ST6GAL1
-
Official Full Name
ST6 beta-galactosamide alpha-2,6-sialyltranferase 1 -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of glycosyltransferase family 29. The encoded protein is a type II membrane protein that catalyzes the transfer of sialic acid from CMP-sialic acid to galactose-containing substrates. The protein, which is normally found in the Golgi but can be proteolytically processed to a soluble form, is involved in the generation of the cell-surface carbohydrate determinants and differentiation antigens HB-6, CD75, and CD76. This gene has been incorrectly referred to as CD75. Three transcript variants encoding two different isoforms have been described. -
Synonyms
ST6GAL1;ST6 beta-galactosamide alpha-2,6-sialyltranferase 1;sialyltransferase 1 (beta galactoside alpha 2,6 sialytransferase) , SIAT1;beta-galactoside alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase 1;ST6Gal I;alpha 2,6-ST 1;B-cell antigen CD75;Alpha2,6-(N)-Sialyltransferase;Alpha2,6-NST;2,6-Sialyltransferase;α2, 6-sialyltransferase (C);alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminide alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Zebrafish
- Rhesus macaque
- Chicken
- Rat
- HEK293
- Mammalian cells
- Mammalian Cell
- Insect Cell
- Human Cell
- E.coli expression system
- In vitro E. coli expression system
- E.coli
- His
- Non
- His&GFP
- His&Fc&Avi
Background
What is ST6GAL1 Protein?
ST6GAL1 gene (ST6 beta-galactoside alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 3 at locus 3q27. This gene encodes a member of glycosyltransferase family 29. The encoded protein is a type II membrane protein that catalyzes the transfer of sialic acid from CMP-sialic acid to galactose-containing substrates. The protein, which is normally found in the Golgi but can be proteolytically processed to a soluble form, is involved in the generation of the cell-surface carbohydrate determinants and differentiation antigens HB-6, CD75, and CD76. The ST6GAL1 protein is consisted of 406 amino acids and ST6GAL1 molecular weight is approximately 46.6 kDa.
What is the Function of ST6GAL1 Protein?
ST6GAL1 is an enzyme that plays a role in a variety of cancers and is primarily responsible for the synthesis of alpha 2, 6-sialic acid at the end of the N-type sugar chain. ST6GAL1 can affect the growth, survival and metastasis of tumor cells through its glycosyltransferase activity. In some cases, high expression of ST6GAL1 is associated with higher tumor grade, metastasis, and poorer patient prognosis. The role of ST6GAL1 in tumor cells is not limited to promoting tumor cell proliferation and invasion, but also involves regulating other cells in the tumor microenvironment, for example by influencing the behavior of immune cells. In addition, ST6GAL1 can promote epithelial-mesenchymal transformation (EMT) and resistance to chemotherapy and radiotherapy by affecting the function of cell surface receptors, such as integrins and death receptors.
ST6GAL1 Related Signaling Pathway
ST6GAL1 can regulate the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway through α2, 6-sialylation, which plays a key role in the survival, proliferation, invasion and metastasis of tumor cells. ST6GAL1 expression is associated with activation of the WNT signaling pathway, which is important in the maintenance of tumor stem cells. The regulation of ST6GAL1 may affect the stability and function of β-catenin. ST6GAL1 interacts with TGF-β signaling pathway, which may affect the dual role of early tumor inhibition and late tumor progression. ST6GAL1 affects a variety of cell adhesion molecules through sialylation, including integrin, cadherin, and immunoglobulin superfamily cell adhesion molecules, which play a crucial role in cell adhesion, migration, and invasion.
ST6GAL1 Related Diseases
Abnormal expression of ST6GAL1 is closely associated with the occurrence, development and treatment resistance of a variety of cancers, including but not limited to pancreatic cancer, colorectal cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, breast cancer, and ovarian cancer, and its high expression in tumor cells is often associated with the aggressiveness of the disease, poor prognosis, and resistance to certain chemotherapy agents.
