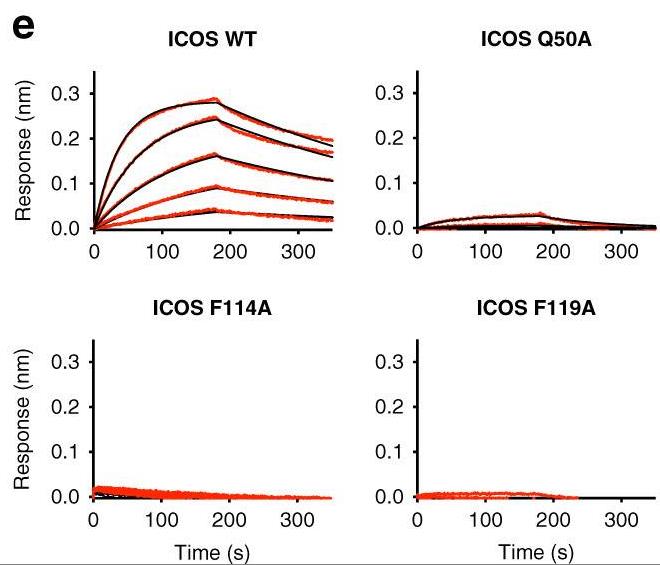
Fig1. Kinetic binding curves of ICOS-L to ICOS WT and ICOS mutants.
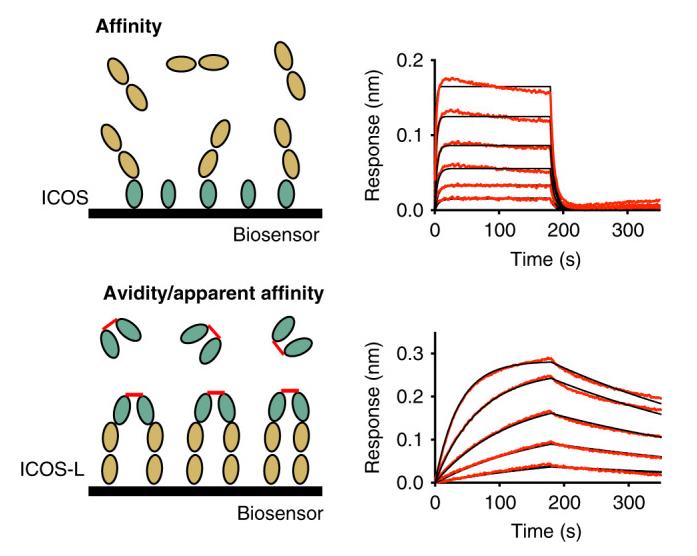
Fig2. Schematic experimental set-up (left) and kinetic binding curves (right) for immobilized ICOS and ICOS-L as analyte (top) measured by BLI.
Case Study 2: Martina Leopizzi, 2024
The earlier studies have shown that EBV-encoded nuclear antigen (EBNA2) upregulates programmed cell death ligand 1 in DLBCL and BLs by downregulating microRNA-34a. Here, researchers investigated whether EBNA2 affects the inducible costimulator (ICOS) ligand (ICOSL). In virus-infected and EBNA2-transfected B-lymphoma cells, ICOSL expression was reduced. The investigation of the molecular mechanisms revealed that this was due to an increase in microRNA-24 (miR-24) by EBNA2. By using ICOSL 3' untranslated region-luciferase reporter system, researchers validated that ICOSL is an authentic miR-24 target. Transfection of anti-miR-24 molecules in EBNA2-expressing lymphoma cells reconstituted ICOSL expression and increased tumor immunogenicity in mixed lymphocyte reactions. Indeed, the reduction of miR-24 in EBNA2-expressing DLBCL further elevated c-MYC and increased apoptosis. Consistent with the in vitro data, EBNA2-positive DLBCL biopsies expressed low ICOSL and high miR-24.
