C4B
-
Official Full Name
complement component 4B (Chido blood group) -
Overview
C4b binding protein (C4BP) regulates complement activation of the classical and lectin pathways. It binds to C4b and accelerates the dissociation of C2a from the C3/C5 convertase C4b,C2a. -
Synonyms
C4b Binding Protein;C4B;complement component 4B (Chido blood group);complement component 4B (Chido blood group)
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- E.coli
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cells
- Human serum
- HEK293
- Human Plasma
- Yeast
- Human Serum
- His
- T7
- GST
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- SUMO
- Myc
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C4B-254H | Recombinant Human C4B protein, His/T7-tagged | E.coli | Human | His&T7 | 680-756 a.a. | |
| C4B-0051H | Recombinant Human C4B Protein, GST-Tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST |
|
|
| C4b-0053M | Recombinant Mouse C4b Protein, GST-Tagged | Wheat Germ | Mouse | GST |
|
|
| C4B-2587M | Recombinant Mouse C4B Protein | Mammalian Cells | Mouse | His |
|
|
| C4B-26130TH | Recombinant Human C4B | Wheat Germ | Human | Non | 100 amino acids |
|
| C4B-27789TH | Recombinant Human C4B | Wheat Germ | Human | Non | 100 amino acids |
|
| C4b-6785M | Recombinant Mouse C4b protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Mouse | His | Asn678-Arg753 |
|
| C4b-7883M | Recombinant Mouse C4b protein, His & T7-tagged | E.coli | Mouse | His&T7 | Pro1450~Gln1723 |
|
| C4b-7884M | Recombinant Mouse C4b protein, His & T7-tagged | E.coli | Mouse | His&T7 | Gln126~Ser366 |
|
| C4B-08H | Recombinant Human C4B protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His |
|
|
| C4B-10H | Native Human C4B Protein | Human serum | Human | Non |
|
|
| C4B-1147M | Recombinant Mouse C4B Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| C4B-1147M-B | Recombinant Mouse C4B Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
||
| C4B-1846H | Native Human C4B Protein | Human Plasma | Human | Non |
|
|
| C4b-2921M | Recombinant Mouse C4b protein(1448-1738aa), His-tagged | E.coli | Mouse | His | 1448-1738aa |
|
| C4B-340H | Recombinant Human C4B Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Gln19-Leu333 |
|
| C4B-341H | Recombinant Human C4B Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Thr1021-Thr1330 |
|
| C4b-342R | Recombinant Rat C4b Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Rat | His | Ala1477-Val1737 |
|
| C4B-343H | Recombinant Human C4B Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Leu958-Gly1335 |
|
| C4B-3818H | Recombinant Human C4B protein, His-SUMO-tagged | E.coli | Human | His&SUMO | 1454-1744aa |
|
| C4b-4333M | Recombinant Mouse C4b protein(1448-1738aa), His&Myc-tagged | E.coli | Mouse | His&Myc | 1448-1738aa |
|
| C4b-4533M | Recombinant Mouse C4b protein | Yeast | Mouse | Non |
|
|
| C4B-5582H | Recombinant Human C4B protein, His-tagged | Yeast | Human | His | 1454-1744aa |
|
| C4B-99H | Native Human C4b Binding Protein | Human Serum | Human | Non |
|
Background
What is C4B protein?
C4B gene (complement C4B) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 6 at locus 6p21. This gene encodes the basic form of complement factor 4, and together with the C4A gene, is part of the classical activation pathway. The protein is expressed as a single chain precursor which is proteolytically cleaved into a trimer of alpha, beta, and gamma chains prior to secretion. The trimer provides a surface for interaction between the antigen-antibody complex and other complement components. The alpha chain may be cleaved to release C4 anaphylatoxin, a mediator of local inflammation. Deficiency of this protein is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. This gene localizes to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class III region on chromosome 6. Varying haplotypes of this gene cluster exist, such that individuals may have 1, 2, or 3 copies of this gene. The C4B protein is consisted of 1744 amino acids and C4B molecular weight is approximately 192.8 kDa.
What is the function of C4B protein?
C4B is an essential non-enzymatic component of the C3 and C5 convertases, which are crucial for the propagation of the classical complement pathway. C4B is an essential non-enzymatic component of the C3 and C5 convertases, which are crucial for the propagation of the classical complement pathway. The human C4 gene exhibits significant genetic diversity, with C4A and C4B being two isotypes that differ in their structure and function. The covalent binding affinity of the thioester carbonyl of C4A and C4B is regulated by polymorphic residues, with specific sites influencing the binding and activation processes. C4B, along with C4A, contributes to the genetic diversity and polymorphism within the human population, which may be driven by selective pressures from various pathogens.
C4B Related Signaling Pathway
C4B is cleaved by C1s into C4a and C4b fragments during the activation of the classical complement pathway. C4b can act as an innate immune effector, playing a role in the clearance of cellular debris by astrocytes through a non-canonical autophagy pathway. Complement components like C3a and C5a, which are related to C4B, act as anaphylatoxins and bind to their respective G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs), C3aR and C5aR1/C5aR2, to mediate inflammatory responses. C4BP (C4b-binding protein) can be exploited by microbes and tumors to evade the complement system, indicating a role in pathogen-host interactions.