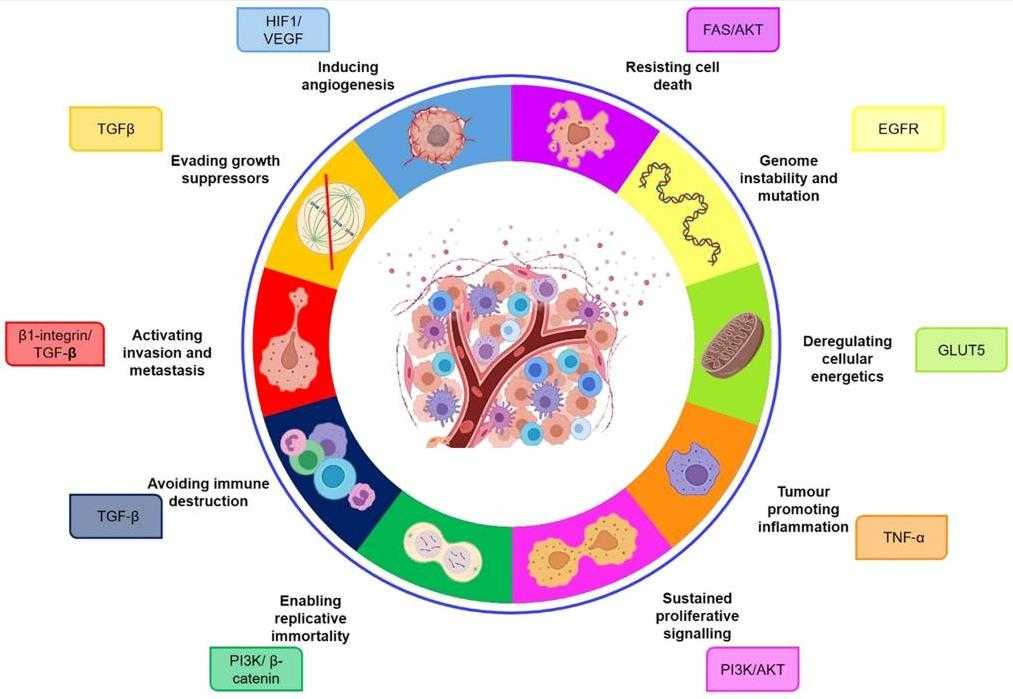
Fig1. The role of ST6 β-galactoside α-2,6-sialyltransferase 1 in the hallmarks of cancer. (Rebecca Garnham, 2019)
Bioapplications of ST6GAL1
ST6GAL1 is an important enzyme that regulates the key cell surface protein sialylation, and its abnormal activity in a variety of cancers makes it a potential target for drug development. Related applications include the development of ST6GAL1 inhibitors as an anticancer strategy, and the use of ST6GAL1 as a biomarker for early diagnosis and prognosis assessment of cancer. As well as exploring its potential for prediction in cancer therapy and monitoring of therapeutic response.
Case Study
Case Study 1: John J Erickson, 2022
Here this study shows that pregnancy-induced post-translational antibody modification enables protection against the prototypical intracellular pathogen Listeria monocytogenes. IgG was separated from neuraminidase by size exclusion chromatography before being resialylated using murine ST6Gal1. Infection susceptibility was reversed in neonatal mice born to preconceptually primed mothers possessing L. monocytogenes-specific IgG or after passive transfer of antibodies from primed pregnant, but not virgin, mice. Although maternal B cells were essential for producing IgGs that mediate vertically transferred protection, they were dispensable for antibody acquisition of protective function, which instead required sialic acid acetyl esterase5 to deacetylate terminal sialic acid residues on IgG variable-region N-linked glycans. Deacetylated L. monocytogenes-specific IgG protected neonates through the sialic acid receptor CD226,7, which suppressed IL-10 production by B cells leading to antibody-mediated protection.
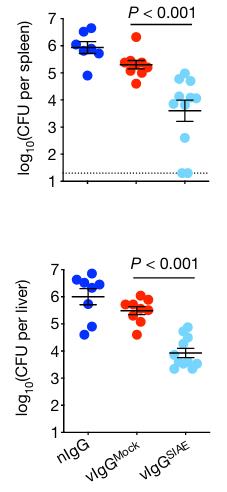
Fig1. The bacterial burden after Lm infection in neonatal mice that were administered SIAE- or mock-treated vIgG.
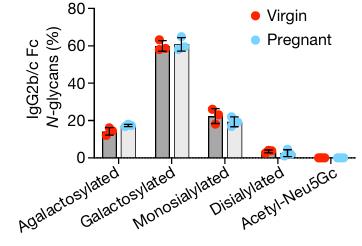
Fig2. The percentage of conserved IgG2 Fc N-glycan sites with each indicated glycoform.
