DDX6
-
Official Full Name
DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box helicase 6 -
Overview
The lymphoma-associated Rck/p54 gene product is a member of the DEAD box protein/RNA helicase family which has a variety of functions including translation initiation, pre-mRNA splicing, and ribosome assembly. Overexpression of human Rck in a guinea pig c -
Synonyms
DDX6;DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box helicase 6;DEAD (Asp Glu Ala Asp) box polypeptide 6 , DEAD/H (Asp Glu Ala Asp/His) box polypeptide 6 (RNA helicase, 54kD) , HLR2;probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX6;RCK;DEAD box-6;oncogene RCK;DEAD box protein
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Chicken
- Mouse
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- E.coli
- GST
- His
- DDK
- Myc
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DDX6-28328TH | Recombinant Human DDX6 protein, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST | 1-483 a.a. | |
| DDX6-1464C | Recombinant Chicken DDX6 | Mammalian Cells | Chicken | His |
|
|
| DDX6-4433M | Recombinant Mouse DDX6 Protein | Mammalian Cells | Mouse | His |
|
|
| DDX6-45H | Recombinant Human DDX6 protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | HEK293 | Human | DDK&Myc |
|
|
| DDX6-6998HCL | Recombinant Human DDX6 293 Cell Lysate | HEK293 | Human | Non |
|
|
| DDX6-2280M | Recombinant Mouse DDX6 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| DDX6-2280M-B | Recombinant Mouse DDX6 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
||
| Ddx6-2515M | Recombinant Mouse Ddx6 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | DDK&Myc |
|
|
| DDX6-6899HF | Recombinant Full Length Human DDX6 Protein, GST-tagged | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | GST | Full L. 483 amino acids |
|
| DDX6-8673H | Recombinant Human DDX6 Full Length protein | E.coli | Human | His | Full L. |
|
Background
What is DDX6 protein?
DDX6 (DEAD-box helicase 6) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 11 at locus 11q23. It is a member of the DEAD-box protein family, which are characterized by their ability to unwind RNA structures, an activity that is crucial for various RNA processing events . DDX6 has been implicated in a range of cellular functions, including translation initiation, pre-mRNA splicing, and ribosome assembly . It is also involved in post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression, as suggested by its role in the regulation of HER2 and FGFR2 in gastric cancer cells . Furthermore, DDX6 is associated with processing bodies (P-bodies), which are cytoplasmic foci involved in mRNA turnover and surveillance. The DDX6 protein is consisted of 483 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 54.4 kDa.
What is the function of DDX6 protein?
As a DEAD-box protein, DDX6 has RNA helicase activity, meaning it can unwind RNA duplexes, which is crucial for various RNA processing events. DDX6 is involved in the initiation of translation, a key step in protein synthesis where the ribosome assembles on the mRNA to begin reading the genetic code. It plays a role in the splicing of pre-mRNA, which is the process where introns (non-coding regions) are removed from the initial RNA transcript to form the mature mRNA. It has been shown to regulate the expression of certain genes at the post-transcriptional level, such as HER2 and FGFR2 in gastric cancer cells, by binding to their mRNAs and affecting their stability or translation efficiency. DDX6 is associated with P-bodies, cytoplasmic foci where mRNAs are stored, processed, or degraded. It plays a role in mRNA turnover and surveillance. The ATPase/helicase motif of DDX6 is essential for efficient viral replication in certain contexts, suggesting its role in the host-virus interaction.
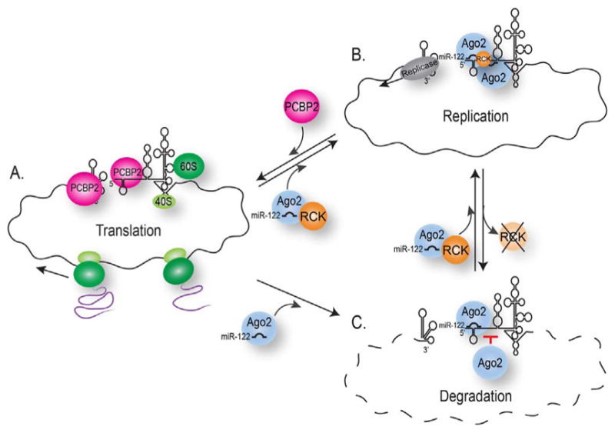
Fig1. A model for the interaction of DDX6 and miR-122 with the HCV genome. (Jason M Biegel, 2017)
DDX6 Related Signaling Pathway
DDX6 is associated with the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) and regulates the binding of specific mrnas in a phosphorylation-dependent manner when stimulated by NMDA receptors. DDX6 interacts with RISC by directly binding to CNOT1, which in turn affects gene silencing. DDX6 is closely related to p65 and IκBα in the NF-κB pathway and is involved in the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases. The DEAD-box RNA helicase family plays a role in the innate immune response, although the exact mechanism is not well understood. DDX family proteins are dysregulated in various tumor tissues, and participate in the occurrence and development of tumors, affecting the proliferation, apoptosis, cell cycle, invasion, metastasis and metabolism of tumor cells.
