DMBT1
-
Official Full Name
deleted in malignant brain tumors 1 -
Overview
Loss of sequences from human chromosome 10q has been associated with the progression of human cancers.The gene DMBT1 was originally isolated based on its deletion in a medulloblastoma cell line.DMBT1 is expressed with transcripts of 6.0, 7.5, and 8.0 kb in fetal lung and with one transcript of 8.0 kb in adult lung, although the 7.5 kb transcript has not been characterized.The DMBT1 protein is a glycoprotein containing multiple scavenger receptor cysteine-rich (SRCR) domains separated by SRCR-interspersed domains (SID).Transcript variant 2 (8.0 kb) has been shown to bind surfactant protein D independently of carbohydrate recognition.This indicates that DMBT1 may not be a classical tumor supressor gene, but rather play a role in the interaction of tumor cells and the immune system. -
Synonyms
DMBT1;deleted in malignant brain tumors 1;deleted in malignant brain tumors 1 protein;GP340;muclin;SAG;gp-340;hensin;glycoprotein 340;salivary agglutinin;surfactant pulmonary-associated D-binding protein;FLJ61058;MGC164738
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Mouse
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- Human Cells
- E.coli
- His
- GST
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMBT1-3231H | Recombinant Human DMBT1 protein(Met1-Ser220), His-tagged | HEK293 | Human | His | 1-220 a.a. | |
| DMBT1-1890R | Recombinant Rat DMBT1 Protein | Mammalian Cells | Rat | His |
|
|
| DMBT1-2700H | Recombinant Human DMBT1 Protein, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST |
|
|
| DMBT1-4641M | Recombinant Mouse DMBT1 Protein | Mammalian Cells | Mouse | His |
|
|
| DMBT1-2407HCL | Recombinant Human DMBT1 cell lysate | Human Cells | Human | Non |
|
|
| DMBT1-1351H | Recombinant Human DMBT1 Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Cys2008-Arg2413 |
|
| DMBT1-1549R | Recombinant Rat DMBT1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Rat | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| DMBT1-1549R-B | Recombinant Rat DMBT1 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Rat |
|
||
| DMBT1-2409M | Recombinant Mouse DMBT1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| DMBT1-2409M-B | Recombinant Mouse DMBT1 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
Background
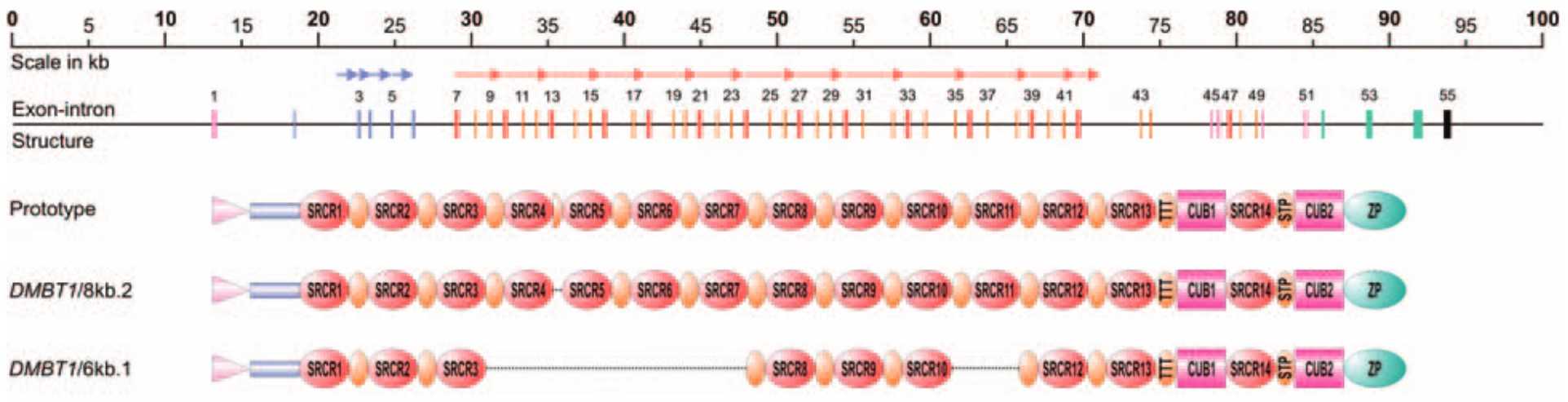
Fig1. Structure of the genomic DMBT1 locus. (Jens Madsen, 2010)
What is DMBT1 protein?
DMBT1 (deleted in malignant brain tumors 1) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 10 at locus 10q26. Loss of sequences from human chromosome 10q has been associated with the progression of human cancers. This gene was originally isolated based on its deletion in a medulloblastoma cell line. This gene is expressed with transcripts of 6.0, 7.5, and 8.0 kb in fetal lung and with one transcript of 8.0 kb in adult lung, although the 7.5 kb transcript has not been characterized. The encoded protein precursor is a glycoprotein containing multiple scavenger receptor cysteine-rich (SRCR) domains separated by SRCR-interspersed domains (SID). Transcript variant 2 (8.0 kb) has been shown to bind surfactant protein D independently of carbohydrate recognition. The DMBT1 protein is consisted of 2413 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 260.7 kDa.