Case Study 2: Robert B Jones, 2023
The ST6GAL1 sialyltransferase, which adds α2-6-linked sialic acids to N-glycosylated proteins, is upregulated in many malignancies including ovarian cancer. In the present study, researchers investigated a role for ST6GAL1 in tumor cell metabolism. ST6GAL1 was overexpressed (OE) in OV4 ovarian cancer cells, which have low endogenous ST6GAL1, or knocked-down (KD) in ID8 ovarian cancer cells, which have high endogenous ST6GAL1. OV4 and ID8 cells with modulated ST6GAL1 expression were grown under normoxic or hypoxic conditions, and metabolism was assessed using Seahorse technology. Results showed that cells with high ST6GAL1 expression maintained a higher rate of oxidative metabolism than control cells following treatment with the hypoxia mimetic, desferrioxamine (DFO). Glycolytic metabolism was also increased in OV4 and ID8 cells with high ST6GAL1 expression, and these cells displayed greater activity of the glycolytic enzymes, hexokinase and phosphofructokinase. Metabolism maps were generated from the combined Seahorse data, which suggested that ST6GAL1 functions to enhance the overall metabolism of tumor cells.
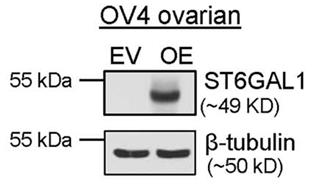
Fig3. OV4 cells were stably transduced with a lentivirus encoding ST6GAL1 and overexpression (OE) was confirmed by immunoblotting.
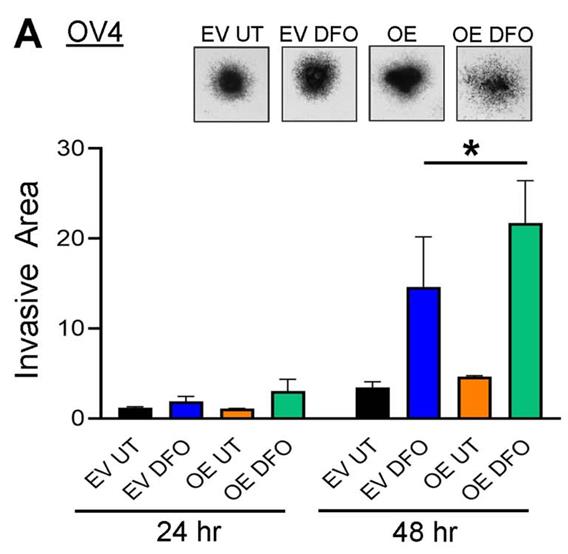
Fig4. OV4 cells were treated with or without DFO and then evaluated for invasion using a 3D spheroid invasion assay.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (ST6GAL1-14H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (ST6GAL1-2720H)
Involved Pathway
ST6GAL1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways ST6GAL1 participated on our site, such as N-Glycan biosynthesis,Other types of O-glycan biosynthesis,Metabolic pathways, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with ST6GAL1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Metabolic pathways | RFK,AGPAT9,AGXT,CERS5,UQCRH,GBE1,PIP5K1AB,NDUFV3,CYP2A12,PDHB |
| N-Glycan biosynthesis | DPAGT1,MGAT1A,ALG3,ALG2,FUT8,B4GALT2,STT3A,MOGS,ALG14,ALG10 |
| Other types of O-glycan biosynthesis | B4GALT3,B4GALT2,OGT.1,B3GAT1A,B3GALTL,POFUT1,ST3GAL3B,MGAT5B,FUT7,ST3GAL3 |
Protein Function
ST6GAL1 has several biochemical functions, for example, beta-galactoside alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase activity,protein binding,sialyltransferase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by ST6GAL1 itself. We selected most functions ST6GAL1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with ST6GAL1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| beta-galactoside alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase activity | ST6GAL2A,ST6GAL2B,ST6GAL2 |
| protein binding | FNIP1,KRTAP10-7,NOL4,ATF2,HBD,NEDD4L,TCP1,RTN3,WWP1,PRPS1 |
| sialyltransferase activity | ST6GALNAC1.2,ST3GAL5,ST6GALNAC4,ST3GAL2L,ST6GAL2B,ST3GAL3A,ST8SIA3,ST6GAL2A,ST8SIA5,ST3GAL5L |
Interacting Protein
ST6GAL1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with ST6GAL1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of ST6GAL1.
f_hcvh;acs
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References