DDX6 Related Diseases
DDX6 is involved in the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases through NF-κB activation. In non-immune cells, β silencing of DDX6 inhibits the NF-κB pathway and inhibits the activation of IL-6 amplifiers. DDX6 is closely related to p65 and IκBα, but not to TRADD, RIP, or TRAF2, suggesting a novel function of DDX6 as a bridging protein in the NF-κB pathway. DDX family members are dysregulated in tumor tissues and participate in the occurrence and development of tumors. DDX6 is involved in the proliferation, apoptosis, cell cycle, invasion, metastasis and metabolism of tumor cells, and can be used as a new molecular marker for tumor diagnosis, evaluation of malignancy and prediction of clinical prognosis. DDX6 is involved in NMDA receptor-dependent signaling pathways, and its activity is essential for NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic plasticity. Imiquimod mediated dermatitis model was inhibited by SIRNA-mediated downregulation of DDX6 gene, suggesting that DDX6 may be involved in the occurrence and development of skin diseases. DDX6 mutations have been shown to cause intellectual disability.
Bioapplications of DDX6
In the context of bioapplications, it has been shown to be a potential therapeutic target for cancer treatment. Inhibition of DDX6 by small molecules or genetic knockout has been shown to induce tumor cell death in vitro and in vivo. It has also been suggested as a potential therapeutic target for neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease and Huntington's disease.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Seiichiro Naito, 2024
The IL-6 amplifier was originally discovered as a mechanism for the enhanced activation of NF-κB in non-immune cells. In the IL-6 amplifier, IL-6-STAT3 and NF-κB stimulation is followed by an excessive production of IL-6, chemokines, and growth factors to develop chronic inflammation preceding the development of inflammatory diseases. Previously, using a shRNA-mediated genome-wide screening, the researchers found that DEAD-Box Helicase 6 (DDX6) is a candidate positive regulator of the amplifier. Here, they investigate whether DDX6 is involved in the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases via the IL-6 amplifier. They found that DDX6-silencing in non-immune cells suppressed the NF-κB pathway and inhibited activation of the IL-6 amplifier, while the forced expression of DDX6 enhanced NF-κB promoter activity independent of the RNA helicase activity of DDX6. The imiquimod-mediated dermatitis model was suppressed by the siRNA-mediated gene downregulation of DDX6. Furthermore, silencing DDX6 significantly reduced the TNF-α-induced phosphorylation of p65/RelA and IκBα, nuclear localization of p65, and the protein levels of IκBα. Mechanistically, DDX6 is strongly associated with p65 and IκBα, but not TRADD, RIP, or TRAF2, suggesting a novel function of DDX6 as an adaptor protein in the NF-κB pathway.
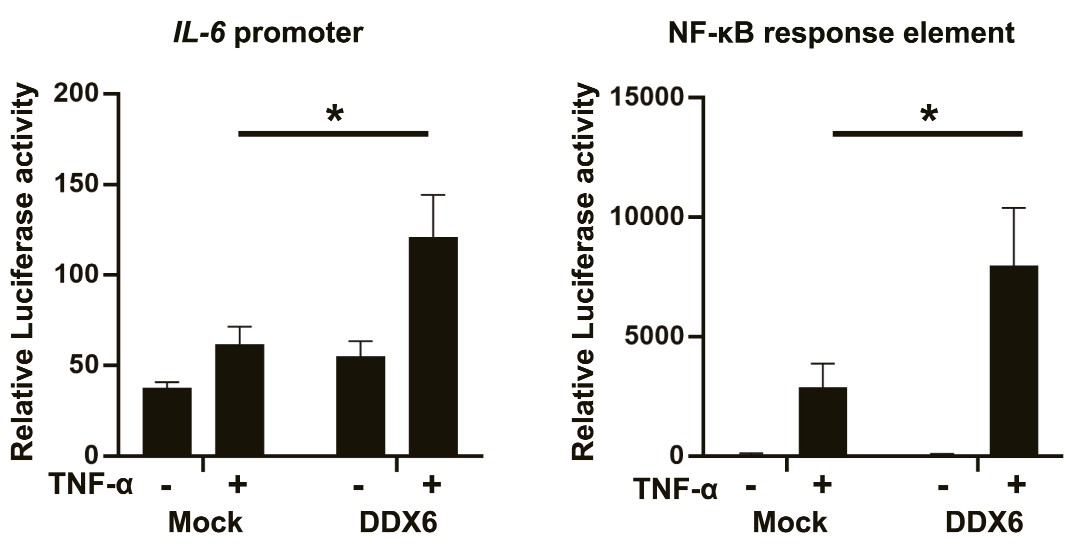
Fig1. Luciferase assay using reporter plasmids containing IL-6 promoter (left) and NF-κB response element (right) in HEK293T cells.
