CEACAM8
-
Official Full Name
carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 8 -
Overview
Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 8 (CEACAM8) also known as CD66b (Cluster of Differentiation 66b), is a human gene. -
Synonyms
CEACAM8;carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 8;CGM6;CD66b;CD67 antigen;carcinoembryonic antigen CGM6;non-specific cross-reacting antigen NCA-95;carcinoembryonic antigen gene family member 6;CD67;NCA-95
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- E.coli
- Human Cells
- Insect cells
- Mammalian Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- Avi
- GST
- SUMO
- Non
- T7
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEACAM8-3233H | Recombinant Human CEACAM8 protein, His-tagged | HEK293 | Human | His | Gln35-Ser319 | |
| CEACAM8-3234H | Active Recombinant Human CEACAM8 protein, His-Avi-tagged, Biotinylated | HEK293 | Human | Avi&His | Met1-Ser319 | |
| CEACAM8-1098H | Recombinant Human CEACAM8 Protein, GST-Tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST |
|
|
| CEACAM8-1162H | Recombinant Human CEACAM8 Protein, His-SUMO-tagged | E.coli | Human | His&SUMO | 35-320 a.a. |
|
| CEACAM8-222H | Recombinant Human CEACAM8, C13&N15-labeled | HEK293 | Human | Non | 35-319 a.a. |
|
| CEACAM8-27504TH | Recombinant Human CEACAM8 | Wheat Germ | Human | Non | 349 amino acids |
|
| CEACAM8-45H | Recombinant Human CEACAM8 protein, T7/His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His&T7 | 35-320 a.a. |
|
| CEACAM8-2246HCL | Recombinant Human CEACAM8 cell lysate | Human Cells | Human | Non |
|
|
| CEACAM8-04H | Recombinant human CEACAM8 protein, His-tagged | Insect cells | Human | His | 35-320 a.a. |
|
| CEACAM8-0849H | Recombinant Human CEACAM8 Protein (Gln35-Asp320), His tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Gln35-Asp320 |
|
| CEACAM8-1007H | Recombinant Human CEACAM8 Protein (Gln35-His141), C-His tagged | Mammalian Cells | Human | His | Gln35-His141 |
|
| CEACAM8-180H | Recombinant Human CEACAM8 Protein, His-tagged | HEK293 | Human | His | 349 |
|
| CEACAM8-2983H | Active Recombinant Human CEACAM8 protein, His-Avi-tagged, Biotinylated | HEK293 | Human | Avi&His | Gln 35-Ser 319 |
|
| CEACAM8-2984H | Active Recombinant Human CEACAM8 protein, His-tagged | HEK293 | Human | His | Gln 35-Ser 319 |
|
| CEACAM8-3276HF | Recombinant Full Length Human CEACAM8 Protein, GST-tagged | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | GST | Full L. 349 amino acids |
|
| CEACAM8-3941H | Recombinant Human CEACAM8 Protein (Met1-Asp320), C-His tagged | Mammalian Cells | Human | His | Met1-Asp320 |
|
| CEACAM8-4921M | Whole Blood CEACAM8 protein-coupled magnetic MicroBeads | Human |
|
|||
| CEACAM8-69HF | Recombinant Full Length Human CEACAM8 Protein | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | Full L. 349 amino acids |
|
|
| CEACAM8-734H | Recombinant Human CEACAM8 Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Gln35-Asp320 |
|
Background
What is CEACAM8 protein?
CEACAM8 gene (CEA cell adhesion molecule 8) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 19 at locus 19q13. CEACAM8, also known as CD66b, NCA-95, and CD67, is a highly glycosylated protein that is mainly expressed in human neutrophils and eosinophils. As a member of the CEA family, CEACAM8 may play a role in interactions between granulocytes or between granulocytes and epithelial cells. CEACAM8, as a cell surface glycoprotein, is involved in cell adhesion in a calcium-independent manner and is capable of heterogenic cell adhesion with other CEACAM family members, such as CEACAM6. It may also be involved in regulating a variety of physiological processes, including tissue structure formation, angiogenesis, insulin homeostasis regulation, and T cell proliferation. The CEACAM8 protein is consisted of 349 amino acids and CEACAM8 molecular weight is approximately 38.2 kDa.
