ENO2
-
Official Full Name
enolase 2 (gamma, neuronal) -
Overview
This gene encodes one of the three enolase isoenzymes found in mammals. This isoenzyme, a homodimer, is found in mature neurons and cells of neuronal origin. A switch from alpha enolase to gamma enolase occurs in neural tissue during development in rats and primates. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
ENO2;enolase 2 (gamma, neuronal);NSE;HEL-S-279;gamma-enolase;neural enolase;neuron-specific enolase;neurone-specific enolase;neuron specific gamma enolase;2-phospho-D-glycerate hydrolyase;2-phospho-D-glycerate hydro-lyase;epididymis secretory protein Li 279
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Chicken
- E.coli
- Hela
- Mammalian Cells
- Human
- Wheat Germ
- Human Brain
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- Non
- GST
- Avi
- Fc
- Flag
- DDK
- Myc
Background
What is ENO2 Protein?
ENO2, also known as enolase 2, is crucial for glycolysis, which is the process cells use to convert sugars into energy. It's mostly found in the brain and nervous tissues, earning it the name neuron-specific enolase (NSE). Because of its presence in neural tissues, ENO2 is quite useful in medical diagnostics; elevated levels can hint at nerve damage or specific cancers, like neuroendocrine tumors. This makes ENO2 an important protein for researchers and clinicians alike, as understanding its levels and activity can provide insights into various neurological disorders and cancerous conditions, aiding in both diagnosis and treatment strategies.What is the Function of ENO2 Protein?
ENO2, also known as enolase 2, plays a crucial role in glycolysis, assisting in breaking down glucose to produce energy within cells. It's particularly important in the brain and nervous tissues, which is why it's also referred to as neuron-specific enolase (NSE). Beyond its metabolic duties, ENO2 is a useful marker in diagnosing certain conditions. For example, its levels can be elevated in cases of nerve damage or certain cancers, like neuroendocrine tumors. This makes ENO2 not just a key player in basic cellular processes but also a valuable tool in medical diagnostics to help understand and detect various diseases.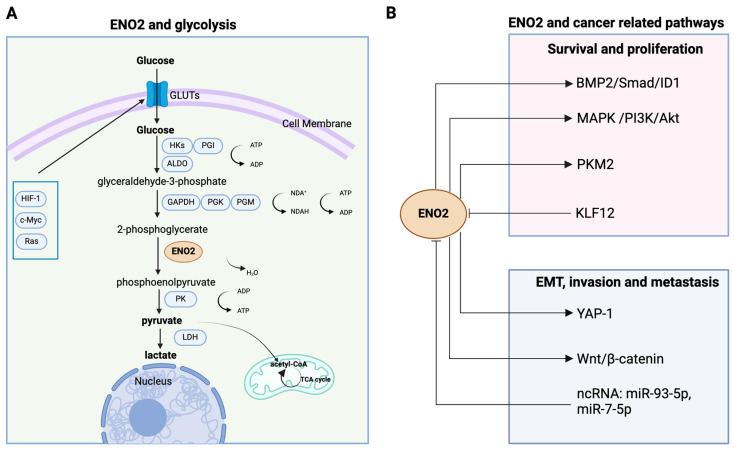
Fig1. Schematic representation of the pleiotropic roles of ENO2 in cancer glycolysis and multiple pathways. (Yuhan Zhou, 2024)
ENO2 Related Signaling Pathway
ENO2, or enolase 2, is involved in signaling pathways that are crucial for cellular energy production, especially in nerve cells. As part of the glycolysis process, ENO2 helps convert glucose into energy, which is vital for supporting the high energy demands of brain and nervous tissues. Beyond its metabolic role, ENO2 can signal changes in cellular environments, particularly under stress or damage conditions. High levels of ENO2 might indicate neuronal stress or certain cancers, acting as a biomarker in these contexts. Therefore, ENO2 is important not only for its role in metabolism but also for providing insights into cellular responses within neurological and cancer-related pathways.ENO2 Related Diseases
