Tert
-
Official Full Name
Telomerase reverse transcriptase -
Overview
Telomerase is a ribonucleoprotein complex that replicates telomere ends by the addition of the Telomere repeat TTAGGG. Human Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase (hTERT) is one of the three core components of the enzyme-the catalytic subunit. Since male germ cells and the majority of human cancers have unlimited replicative capacity, they observe high levels of telomerase activity. hTERT is repressed in most somatic cells expect in proliferating progenitor cells and activated lymphocytes. In contrast, hTERT is activated in approximately 85% of human cancer tissues. Due to the biological function of hTERT, it has been seen as the most general of tumor markers known and has significant potential for diagnostics, prognostics, and therapeutics. -
Synonyms
DKCA2;DKCB4;EST2;PFBMFT1;TCS1;TP2;TRT;hEST2;hTRT;telomerase catalytic subunit;telomerase-associated protein 2
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Rat
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Synthetic
- HEK293
- E. coli
- His
- SUMO
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- GST
Background
What is TERT protein?
TERT gene (telomerase reverse transcriptase) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 5 at locus 5p15. The enzyme consists of a protein component with reverse transcriptase activity, encoded by this gene, and an RNA component which serves as a template for the telomere repeat. Telomerase expression plays a role in cellular senescence, as it is normally repressed in postnatal somatic cells resulting in progressive shortening of telomeres. Deregulation of telomerase expression in somatic cells may be involved in oncogenesis. Studies in mouse suggest that telomerase also participates in chromosomal repair, since de novo synthesis of telomere repeats may occur at double-stranded breaks. The TERT protein is consisted of 1132 amino acids and TERT molecular weight is approximately 127.0 kDa.
What is the function of TERT protein?
The TERT protein, or telomerase reverse transcriptase, is a critical component of the telomerase enzyme that helps maintain telomeres, the protective caps at the ends of chromosomes. Its primary function is to add repetitive DNA sequences to the ends of chromosomes during cell division, which is essential for cellular immortality and preventing cellular senescence. TERT is typically expressed at low levels in most normal cells but is often upregulated in cancer cells, allowing them to bypass senescence and proliferate indefinitely. Besides its role in telomere maintenance, TERT also has non-canonical functions in cancer cells, such as influencing cell proliferation, apoptosis, cell cycle regulation, and even the tumor microenvironment, including angiogenesis and immune response.
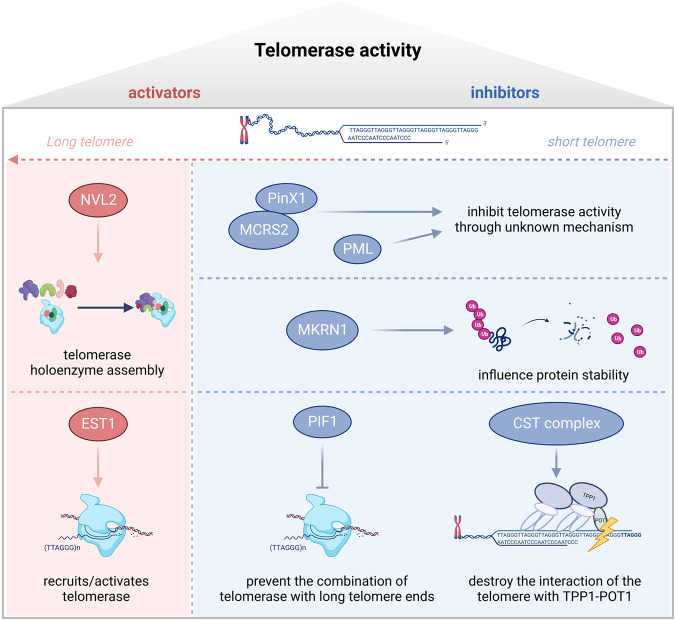
Fig1. Activators and inhibitors targeting telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT), involved in regulating telomerase activity. (Mingdi Liu, 2024)
TERT related signaling pathway
The TERT protein, a component of telomerase, plays a critical role in maintaining telomeres and thus supports cellular immortality by adding DNA sequences to chromosome ends during cell division. It is often upregulated in cancer cells, enabling them to bypass senescence. TERT is regulated by various signaling pathways, including transcriptional regulation by factors like c-Myc and Sp1, and epigenetic modifications such as DNA methylation and histone modifications. Mutations in the TERT promoter, common in many cancers, lead to its overexpression and are associated with increased telomerase activity. Post-translational modifications like phosphorylation and ubiquitination also regulate TERT's stability, activity, and subcellular localization. Furthermore, TERT has non-canonical roles in cell processes beyond telomere maintenance, including DNA repair, gene transcription, and cell cycle regulation, all of which contribute to cancer cell characteristics like resistance to apoptosis, limitless replication potential, and sustained angiogenesis.