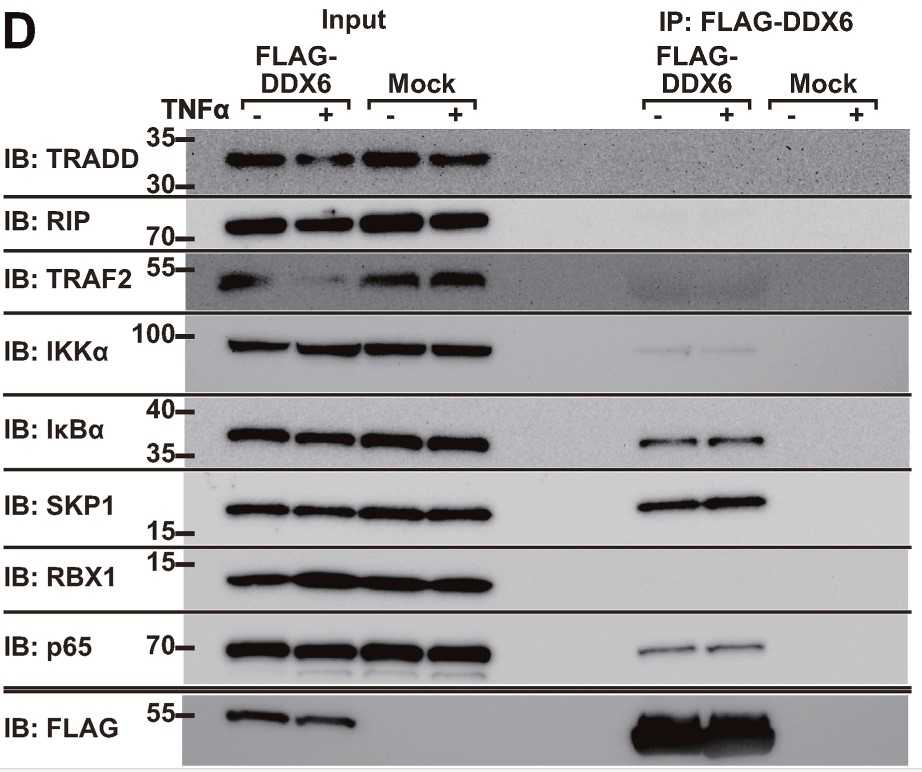
Fig2. Immunoprecipitation was performed on HEK293T cells.
Case Study 2: Chia-Yu Shih, 2023
The DEAD-box proteins, one family of RNA-binding proteins (RBPs), participate in post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression with multiple aspects. Among them, DDX6 is an essential component of the cytoplasmic RNA processing body (P-body) and is involved in translational repression, miRNA-meditated gene silencing, and RNA decay. In addition to the cytoplasmic function, DDX6 is also present in the nucleus, but the nuclear function remains unknown. To decipher the potential role of DDX6 in the nucleus, the researchers performed mass spectrometry analysis of immunoprecipitated DDX6 from a HeLa nuclear extract. They found that adenosine deaminases that act on RNA 1 (ADAR1) interact with DDX6 in the nucleus. Utilizing the newly developed dual-fluorescence reporter assay, they elucidated the DDX6 function as negative regulators in cellular ADAR1p110 and ADAR2. In addition, depletion of DDX6 and ADARs results in the opposite effect on facilitation of RA-induced differentiation of neuronal lineage cells.
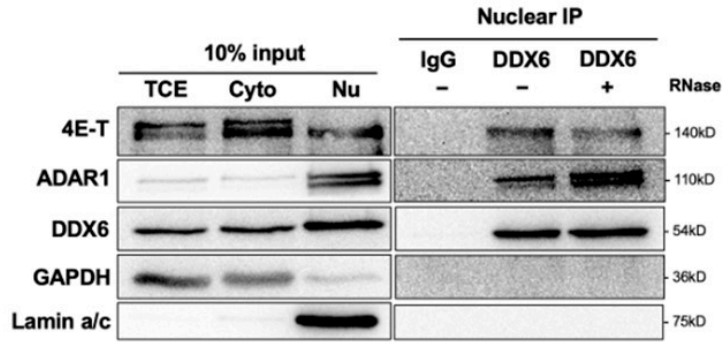
Fig3. Anti-DDX6 immunoprecipitation was conducted in HEK293T cells that overexpressed ADAR1.
