CASP9
-
Official Full Name
caspase 9, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of the cysteine-aspartic acid protease (caspase) family. Sequential activation of caspases plays a central role in the execution-phase of cell apoptosis. Caspases exist as inactive proenzymes which undergo proteolytic processing at conserved aspartic residues to produce two subunits, large and small, that dimerize to form the active enzyme. This protein can undergo autoproteolytic processing and activation by the apoptosome, a protein complex of cytochrome c and the apoptotic peptidase activating factor 1; this step is thought to be one of the earliest in the caspase activation cascade. This protein is thought to play a central role in apoptosis and to be a tumor suppressor. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, May 2013] -
Synonyms
CASP9;caspase 9, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase;MCH6;APAF3;APAF-3;PPP1R56;ICE-LAP6;caspase-9;apoptotic protease MCH-6;ICE-like apoptotic protease 6;apoptotic protease activating factor 3;protein phosphatase 1, regulatory subunit 56
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- Rat
- E.coli
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Non
- His
- GST
- DDK
- Myc
- SUMO
- Avi
- Fc
- Flag
Background

Fig1. Caspase-9 activation, cleavage substrates, and cellular functions. (Maria I Avrutsky, 2021)
What is CASP9 protein?
CASP9 gene (caspase 9) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1p36. This gene encodes a member of the cysteine-aspartic acid protease (caspase) family. Caspases exist as inactive proenzymes which undergo proteolytic processing at conserved aspartic residues to produce two subunits, large and small, that dimerize to form the active enzyme. This protein can undergo autoproteolytic processing and activation by the apoptosome, a protein complex of cytochrome c and the apoptotic peptidase activating factor 1; this step is thought to be one of the earliest in the caspase activation cascade. This protein is thought to play a central role in apoptosis and to be a tumor suppressor. The CASP9 protein is consisted of 416 amino acids and CASP9 molecular weight is approximately 46.3 kDa.
What is the function of CASP9 protein?
The CASP9 protein is an enzyme that plays a key role in apoptosis (programmed cell death). It belongs to the cysteine protease family and, in particular, acts as a initiating caspase, capable of triggering an intrinsic apoptosis pathway. CASP9 is essential for autophagosome maturation by regulating mitochondrial homeostasis and also plays a role in a variety of non-apoptotic functions, including macroautophagy or autophagy regulation. In addition, CASP9 is also involved in the processing of stress responses by cells, for example, under amino acid deprivation conditions, activation of CASP9 can promote the activation of autophagy without accompanying apoptotic features. During autophagy, pharmacological inhibition or gene knockout of CASP9 can reduce autophagy flux and affect the maturation of autophagosomes.