What is the function of DMBT1 protein?
DMBT1 is a host defense mechanism and immunomodulatory protein that is widely expressed in humans and other mammals. It is a highly glycosylated polypeptide protein that performs its biological function by binding to membrane glycoproteins or cell surface receptors mainly through its multiple n-glycosylation sites. The DMBT1 protein also has antibacterial and antiviral effects and is able to interact with a variety of microorganisms and viruses. In addition, it can also promote the enhancement of host cells and immune cells and other immunomodulatory functions. DMBT1/SAG/gp-340 belongs to the scavorator receptor cysteine-rich (SRCR) superfamily of proteins and is a secreted protein capable of recognizing a variety of pathogens.
DMBT1 Related Signaling Pathway
DMBT1 is down-regulated in human chronic glomerulonephritis (CGN) and is associated with the WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway. Studies have shown that overexpression of DMBT1 gene can inhibit cell migration and invasion, while WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway and its downstream cytokines are inhibited. Studies have shown that DMBT1 can inhibit the progression of gallbladder cancer by targeting PTEN through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. As a secreted glycoprotein, DMBT1 has a broad bacterial binding spectrum and is associated with inhibition of LPS-induced TLR4-mediated NF-κB activation and pathogenesis of Crohn's disease.
DMBT1 Related Diseases
The mutation inactivation of DMBT1 gene is believed to be closely related to the occurrence of various tumors. It is considered to be a candidate tumor suppressor gene, and the loss or decrease of its expression is related to the occurrence and development of tumors. For example, in primary lung cancer, the expression level of DMBT1 is significantly correlated with the degree of differentiation of tumor cells and the presence or absence of metastasis. DMBT1 is involved in inflammation and has been shown to play a role in inflammatory diseases such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. DMBT1 may be a novel early biomarker of ARDS by influencing alveolar epithelial cells, alveolar capillaries and inflammatory response. DMBT1 is also associated with breast cancer, retinitis pigmentosa, iron overload and other diseases.
Bioapplications of DMBT1
DMBT1 recombinant protein can be applied to biometrics, biochips and protein affinity chromatography. The recombinant DMBT1 protein can be used as a biosensor to detect harmful microorganisms and viruses in the environment. The DMBT1 protein was found to alleviate nasal airway inflammation in a mouse model of nasal polyps, suggesting that it may have potential applications in the treatment of related diseases.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Jianfang Li, 2017
It is generally thought that mucosal fluids protect underlying epithelial surfaces against opportunistic infection via their antimicrobial activity. However, the published data show that human tear fluid can protect against the major opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa independently of bacteriostatic activity. Here, the researchers explored the mechanisms for tear protection, focusing on impacts of tear fluid on bacterial virulence factor expression. Results showed that tear fluid suppressed twitching motility, a type of surface-associated movement conferred by pili. Inhibition of twitching by tear fluid was dose-dependent with dilutions to 6.25% retaining activity. Purified lactoferrin, lysozyme, and contrived tears containing these, and many other, tear components lacked the activity. Systematic protein fractionation, mass spectrometry, and immunoprecipitation identified the glycoprotein DMBT1 (Deleted in Malignant Brain Tumors 1) in tear fluid as required. DMBT1 purified from human saliva also inhibited twitching, as well as P. aeruginosa traversal of human corneal epithelial cells in vitro, and reduced disease pathology in a murine model of corneal infection. DMBT1 did not affect PilA expression, nor bacterial intracellular cyclicAMP levels, and suppressed twitching motility of P. aeruginosa chemotaxis mutants (chpB, pilK), and an adenylate cyclase mutant (cyaB). However, dot-immunoblot assays showed purified DMBT1 binding of pili extracted from PAO1 suggesting that twitching inhibition may involve a direct interaction with pili.

Fig1. DMBT1-depleted human tear fluid does not inhibit twitching motility of PAO1.

Fig2. CyclicAMP levels of P. aeruginosa PAO1 treated with DMBT1 (100 ng/μl).