Fig1. Model of complement antagonism of the classical pathway by Flavivirus NS1. (Panisadee Avirutnan, 2011)
C4B Related Diseases
C4B is a key component of the complement system and has been implicated in a variety of diseases. According to the search results, C4B-related diseases include rheumatoid arthritis (an autoimmune disease that presents with joint inflammation and possible joint deformities) and meningioma (a tumor that occurs in the meninges). These diseases may be associated with abnormal expression or function of C4B, suggesting that C4B plays an important role in inflammation and immune responses. In addition, C4B may also be involved in the regulation of the complement system, and its abnormality may affect the body's defense against pathogens, which in turn is associated with some infectious diseases.
Bioapplications of C4B
As a key component in complement system, C4B has a wide range of application prospects. Because of its important role in disease, C4B is considered a potential drug target and biomarker. By studying C4B expression, regulatory mechanism and interaction with other proteins, new therapeutic targets and drugs can be discovered. In addition, C4B serves as a biomarker that can be used to assess disease development and treatment effects by monitoring its levels in the blood or tissues. A number of C4B-related drugs and treatments are currently under development and research.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Jordan L Woehl, 2017
The extracellular adherence protein (Eap) plays a crucial role in pathogenesis and survival of Staphylococcus aureus by inhibiting the classical and lectin pathways of complement. Researchers have previously shown that Eap binds with nanomolar affinity to complement C4b and disrupts the initial interaction between C4b and C2, thereby inhibiting formation of the classical and lectin pathway C3 pro-convertase. Although an underlying mechanism has been identified, the structural basis for Eap binding to C4b is poorly understood. Taking advantage of the high lysine content of Eap, researchers used a zero-length crosslinking approach to map the Eap binding site to both the α'- and γ-chains of C4b. They also probed the C4b/Eap interface through a chemical footprinting approach involving lysine modification, proteolytic digestion, and mass spectrometry. They found that simultaneous mutation of these lysines to either alanine or glutamate diminished C4b binding and complement inhibition by Eap.

Fig1. The ability of untagged Eap repeats to compete the AlphaScreen signal generated by C4b-biotin was assessed.

Fig2. Competition binding between recombinant C4b-C345c and native C4b.
Case Study 2: Panisadee Avirutnan, 2011
The complement system plays a pivotal protective role in the innate immune response to many pathogens including flaviviruses. Flavivirus nonstructural protein 1 (NS1) is a secreted nonstructural glycoprotein that accumulates in plasma to high levels and is displayed on the surface of infected cells but absent from viral particles. Previous work has defined an immune evasion role of flavivirus NS1 in limiting complement activation by forming a complex with C1s and C4 to promote cleavage of C4 to C4b. In this study, researchers demonstrate a second mechanism, also involving C4 and its active fragment C4b, by which NS1 antagonizes complement activation. Dengue, West Nile, or yellow fever virus NS1 directly associated with C4b binding protein (C4BP), a complement regulatory plasma protein that attenuates the classical and lectin pathways. Soluble NS1 recruited C4BP to inactivate C4b in solution and on the plasma membrane. Mapping studies revealed that the interaction sites of NS1 on C4BP partially overlap with the C4b binding sites.
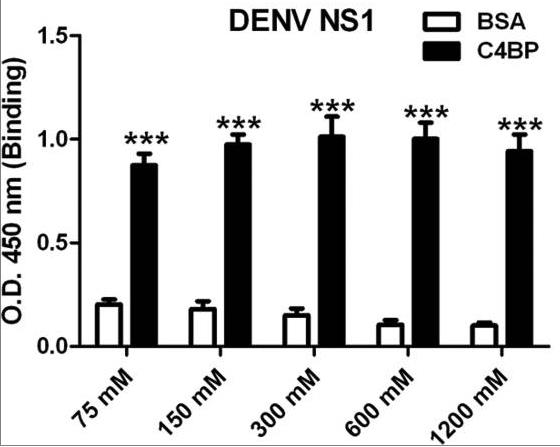
Fig3. Binding of NS1 with C4BP is not affected by salt concentration.

Fig4. DENV recruit C4BP to degrade C4b.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (C4B-0051H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (C4B-343H)
Involved Pathway
C4B involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways C4B participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with C4B were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
Protein Function
C4B has several biochemical functions, for example, . Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by C4B itself. We selected most functions C4B had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with C4B. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|
Interacting Protein
C4B has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with C4B here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of C4B.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Herrero, R; Real, LM; et al. Association of complement receptor 2 polymorphisms with innate resistance to HIV-1 infection. GENES AND IMMUNITY 16:134-141(2015).
- Johnson, JB; Borisevich, V; et al. A Novel Factor I Activity in Nipah Virus Inhibits Human Complement Pathways through Cleavage of C3b. JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY 89:989-998(2015).