Fig2. A schematic diagram suggesting that mitochondrial homeostasis and autophagosome maturation requires CASP9. (Hyun-Kyu An, 2020)
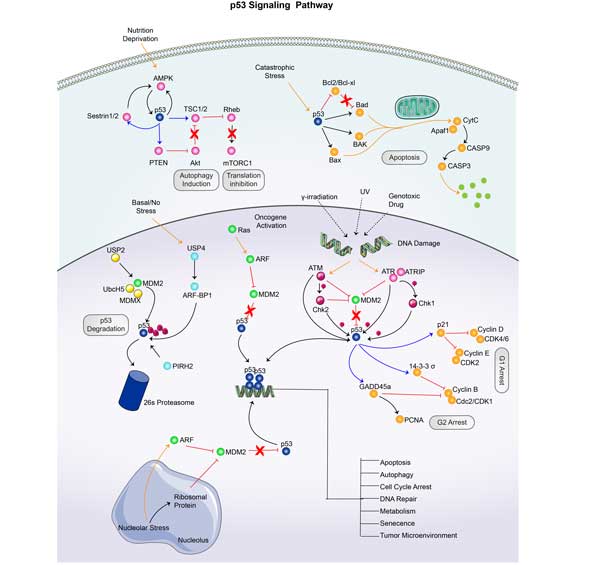
CASP9 Related Signaling Pathway
CASP9 initiates caspase and participates in mitochondria-mediated intrinsic apoptosis pathway. When mitochondria are damaged, Cytochrome C is released, which binds to Apoptotic protease activating factor-1 (APAF-1) to form Apoptosome, The activity of CASP9 can be inhibited by anti-apoptotic proteins such as XIAP (X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein), which can bind and inhibit CASP9, preventing it from further activating downstream caspases. Thus inhibiting apoptosis. CASP9 is essential for autophagosome maturation by maintaining mitochondrial homeostasis. Studies have shown that pharmacological inhibition or gene ablation of CASP9 can reduce autophagy flux and affect the maturation of autophagosomes.
CASP9 Related Diseases
Polymorphisms in the CASP9 gene have been linked to a variety of diseases, including but not limited to cancer, neurological disorders, autoimmune diseases, and lumbar disc disease. Specifically, CASP9 has been linked to clinical evidence of acute and chronic neurodegeneration, retinal neuropathy, slow channel myasthenia syndrome, lumbar disc disease, cardiomyopathy, atherosclerosis, and autoimmune diseases in humans. In cancer, CASP9 polymorphism is associated with the occurrence and development of different cancers, and is associated with tumor inhibition and chemotherapy sensitivity. In neurological diseases, activation of CASP9 has been linked to the progression of multiple neurodegenerative diseases, and its activation can lead to neuronal damage and dysfunction. In autoimmune diseases, the activity of CASP9 may be involved in regulating the immune response and cell death, and its abnormalities may contribute to the development of the disease. In lumbar disc disease, CASP9 expression correlates with disease severity and may play a role in disc degeneration.
Bioapplications of CASP9
It serves as a critical biomarker for monitoring cellular responses to various stimuli, including chemotherapies, stress agents, and radiation. In the context of cancer therapy, CASP9 is a promising target for sensitizing tumor cells to chemotherapy and for the development of conditional safety switches in adoptive T cell therapies, such as CAR T cells, to mitigate adverse effects like graft-versus-host disease. Furthermore, the exploration of CASP9's non-apoptotic roles in cellular processes like myoblast differentiation and immune response opens avenues for its potential use in regenerative medicine and immunotherapy. The study of CASP9's alternative splicing and the development of selective inhibitors provide tools for dissecting its complex signaling pathways in health and disease.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Jie Han, 2021
Recently, we reported that increased expression of CASP9 pro-domain, at the endosomal membrane in response to HSP90 inhibition, mediates a cell-protective effect that does not involve CASP9 apoptotic activity. Researchers report here that a non-apoptotic activity of endosomal membrane CASP9 facilitates the retrograde transport of IGF2R/CI-MPR from the endosomes to the trans-Golgi network, indicating the involvement of CASP9 in endosomal sorting and lysosomal biogenesis. In the absence of CASP9, IGF2R undergoes significant degradation, and its rescue is achieved by the re-expression of a non-catalytic CASP9 mutant. This endosomal activity of CASP9 is potentially mediated by herein newly identified interactions of CASP9 with the components of the endosomal membrane transport complexes. These endosomal complexes include the retromer VPS35 and the SNX dimers, SNX1-SNX5 and SNX2-SNX6, which are involved in the IGF2R retrieval mechanism. Additionally, CASP9 interacts with HGS/HRS/ESCRT-0 and the CLTC (clathrin heavy chain) that participate in the initiation of the endosomal ESCRT degradation pathway.

Fig1. CASP9 expression alters the distribution pattern of RAB7A.