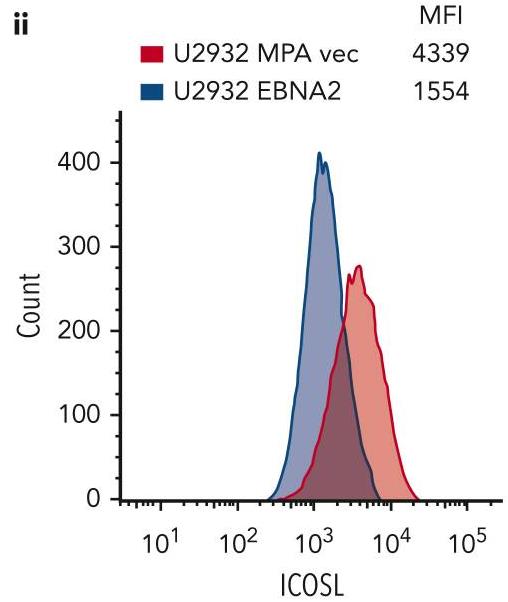
Fig3. ICOSL MFI was assessed by flow cytometry.
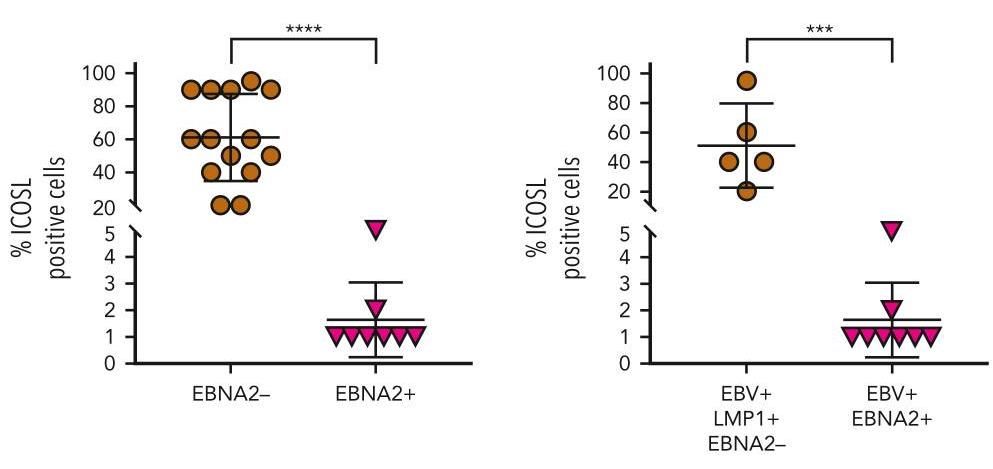
Fig4. Scattered dot plot analysis representing ICOSL-positive cells in each case.
Quality Guarantee
.
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (ICOSLG-051H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (ICOSLG-7689H)
Involved Pathway
ICOSLG involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways ICOSLG participated on our site, such as Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs),Intestinal i,ne network for IgA production, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with ICOSLG were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| ne network for IgA production | HLA-DQB1,TGFB1,CCR10,HLA-DQA1,IL15,TNFRSF17,HLA-DPA1,BLA,CCR9A,HLA-DQA2 |
| Intestinal i | IL6,HLA-DOB,MHC2DAB,MHC2A,Il2,BLA,TGFB1A,CD40,CXCL12A,AICDA |
| Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) | BMA1,NRXN1A,L1CAM,HLA-B,Ntng2,CLDN22,PVR,NRXN3,SELP,ITGB2L |
Protein Function
ICOSLG has several biochemical functions, for example, receptor binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by ICOSLG itself. We selected most functions ICOSLG had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with ICOSLG. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| receptor binding | Ren1,LYN,FGF24,FYNA,TENC1,PTPRD,CAT,Fert2,CD276,LAMA4 |
Interacting Protein
ICOSLG has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with ICOSLG here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of ICOSLG.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Sakthivel, P; Gereke, M; et al. Attenuation of Immune-Mediated Influenza Pneumonia by Targeting the Inducible Co-Stimulator (ICOS) Molecule on T Cells. PLOS ONE 9:-(2014).
- Fan, XZ; Quezada, SA; et al. Engagement of the ICOS pathway markedly enhances efficacy of CTLA-4 blockade in cancer immunotherapy. JOURNAL OF EXPERIMENTAL MEDICINE 211:715-725(2014).