What is the function of CEACAM8 protein?
CEACAM8 is thought to be involved in interactions between granulocytes or between granulocytes and epithelial cells. As a calcium-independent cell adhesion molecule, CEACAM8 is capable of heterogenic cell adhesion with other CEA family members, such as CEACAM6, and this interaction occurs primarily in activated neutrophils. The expression level of CEACAM8 is significantly elevated in the blood of some patients with acute infection, and is significantly correlated with the expression of CEACAM8 on the surface of neutrophils and the number of circulating neutrophils, suggesting that CEACAM8 may serve as a biomarker of granulocyte activity in vivo. The expression of CEACAM8 was mainly concentrated in bone marrow, and cytoplasmic expression was detected in lymphoid tissue. In terms of tissue expression clustering (RNA), CEACAM8 belongs to the myelo-innate immune response category and has a high tissue-specific score, indicating that it is specifically expressed in bone marrow.
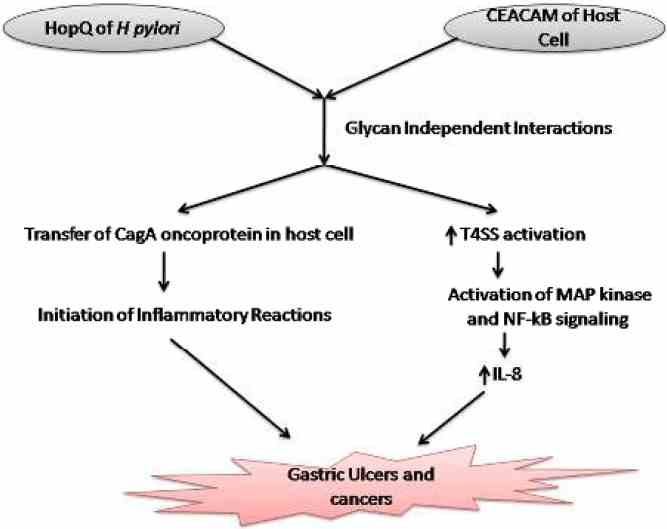
Fig1. Schematic representation of glycan independent interactions of HopQ of Helicobacter pylori and CEACAMs of human epithelial cells. (Ran Xia, 2019)
CEACAM8 Related Signaling Pathway
CEACAM8 plays a role in cell adhesion and signaling, especially in activated neutrophils. CEACAM8 is a cell surface glycoprotein that is involved in cell adhesion independent of calcium ions, and can engage in heterogeneous cell adhesion with other CEA family members, such as CEACAM6. In terms of signaling, CEACAM8, through its interactions with other members of the CEA family, may be involved in regulating immune response and cellular behavior. For example, soluble CEACAM8 can interact with CEACAM1 to inhibit immune responses triggered by Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2). In addition, the heteroadhesive effect of CEACAM8 plays a role in the activation of neutrophils, which may be involved in the regulation of inflammatory responses and cell migration.
CEACAM8 Related Diseases
CEACAM8 expression levels are significantly elevated in the blood of patients with acute infection and may serve as a biomarker of granulocyte activity in the body, helping to monitor inflammation and infection processes. The change of CEACAM8 expression level in some cancers may be related to tumor progression and prognosis. CEACAM8 may be involved in regulating the immune response through interactions with other members of the CEA family. CEACAM8 may play a role in respiratory diseases such as severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) as a biomarker to help monitor the course of the disease. In some reproductive system tumors, CEACAM8 expression may also be associated with disease progression and prognosis.
