RAD52
-
Official Full Name
RAD52 homolog -
Overview
Repair of DNA double-stranded breaks (DSBs) can occur via nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ), homologous recombination (HR), or other DSB repair pathways. In yeast, one family of proteins involved in HR is the Rad52 group, which includes Rad52 itself, Rad51 -
Synonyms
RAD52;RAD52 homolog (S. cerevisiae);RAD52 (S. cerevisiae) homolog;DNA repair protein RAD52 homolog;recombination protein RAD52;rhabdomyosarcoma antigen MU-RMS-40.23
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Zebrafish
- Chicken
- Baker's yeast
- S.cerevisiae
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cell
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- Mammalian cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- HEK293T
- Non
- His
- GST
- Myc&DDK
- Flag
- His&Fc&Avi
- His&SUMO
Background
What is RAD52 protein?
RAD52 gene (RAD52 homolog, DNA repair protein) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 12 at locus 12p13. This gene product was shown to bind single-stranded DNA ends, and mediate the DNA-DNA interaction necessary for the annealing of complementary DNA strands. It was also found to interact with DNA recombination protein RAD51, which suggested its role in RAD51 related DNA recombination and repair. The RAD52 protein is consisted of 418 amino acids and RAD52 molecular weight is approximately 46.2 kDa.
What is the function of RAD52 protein?
The RAD52 protein plays a key role in DNA repair, especially when dealing with DNA double strand breaks (DSBs). It is involved in the process of homologous recombination (HR), which helps cells repair DNA damage and maintain genomic stability. RAD52 assists in DNA recombination between homologous sequences by facilitating the annealing and joining of DNA strands. In addition, RAD52 is involved in repair events associated with RNA templates, such as the repair of R-loops that are formed during transcription. RAD52's activity is essential to prevent the development of certain types of cancer, whose dysfunction can lead to genomic instability and the onset of disease.
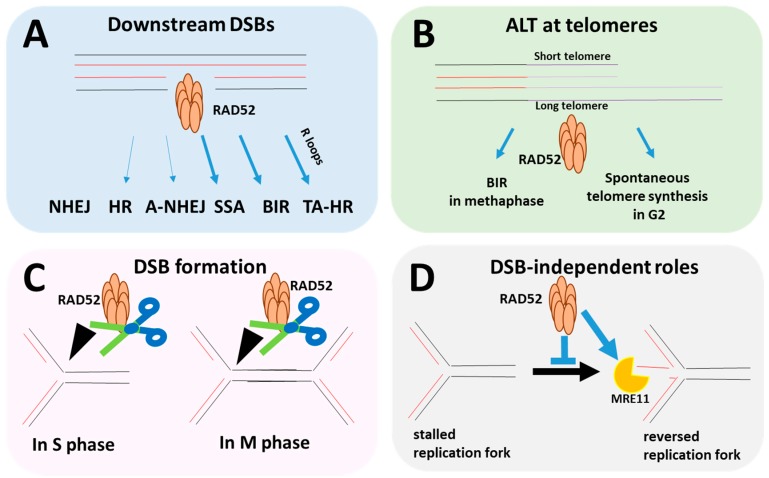
Fig1. Multiple roles of RAD52 during DNA replication and repair. (Vanesa Gottifredi, 2020)
RAD52 related signaling pathway
Rad52-associated signaling pathways are mainly involved in the repair process of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBS), especially in homologous recombination (HR) and non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). When DSB occurs in DNA, RAD52 is recruited to the damage site and participates in the transmission and repair process of DNA damage signal together with MRN complex (MRE11, RAD50, NBS1) and ATM kinase. RAD52 can promote the annealing and exchange of single-strand DNA, facilitate the loading of RAD51 in HR repair, and interact with proteins such as BRCA1 and BRCA2 to ensure efficient DNA repair.
RAD52 related diseases
Rad52-associated diseases are primarily associated with defects in DNA repair, which can lead to genomic instability and increased susceptibility to cancer. Mutations or loss of function in the RAD52 gene are associated with inherited cancer syndromes such as Fanconi anemia and breast/ovarian cancer. In these diseases, because the homologous recombination repair pathway involved in RAD52 is blocked, the cell's ability to repair DNA damage is reduced, resulting in the accumulation of chromosomal abnormalities and gene mutations, which in turn increases the risk of cancer. In addition, abnormal expression of RAD52 may also be associated with the development of some sporadic cancers, such as breast, ovarian, and pancreatic cancers.
Bioapplications of RAD52
Recombinant human RAD52 (rhRAD52) has potential bioapplications in the field of cancer research and therapy. As RAD52 is involved in DNA repair processes, particularly in homologous recombination, its recombinant form could be used to study DNA repair mechanisms and the role of RAD52 in cancer development. Additionally, rhRAD52 could potentially be used as a therapeutic agent to enhance DNA repair in cancer cells, making them more susceptible to radiation or chemotherapy treatments. Furthermore, rhRAD52 could also be explored as a target for developing new cancer therapies that specifically inhibit its function, thereby sensitizing cancer cells to DNA-damaging agents.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Ryohei Tsuchiya, 2023
RAD52 is a protein that binds to single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) and aids in the repair of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) by facilitating the rejoining of matching DNA strands. It also potentially contributes to a novel DSB repair mechanism involving RNA transcripts, where it may interact with RNA and catalyze RNA-DNA exchange. However, the precise mechanisms remain elusive. In this study, RAD52's biochemical properties were examined using its domain fragments, revealing that the N-terminal region is key for binding to single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) and promoting RNA-DNA exchange. The C-terminal region modulates these activities, enhancing the reverse RNA-DNA exchange activity of the N-terminal fragment without affecting DNA-DNA exchanges. These findings clarify the distinct roles of RAD52's domains in DNA and RNA-dependent repair processes.