ENO2, or enolase 2, is a significant enzyme primarily found in the brain and some other tissues. It plays a critical role in glycolysis, the process our bodies use to break down glucose into energy. Now, when something goes off-kilter with ENO2, it can lead to various neurological disorders given its high presence in the nerve tissues. For instance, it's been linked with certain types of cancers, particularly neuroendocrine tumors, because of its role in differentiating tissue origins in tumor cells. Beyond the cancer spectrum, alterations or irregular expressions of ENO2 might also be implicated in neurodegenerative diseases. These conditions encompass a wide array of issues that predominantly hit the nervous system’s functionality, potentially leading to serious outcomes like impaired movement or cognitive function. Understanding ENO2’s role gives researchers a vital clue in diagnosing and treating these tricky diseases, but it's an ongoing field of study with many mysteries still to unravel.Bioapplications of ENO2
Primarily hanging out in the brain and nerve tissues, ENO2 becomes all kinds of useful in medical and research fields. One major application is in the world of diagnostics. Due to its specific presence in certain cell types, ENO2 can serve as a biomarker. It's particularly handy in distinguishing neuron-specific activities, which helps in detecting neuroendocrine tumors and even some types of lung cancer. In clinical diagnostics, spotting ENO2 can assist doctors in figuring out the tissue origin of certain tumors, leading to more personalized and effective treatment plans. Beyond the doctor's office, researchers also explore ENO2 in their quest to understand neurological diseases. Since it's a major player in neural tissues, studying its behavior can lead to breakthroughs in identifying the underlying issues of complex diseases such as Alzheimer's or Parkinson's. So, while ENO2 may seem like a small cog in the biological wheel, its applications span a wide range of important medical and scientific endeavors.Case Study
Case Study 1: Feng J. et al. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2024
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) involves complex molecular processes. ENO2 and HOXC6 are key players in OSCC and the Warburg effect, but their interaction isn't fully understood. Researchers found ENO2 upregulated in OSCC, influencing cell migration, invasion, and glycolysis. HOXC6 was identified as a regulator of ENO2. Silencing HOXC6 reduced ENO2 expression, as confirmed by assays. High ENO2 levels are linked to poor survival in OSCC. Silencing ENO2 reduced OSCC aggressiveness and glycolysis. HOXC6 positively correlates with ENO2, acting as its direct activator and driving the Warburg effect in OSCC.-
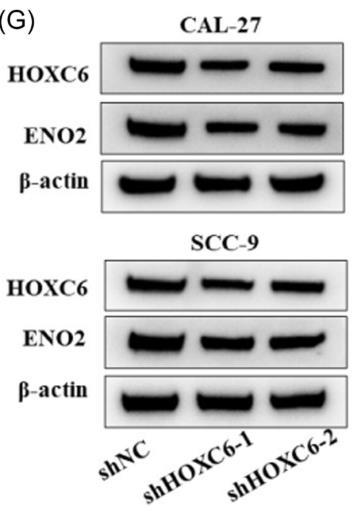 Fig1. Western blot showing the relative expression of HOXC6 and ENO2 in CAL-27 and SCC-9 cells transfected with sh-HOXC6/NC.
Fig1. Western blot showing the relative expression of HOXC6 and ENO2 in CAL-27 and SCC-9 cells transfected with sh-HOXC6/NC. -
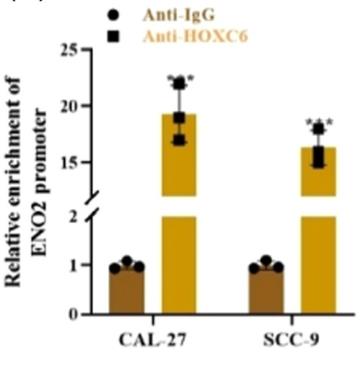 Fig2. ChIP assay revealing the relative enrichment of the ENO2 promoter in CAL-27 and SCC-9 cells treated with anti-IgG/HOXC6.
Fig2. ChIP assay revealing the relative enrichment of the ENO2 promoter in CAL-27 and SCC-9 cells treated with anti-IgG/HOXC6.