Bioapplications of CEACAM8
In cancer research, abnormal expression of CEACAM8 is associated with the occurrence, development, and prognosis of a variety of tumors, making it a potential cancer diagnostic marker and therapeutic target. In particular, changes in CEACAM8 expression levels in tumors such as colorectal cancer may indicate the aggressiveness and metastasis of the disease. Based on the role of CEACAM8 in disease, antibodies or small molecule drugs targeting its function can be developed to treat related diseases. The study of the mechanism of CEACAM8 in the pathological process is helpful to further understand the molecular mechanism of related diseases and provide a new perspective for pathological research. Clinical trials related to CEACAM8 may help to evaluate its efficacy and safety as a treatment.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Utku Horzum, 2021
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) populate the peripheral blood and contribute to immune regulation in cancer. However, there is limited knowledge on the myeloid cell types with proinflammatory capacities that may serve as opponents of MDSC. In the circulation of cancer patients, a monocyte subpopulation was identified with a specific immunophenotype and transcriptomic signature. They were predominantly CD14+CD33hiCD16-/+HLA-DR+/hi cells that typically expressed CD66b. In accordance with the transcriptomics data, NALP3, LOX-1 and PAI-1 levels were also significantly upregulated. The CD66b+ monocytes displayed high phagocytic activity, matrix adhesion and migration, and provided costimulation for T cell proliferation and IFN-γ secretion; thus, they did not suppress T cell responses. Irrespective of clinical stage, they were identified in various cancers.
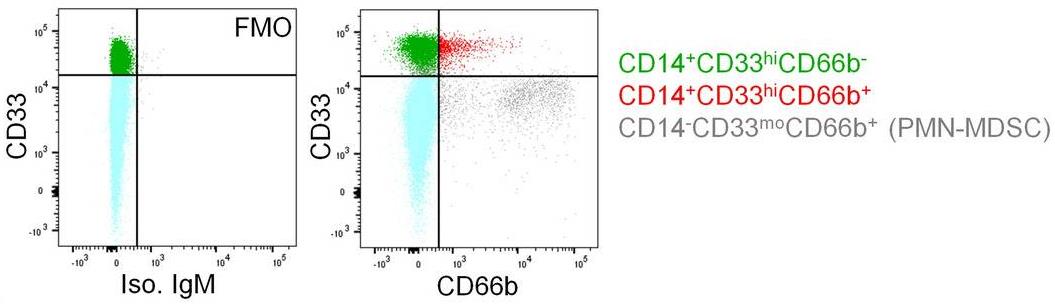
Fig1. Fluorescence minus one (FMO) analysis for CD66b staining.
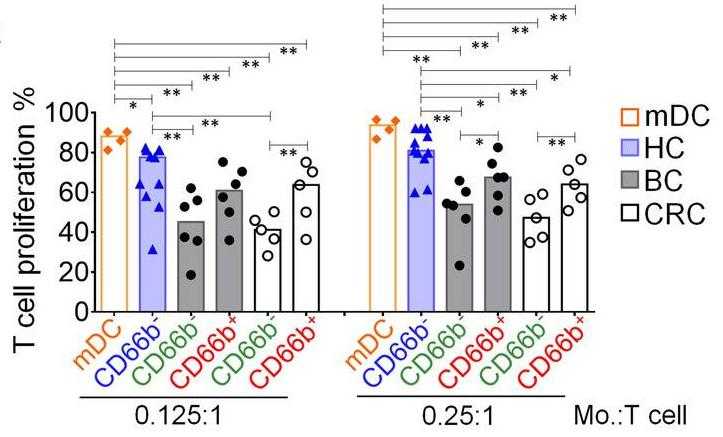
Fig2. Influence of CD66b+ or CD66b− monocytes.