TERT related diseases
The TERT protein, a central component of telomerase, is vital for maintaining telomeres and is implicated in various diseases. Its overexpression, often due to promoter mutations, is a common factor in many cancers, including melanoma, glioblastoma, and urothelial carcinoma, where it allows cells to bypass senescence. Germline TERT mutations are linked to premature aging syndromes like dyskeratosis congenita. Somatic TERT mutations are associated with pulmonary fibrosis, affecting the lungs. TERT's downregulation is seen in neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's, impacting cognitive function. Additionally, TERT mutations are found in aplastic anemia, a bone marrow failure syndrome. Ongoing research is exploring therapeutic applications, such as TERT inhibitors for cancer and activators to address aging and related pathologies.
Bioapplications of TERT
The TERT protein's applications in biomedicine are significant, particularly in cancer research and therapy. TERT is frequently overexpressed in cancer cells, which allows them to bypass senescence, making it a promising target for cancer treatment. Small molecule inhibitors and TERT-targeting vaccines are under investigation to exploit this characteristic. Additionally, TERT's role in maintaining telomeres is being explored to develop treatments addressing the accelerated aging syndrome dyskeratosis congenita. Furthermore, TERT's involvement in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's is being examined for potential therapeutic interventions, as its downregulation can lead to cognitive decline. Overall, TERT's applications in biomedicine are broad, with ongoing research aiming to uncover new strategies for a variety of diseases.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Chenjing Ma, 2023
The telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) is key for telomere maintenance and cellular longevity. This study explored the impact of exogenous human TERT (hTERT) on primary Periplaneta americana cells via a recombinant virus. Results showed that hTERT expression boosted telomerase activity and cell growth by reducing the doubling time, indicating that introducing hTERT might be a strategy for immortalizing insect cells and establishing novel cell lines. This research provides insights into telomere extension mechanisms in insects and potential applications in cell line development.
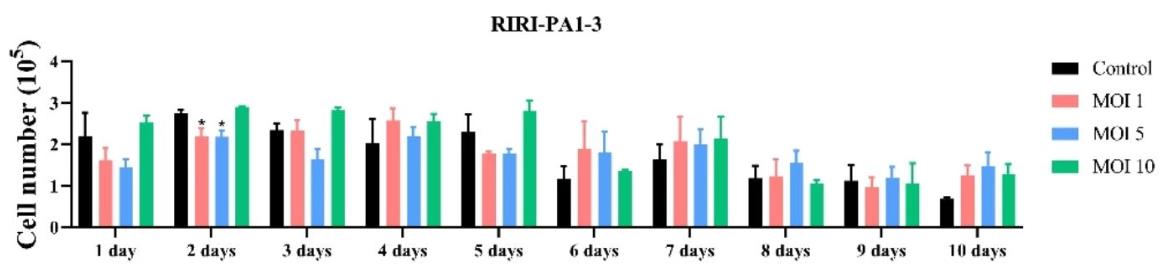
Fig1. Changes in cell number in RIRI-PA1-3 cells with AcMNPV-hTERT infected for 1 to 10 days.
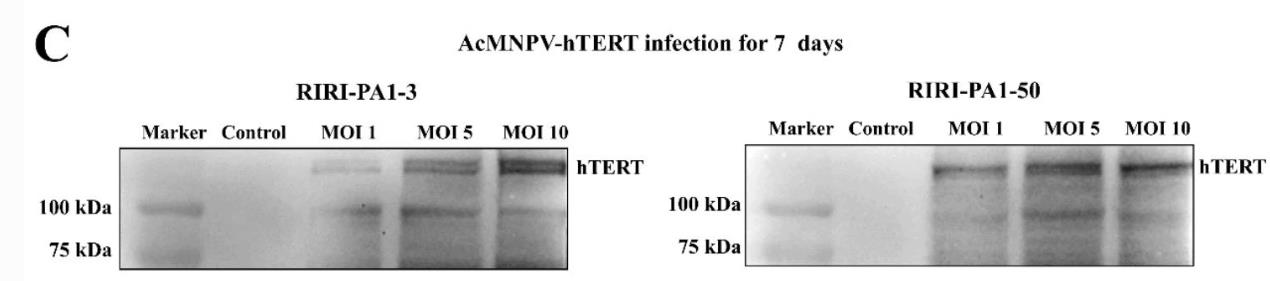
Fig2. Western blot analysis of recombinant hTERT protein expression in RIRI-PA1-3 and RIRI-PA1-50 infected with AcMNPV-hTERT.