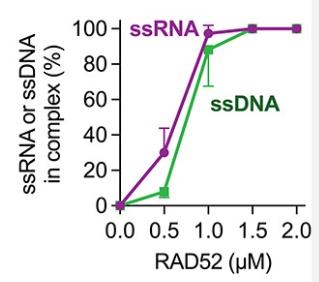
Fig1. Percentages of complexes formed by RAD52.
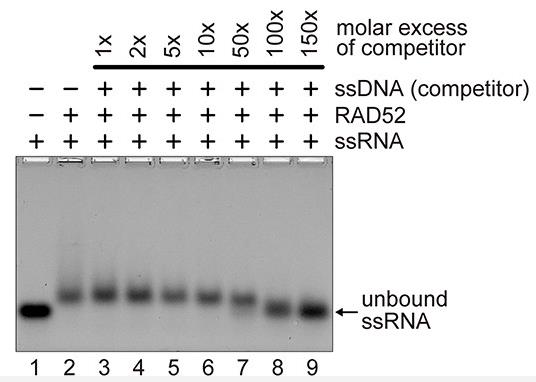
Fig2. RAD52 binding to ssRNA was competed with excess amounts of ssDNA.
Case Study 2: Shuo Liu, 2023
G-quadruplex (G4) DNA sequences in the human genome can lead to DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) and instability. This research shows that RAD52 is vital for preventing DSBs at G4 sites, with cells lacking RAD52 being more susceptible to G4-stabilizing compounds. RAD52 facilitates homologous recombination repair by recruiting XPF to resolve G4 structures at DSBs. Moreover, MUS81 cleaves stalled replication forks at G4s, and RAD52's absence, combined with the loss of G4-unwinding helicase FANCJ, leads to increased DSBs upon G4 stabilization, highlighting a synthetic lethal interaction between RAD52 and FANCJ.
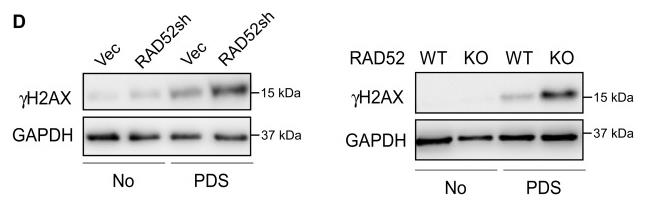
Fig3. WB of U2OS cells expressing vector or shRNA for RAD52 (left) and U2OS and U2OS-derived RAD52 KO cells (right).
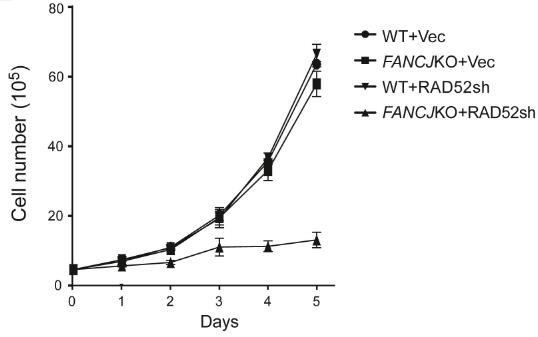
Fig4. U2OS WT and FANCJ KO cells were infected with RAD52 shRNA lentiviruses or vector control, and cell growth curves were plotted.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (RAD52-1565HFL)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (RAD52-957S)
Involved Pathway
RAD52 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways RAD52 participated on our site, such as Homologous recombination, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with RAD52 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Homologous recombination | MUS81,XRCC3,SYCP3,RPA1,RAD51L1,RPA3,MRE11A,RPA4,RPA2,RAD54L |
Protein Function
RAD52 has several biochemical functions, for example, DNA binding,damaged DNA binding,identical protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by RAD52 itself. We selected most functions RAD52 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with RAD52. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| DNA binding | ZFP280D,HIST1H2BJ,ZNF461,CDK5R2,SSH2B,ZNF606,ZNF133,ZNF582,HIST1H2AB,HOXA4A |
| protein binding | CEACAM6,EME1,CDYL2,FGFR1,DMKN,SHMT2,CCDC155,NKRF,TNPO2,BSCL2 |
| identical protein binding | NUP153,LRP6,CSK,PDCD6,COL2A1,S100B,CEP57L1,SNX16,NCAM1,MMP9 |
| damaged DNA binding | APEX1,TRP53,NEIL3,NEIL1,PCNA,DCLRE1A,RAD23AB,XRCC1,FEN1,TRP63 |
Interacting Protein
RAD52 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with RAD52 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of RAD52.
WRN;RAD51;RPA3;ALDOA;GAPDH;ENO1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Bang, JY; Kim, KS; et al. Anti-angiogenic effects of the water extract of HangAmDan (WEHAD), a Korean traditional medicine. SCIENCE CHINA-LIFE SCIENCES 54:248-254(2011).
- Offer, SM; Pan-Hammarstrom, Q; et al. Unique DNA Repair Gene Variations and Potential Associations with the Primary Antibody Deficiency Syndromes IgAD and CVID. PLOS ONE 5:-(2010).