Case Study 2: Juhan Yoon, 2007
Eosinophils and their products are likely important in the pathophysiology of allergic diseases, such as bronchial asthma, and in host immunity to parasitic organisms. However, the mechanisms for proinflammatory mediator release by eosinophils are poorly understood. CD66b is an activation marker for human granulocytes; however, its biological functions are largely unknown in eosinophils. In this study, CD66b is highly expressed on the surface of human peripheral blood eosinophils isolated from healthy individuals. Engagement of CD66b, but not CD66a, by mAb or a natural ligand, galectin-3, activated a Src kinase family molecule, hemopoietic cell kinase (Hck), and induced cellular adhesion, superoxide production, and degranulation of eosinophils. CD66b molecules were localized in lipid rafts, and disruption of lipid rafts or removal of the GPI anchor inhibited the adhesion and activation of eosinophils. Importantly, CD66b was constitutively and physically associated with a beta2 integrin, CD11b, and cross-linking of CD66b induced a striking clustering of CD11b molecules.
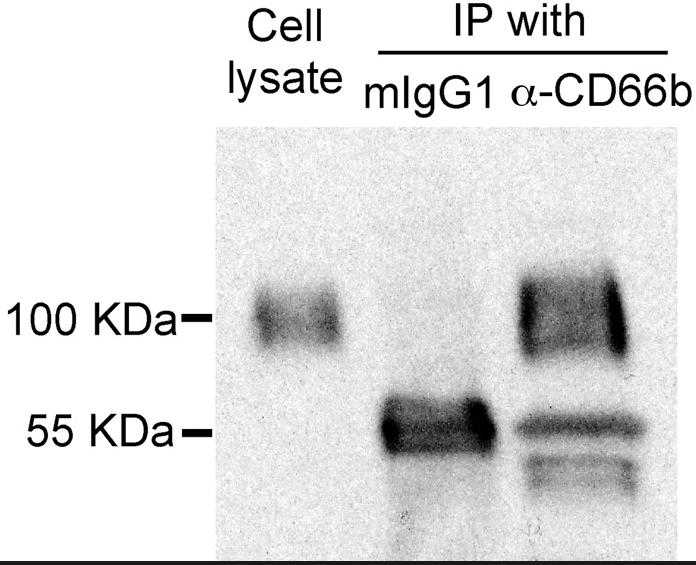
Fig3. CD66b expression was detected by using immunoprecipitation (IP).
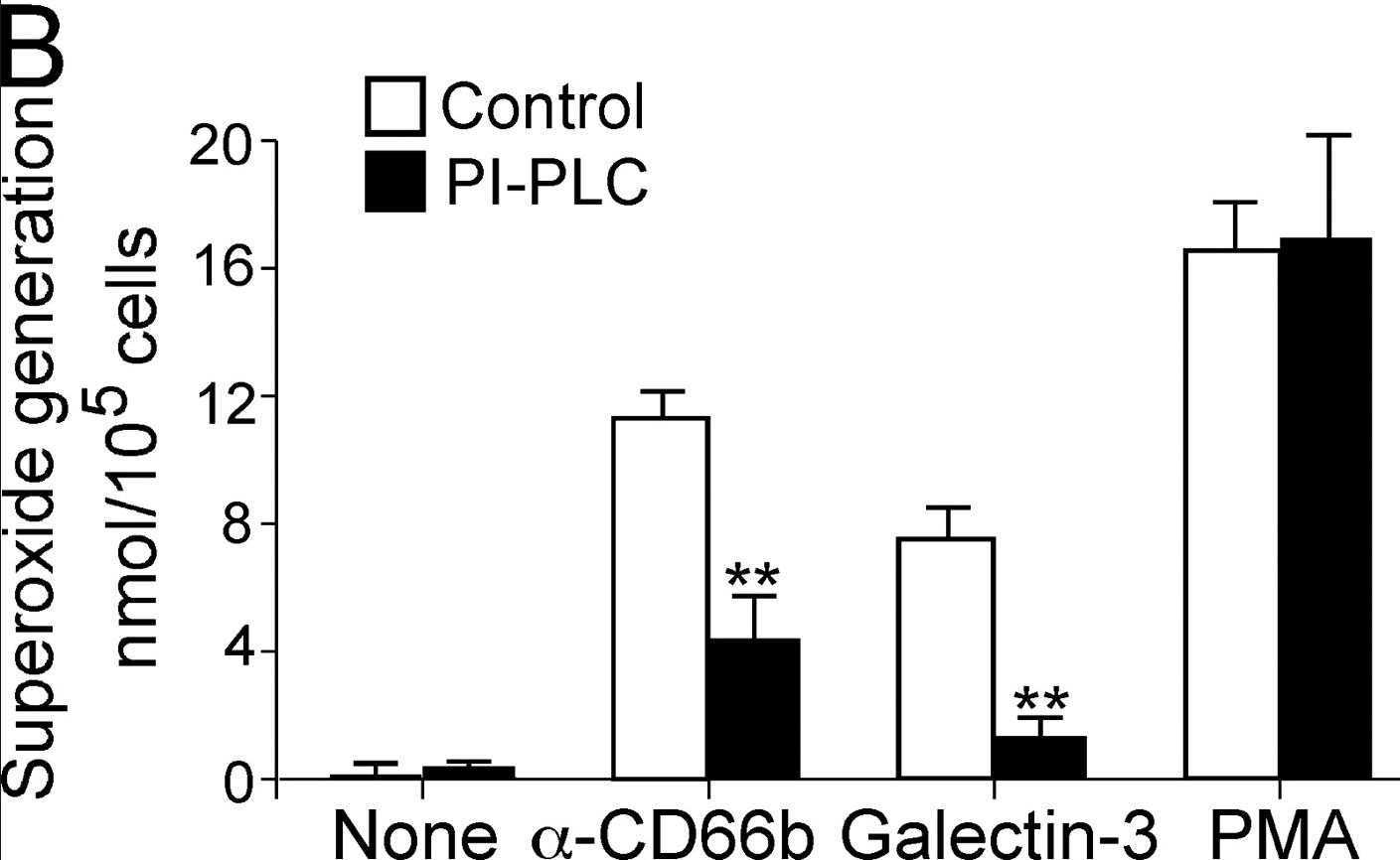
Fig4. Superoxide generation was measured after preincubation with immobilized anti-CD66b or other reagents.
Quality Guarantee
.
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CEACAM8-3233H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CEACAM8-1098H)
Involved Pathway