Case Study 2: Wenbin Li, 2020
NCOA3 has been identified as a novel regulator of TERT expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). It binds to the TERT promoter and transcriptionally activates TERT, which in turn promotes tumor growth and progression. The interaction between NCOA3 and SP1 is crucial for this regulation, and high expression levels of both NCOA3 and TERT in HCC tissues correlate with poor prognosis for patients.
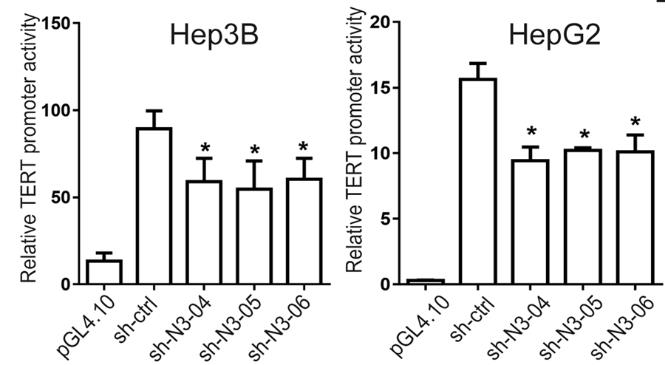
Fig3. TERT promoter activity was decreased with NCOA3 knockdown.
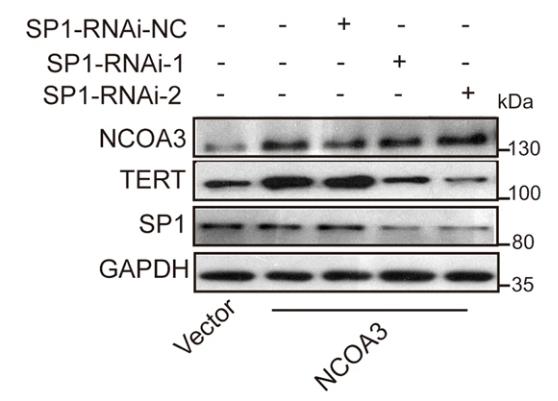
Fig4. TERT expression was detected in Hep3B cells without or with SP1 knockdown.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TERT-438H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (TERT-32H)
Involved Pathway
Tert involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Tert participated on our site, such as HTLV-I infection, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Tert were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| HTLV-I infection | BAX,TP53INP1,MYB,FZD2,IL6,DVL3,XBP1,HLA-F,WNT5A,RELB |
Protein Function
Tert has several biochemical functions, for example, DNA binding,RNA binding,RNA-directed DNA polymerase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Tert itself. We selected most functions Tert had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Tert. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| RNA binding | RBM6,RNASEH2A,FMR1,NHP2L1A,PABPN1,XPO5,U2AF2B,RBMS1,LSM5,CPSF5 |
| protein homodimerization activity | TGFB1,QPRT,NPR3,ACAT1,MYH9,VPS4B,MTERFD3,PLEK,HLCS,UNC13A |
| DNA binding | NR4A1,ZIM3,ZBTB25,ZNF625,PPARGC1A,XBP1,NR1I3,ZNF41,TEAD2,ZNF511 |
| tRNA binding | XPOT,DARS2,ALKBH8,IGHMBP2,FDXACB1,TRNT1,AARSD1,FARS2,AARS,TRMU |
| protein binding | ASF1B,ARMC2,NTM,ITGB5,CACYBP,RAP1GDS1,ZFC3H1,FAM3C,SMARCA4,TRAFD1 |
| metal ion binding | POLR2B,MYLIPA,QTRT1,ALOX8,PLA2G4AA,GPR39,ZFP276,C1GALT1B,TRAF4B,GLRX3 |
| telomerase activity | PTGES3,PRIM2,CCDC111,UAP1L1,CTU1,DKC1 |
| transcription coactivator binding | PASD1,RORA,NR4A3,ZBTB49 |
| telomeric DNA binding | TERFA,PIF1,TERF1,POT1A,TERF2,CTC1,HNRNPD,XRCC5,TINF2,SMG6 |
Interacting Protein
Tert has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Tert here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Tert.
terc_human_rna;RUVBL1
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References