Case Study 2: Hanna Müller, 2015
Deleted in malignant brain tumors 1 (DMBT1) is an innate defence protein expressed in the lungs of preterm infants and adults. Recent studies showed that DMBT1 is important in angiogenesis and can bind to different growth factors including VEGF. The researchers aimed at examining relationships between VEGF and IL-6 levels to DMBT1 expression in the lungs of preterm and term infants and in lung epithelial cells in vitro. To examine the effect of DMBT1 on VEGF and IL-6 expression we compared type II lung epithelial A549 cells stably transfected with a DMBT1 expression plasmid (DMBT1+ cells) to A549 cells stably transfected with an empty expression plasmid (DMBT1- cells). The concentrations of VEGF and IL-6 were determined via ELISA in the supernatant of the unstimulated cells and after stimulation with LPS, TNFα and Phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA). Unstimulated DMBT1+ A549 cells showed significantly higher VEGF expression than DMBT1- cells. Significantly elevated VEGF levels were also confirmed for DMBT1+ cells after stimulation with TNFα, LPS and PMA. The IL-6 levels were comparable in DMBT1+ versus DMBT1- cells without stimulation, but they were significantly reduced in DMBT1+ cells after stimulation with TNFα, LPS and PMA.
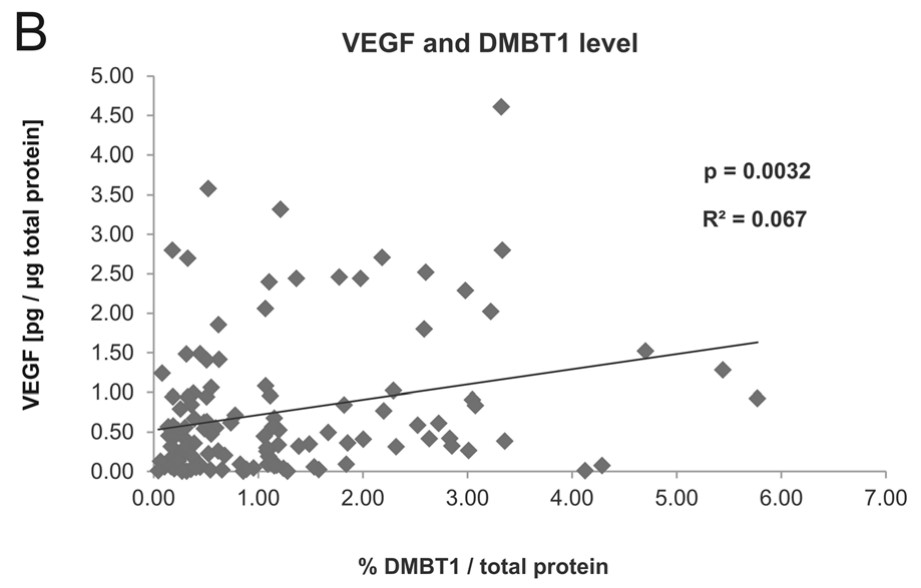
Fig3. Positive correlation of VEGF levels with relative DMBT1 levels in the tracheal aspirates.

Fig4. DMBT1 expression in DMBT1+ and DMBT1- cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (DDMBT1-2700H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (DMBT1-1351H)
Involved Pathway
DMBT1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways DMBT1 participated on our site, such as Metabolism of proteins,Salivary secretion,Surfactant metabolism, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with DMBT1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Surfactant metabolism | SLC34A2A,ZDHHC2,CTSH,CKAP4,SFTPC,GPR116,GATA6,SFTPBB,LMCD1,CCDC59 |
| Salivary secretion | Slc4a2,CALML3,CST4,PRKACA,LYZ1,PMAP-36,KCNN4,PRH2,CST3,PRKCA |
| Metabolism of proteins | SEC16B,TRAPPC6B,RING1,CBX4,TTR,GPR116,EXOC3,ODAM,ADAMTS8,MIA3 |
Protein Function
DMBT1 has several biochemical functions, for example, calcium-dependent protein binding,protein binding,scavenger receptor activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by DMBT1 itself. We selected most functions DMBT1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with DMBT1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | OSBP,SNAP47,CEP290,AP5Z1,PHF23,PREP,ZNF747,VASNA,TESK1,DCUN1D4 |
| signaling pattern recognition receptor activity | TRIM5,FCN1,MARCO,COLEC12,CLEC7A,TLR2 |
| scavenger receptor activity | PRG4B,TMPRSS3,SCARF2,SRCRB4D,SCARA3,TMPRSS4,PGBD1,CD163L1,VTN,LOXL2 |
| calcium-dependent protein binding | SYT1,TSG101,MYO1D,SLC9A1,CALM3,CASQ2,ANXA1,MBL2,S100A11,C9orf9 |
Interacting Protein
DMBT1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with DMBT1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of DMBT1.
CAV1;CDK5RAP3;P/V/C;CDK6;PARD6B
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Higashi, K; Asano, K; et al. Expression of the Clustered NeuAc alpha 2-3Gal beta O-Glycan Determines the Cell Differentiation State of the Cells. JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY 289:25833-25843(2014).
- Petersen, CP; Weis, VG; et al. Macrophages Promote Progression of Spasmolytic Polypeptide-Expressing Metaplasia After Acute Loss of Parietal Cells. GASTROENTEROLOGY 146:1727-+(2014).