CEACAM8 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CEACAM8 participated on our site, such as Cell surface interactions at the vascular wall,Extracellular matrix organization,Fibronectin matrix formation, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CEACAM8 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Hemostasis | HRG,AKAP10,IRF1B,RAPGEF4,STXBP3A,SRGN,KIFC1,ABHD6B,TAE1,CFHL3 |
| Fibronectin matrix formation | CEACAM1,FN1B,CEACAM6 |
| Extracellular matrix organization | PPIB,PTPRS,DDR2,SERPINH1A,PCOLCE,LAMC3,HAPLN1,FURINA,TPSAB1,DST |
| Cell surface interactions at the vascular wall | FCER1GL,SLC7A10,SLC16A8,GAS6,DOK2,BSG,MERTK,SLC7A6,GRB7,PROCR |
Protein Function
CEACAM8 has several biochemical functions, for example, . Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CEACAM8 itself. We selected most functions CEACAM8 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CEACAM8. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|
Interacting Protein
CEACAM8 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CEACAM8 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CEACAM8.
CEACAM1;CEACAM6;ZNF16
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Seifert, M; Przekopowitz, M; et al. Functional capacities of human IgM memory B cells in early inflammatory responses and secondary germinal center reactions. PROCEEDINGS OF THE NATIONAL ACADEMY OF SCIENCES OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA 112:E546-E555(2015).
- Wakabayashi-Nakao, K; Hatakeyama, K; et al. Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 4 (CEACAM4) is specifically expressed in medullary thyroid carcinoma cells. BIOMEDICAL RESEARCH-TOKYO 35:237-242(2014).