Case Study 2: Sun C. et al. J Cell Physiol. 2021
In papillary renal cell carcinoma (pRCC), ENO2 is linked to genetic issues and worse prognosis, especially in younger patients. It's overexpressed, driving glycolysis and cell growth. Silencing ENO2 reduces tumor growth and alters glycolytic genes. Though TT-232 alone isn't effective, combined with ENO2 silencing, it shows strong effects in mouse models. ENO2's role in glycolysis highlights its potential as a therapeutic target.-
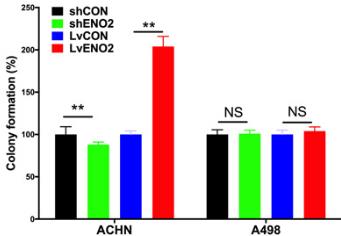 Fig3. Colony formation assay showing effects of overexpression and silencing ENO2 on anchorage-independent growth of ACHN and A498 cells.
Fig3. Colony formation assay showing effects of overexpression and silencing ENO2 on anchorage-independent growth of ACHN and A498 cells. -
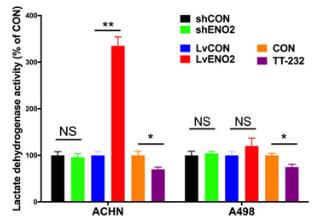 Fig4. LDH level in of ACHN and A498 cells treated with ENO2 overexpression.
Fig4. LDH level in of ACHN and A498 cells treated with ENO2 overexpression.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (ENO2-3313H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (ENO2-3313H) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (ENO2-6181H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (ENO2-6181H)
Involved Pathway
ENO2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways ENO2 participated on our site, such as Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis,Metabolic pathways,Carbon metabolism, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with ENO2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Carbon metabolism | MDH1,SUCLA2,GOT2A,IDH2,GPR19,TKTL2,PGK2,H6PD,OGDHL,FBP1A |
| HIF- signaling pathway | ENO1,MAP2K2,PIK3R3,MAPK3,PIK3CB,EIF4E1B,NOX1,PIK3R1,LTBR,HK3 |
| Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis | ALDH7A1,HK2,LDHAL6B,LDHBA,TPI1,ALDOB,BPGM,LDHAL6A,GAPDHS,ADH1C |
| Biosynthesis of amino acids | PFKMA,PCXB,IDH1,ASS1,PC,THA1,ALDOA,GPT2L,BCAT1,ALDH18A1 |
| Metabolic pathways | RDH10B,IDI1,Ckmm,CYP26B1,CYCS,SC5DL,INPP5A,ATP6V1B1,NDUFC2-KCTD14,IDUA |
| RNA degradation | TOB1A,PABPC1L2A,EDC4,CNOT7,PAPD7,PFKP,DCP2,PABPC3,RQCD1,EXOSC10 |