Fig2. Co-IP of physiologically expressed CASP9 and HGS.
Case Study 2: Jie Han, 2018
Currently, autophagy inhibition is being tested in the clinic as a therapeutic component for tumors that utilize this degradation process as a drug resistance mechanism. The current study provides evidence that HSP90 (heat shock protein 90) inhibition diminishes the expression of ATG7, thereby impeding the cellular capability of mounting an effective autophagic response in NSCLC cells. Additionally, an elevation in the expression level of CASP9 (caspase 9) prodomain in KRAS-mutant NSCLC cells surviving HSP90 inhibition appears to serve as a cell survival mechanism. Initial characterization of this survival mechanism suggests that the altered expression of CASP9 is mainly ATG7 independent; it does not involve the apoptotic activity of CASP9; and it localizes to a late endosomal and pre-lysosomal phase of the degradation cascade. HSP90 inhibitors are identified here as a pharmacological approach for targeting autophagy via destabilization of ATG7, while an induced expression of CASP9, but not its apoptotic activity, is identified as a resistance mechanism to the cellular stress brought about by HSP90 inhibition.

Fig3. Ganetespib-mediated ATG7 destabilization and CASP9 stabilization in an array of KRAS-mutant NSCLC cell lines.

Fig4. Ganetespib treatment disrupts the ATG7-CASP9 complex.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CASP9-35H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CASP9-626H)
Involved Pathway
CASP9 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CASP9 participated on our site, such as p signaling pathway,PIK-Akt signaling pathway,Apoptosis, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CASP9 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| PIK-Akt signaling pathway | GNGT1,FGF19,MAP2K1,FOXO3,KRAS,TSC2,PRLR,RXRA,EIF4E1B,ITGB4 |
| Alzheimers disease | ATP5E,ATP5O,BACE1,NDUFC2-KCTD14,ATP5H,ITPR2,COX6C,NAE1,PLCB1,LPL |
| Non-small cell lung cancer | PIK3R5,PRKCB,MAPK3,NRAS,PIK3R3,KRAS,TP53,HRAS,RXRA,PIK3R1 |
| Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) | APAF1,BAX,SLC1A2,MAP3K5,TNFRSF1A,GRIN1,GRIN2A,BCL2,PRPH,ALS2 |
| Endometrial cancer | FOXO3,GRB2,CCND1,RAF1,SOS1,CTNNA3,MAP2K2,TP53,PIK3R3,CDH1 |
| Viral myocarditis | RAC1,HLA-DQB1,H2-AB1,HLA-DMB,FYN,ITGB2L,RAC3,CD86,HLA-DQA2,ACTG1 |
| Hepatitis B | EGR2,IFNA17,MAPK9,GRB2,CASP8,TP53,MMP9,TBK1,TGFB3,CREB3L3 |
| Huntingtons disease | NDUFA7,POLR2J2,NDUFA4,mt-Atp8,GNAQ,NDUFC2,TFAM,UQCRH,SOD2,COX4I1 |
| Legionellosis | CASP8,CLK1,TNF,HSPA2,VCP,NLRC4,HSPA1L,SAR1B,C3,IL1B |
Protein Function
CASP9 has several biochemical functions, for example, SH3 domain binding,cysteine-type endopeptidase activity,cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic signaling pathway. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CASP9 itself. We selected most functions CASP9 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CASP9. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | RING1,PTPN9,TRIP13,TRIAP1,RUSC2,LATS2,ADAMTS4,TCF3,SPCS1,C7orf49 |
| peptidase activity | MPND,ASTL,GZMF,NAPSA,ELANE,HE1B,CTSLA,CAPN8,GZME,MALT1 |
| cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic signaling pathway | CASP8,CASP14,CASP2,CASP8L1,CFLAR,CASP10,CFLARA |
| protein kinase binding | TBC1D14,PTEN,NME2,MAPT,ATG13,NSF,FAM83B,ATF2,AP2A1,TELO2 |
| enzyme activator activity | SFTPBB,GM1679,CTSA,RICTOR,APOA5,ASAP2,ARL1,DCP1A,PITRM1,ALDH1A2 |
| cysteine-type endopeptidase activity | USP20,USP17L2,LGMN,CTLA2B,USP10,CTSB,CASPB,MALT1A,USP25,USP4 |
| SH3 domain binding | DRD4,FAM125A,KHDRBS3,SHANK1,GRB2,MVB12A,SH3BP1,SHANK2,INPPL1B,SH3BP2 |
Interacting Protein
CASP9 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CASP9 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CASP9.
XIAP;APAF1
CASP9 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References