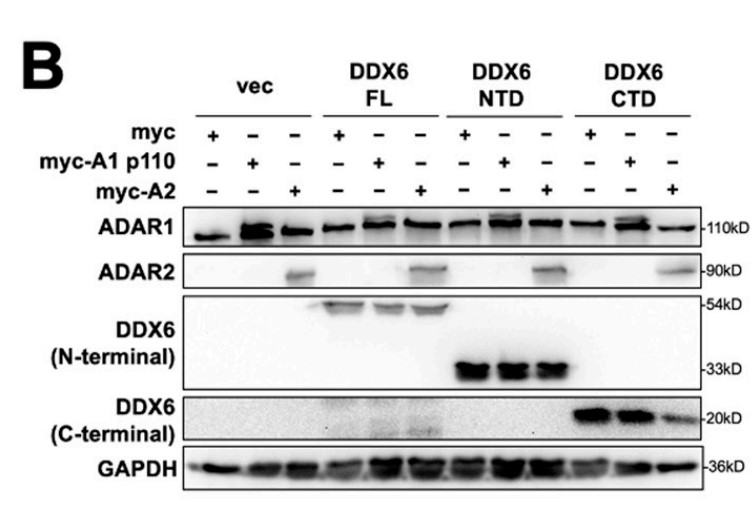
Fig4. WB analysis showed expressions of exogenous myc-ADARs and various DDX6 constructs.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (DDX6-28328TH)
Involved Pathway
DDX6 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways DDX6 participated on our site, such as Deadenylation-dependent mRNA decay,Gene Expression,RNA degradation, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with DDX6 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| mRNA decay by 5 to 3 exoribonuclease | LSM6,DCP1B |
| RNA degradation | LSM7,CNOT3B,TOB1B,groL,CNOT3A,DnaK,CNOT10,EXOSC5,PFKMA,PFKM |
| Gene Expression | ZNF350,HNRNPD,EED,ZNF771,RNPC3,ZNF212,APEH,TRMT112,SNAPC2,ZNF670 |
| Deadenylation-dependent mRNA decay | D1BWG0212E,DCP1B,EIF4E,EIF4EB,TNKS1BP1,EIF4B,PAIP1,EIF4G1,EIF4A1,DCP2 |
Protein Function
DDX6 has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,ATP-dependent RNA helicase activity,RNA helicase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by DDX6 itself. We selected most functions DDX6 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with DDX6. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| ATP-dependent RNA helicase activity | DDX54,DDX51,DDX3,EIF4A3,DDX39B,DDX10,SKIV2L,DDX3X,EIF4A1,EIF4A1A |
| poly(A) RNA binding | FAM46A,RBM3,HSP90AB1,EIF1,RPL13,NOP56,TRIM28,DHX9,EEF1A1,HSPE1 |
| protein domain specific binding | OSBP,STAMBP,LIN7B,HIST2H4,HIST1H4N,HPCAL4,NDE1,ERCC1,ARFIP2B,DBNL |
| helicase activity | BLM,SETX,IFIH1,GTF2F2A,MOV10B.1,ACTG2,TDRD9,YTHDC2,MCM3L,MOV10 |
| RNA helicase activity | FAM120B,CHST13,UAP1L1,PRIM2,RAD54B,DHX15,DHX9,CTU1,DDX10,DHX16 |
| protein binding | RPS25,MARK3,FGFRL1A,MAGEA1,RANBP3,RALGAPA1,ATG16L1,CAV1,DPH1,CDC42EP1 |
| ATP binding | PSMC3,PYGL,ALPK1,WARS,THRAP3,TDRD9,AKT3A,THG1L,PKM,SMC5 |
Interacting Protein
DDX6 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with DDX6 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of DDX6.
DCP1A;EDC3;YBX1;TRIM37
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Johanneson, B; Chen, D; et al. Systematic validation of hypothesis-driven candidate genes for cervical cancer in a genome-wide association study. CARCINOGENESIS 35:2084-2088(2014).
- Kawahara, C; Yokota, S; et al. DDX6 localizes to nuage structures and the annulus of mammalian spermatogenic cells. HISTOCHEMISTRY AND CELL BIOLOGY 141:111-121(2014).