-
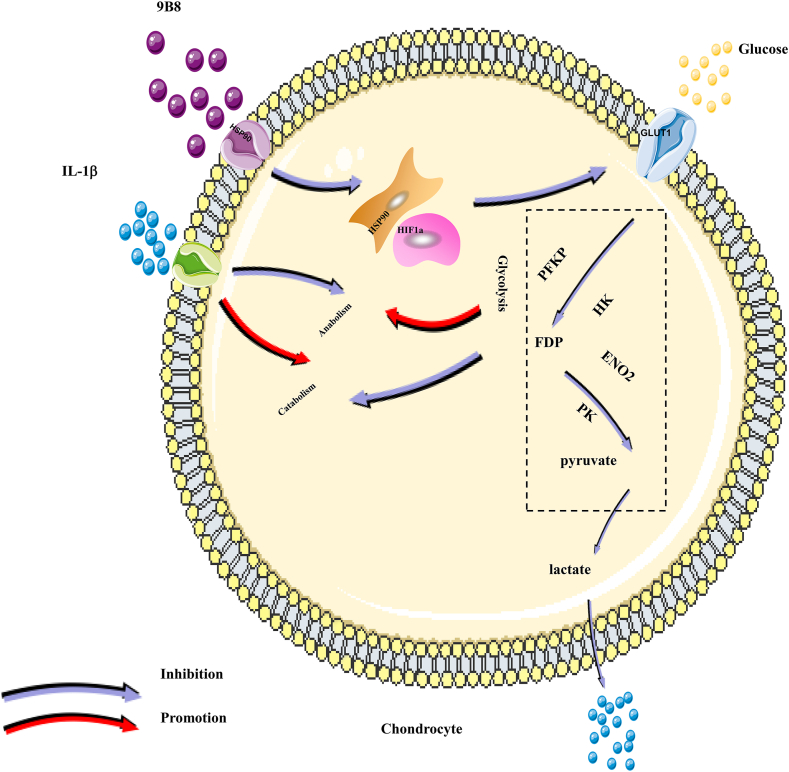 Fig1. Schematic Diagram of the potential protective effects of 9B8 on IL-1β-induced inflammatory injury in chondrocytes. (Shunan Yu, 2024)
Fig1. Schematic Diagram of the potential protective effects of 9B8 on IL-1β-induced inflammatory injury in chondrocytes. (Shunan Yu, 2024) -
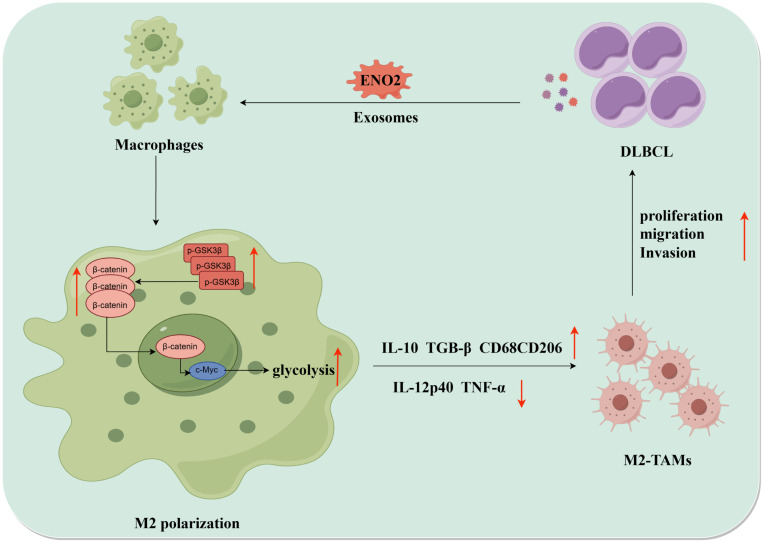 Fig2. The diagrammatic representation depicted the positive feedback loop between DLBCL cells and TAMs. (Ruonan Shao, 2024)
Fig2. The diagrammatic representation depicted the positive feedback loop between DLBCL cells and TAMs. (Ruonan Shao, 2024)
Protein Function
ENO2 has several biochemical functions, for example, lyase activity,magnesium ion binding,metal ion binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by ENO2 itself. We selected most functions ENO2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with ENO2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein heterodimerization activity | PVALB,CEBPE,BIRC5,CAPN2,HNF1B,HIST4H4,HIST1H2AC,ADORA2A,CEBPG,CUL3 |
| magnesium ion binding | PIF1,THG1L,TSSK4,MTPAP,RPS6KA3,NT5C1B,STK36,NT5C1AA,GLUL,OPA1 |
| lyase activity | ECHDC2,CAR5A,GC3,HMGB1,THA1,NPR1A,FH1,MOCOS,PDXDC1,GLDC |
| protein homodimerization activity | DROSHA,GPD1B,CDH13,RXRB,XDH,ZFP365,HPS4,NR4A2,ACVR1,SQSTM1 |
| phosphopyruvate hydratase activity | ENO1A,ENO1,ENO3,ENO1B,ENO4,GM5506 |
| metal ion binding | UPB1,ZNF398,ZNF550,NT5DC1,ZFP319,ARSH,PPP4CA,HMGCL,BTY,ZNF652 |
Interacting Protein
ENO2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with ENO2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of ENO2.
Ywhae;Ywhaz;Kcnma1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Fernandez-Garcia, A; Alvarez-Garcia, G; et al. Identification of Besnoitia besnoiti proteins that showed differences in abundance between tachyzoite and bradyzoite stages by difference gel electrophoresis. PARASITOLOGY 140:999-1008(2013).
- Nakamura, N; Dai, QS; et al. Disruption of a Spermatogenic Cell-Specific Mouse Enolase 4 (Eno4) Gene Causes Sperm Structural Defects and Male Infertility. BIOLOGY OF REPRODUCTION 88:-(2013).


