RAC1
-
Official Full Name
ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (rho family, small GTP binding protein Rac1) -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a GTPase which belongs to the RAS superfamily of small GTP-binding proteins. Members of this superfamily appear to regulate a diverse array of cellular events, including the control of cell growth, cytoskeletal reorganization, and the activation of protein kinases. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2009] -
Synonyms
RAC1;ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (rho family, small GTP binding protein Rac1);MIG5;Rac-1;TC-25;p21-Rac1;ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1;ras-like protein TC25;cell migration-inducing gene 5 protein
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Chicken
- E.coli
- Insect Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- His
- GST
- Non
- Flag
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
Background
What is RAC1 protein?
RAC1 gene (Rac family small GTPase 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 7 at locus 7p22. RAC1 protein, a member of the Rho GTPase family, is a key regulator of cell migration, adhesion, and morphology. It plays a significant role in various physiological and pathological processes, including embryonic development, tissue repair, and immune responses. Rac1 is highly expressed in many tumors and is associated with poor prognosis. It influences tumor progression by regulating cell cycle, apoptosis, proliferation, invasion, migration, and angiogenesis. The RAC1 protein is consisted of 192 amino acids and RAC1 molecular weight is approximately 21.5 kDa.
What is the function of RAC1 protein?
The RAC1 protein, a member of the Rho GTPase family, is a key regulator of cellular processes such as migration, adhesion, and the actin cytoskeleton's dynamics. It plays a crucial role in developmental morphogenesis, tissue repair, and immune responses. RAC1 is also implicated in cancer development and progression, as it influences cell proliferation, survival, invasion, and metastasis. Due to its significant involvement in tumorigenesis and therapy resistance, RAC1 is considered a potential therapeutic target for cancer treatment strategies.

Fig1. Schematic illustration of RAC signaling pathways and effector functions. (Hemant K Bid, 2013)
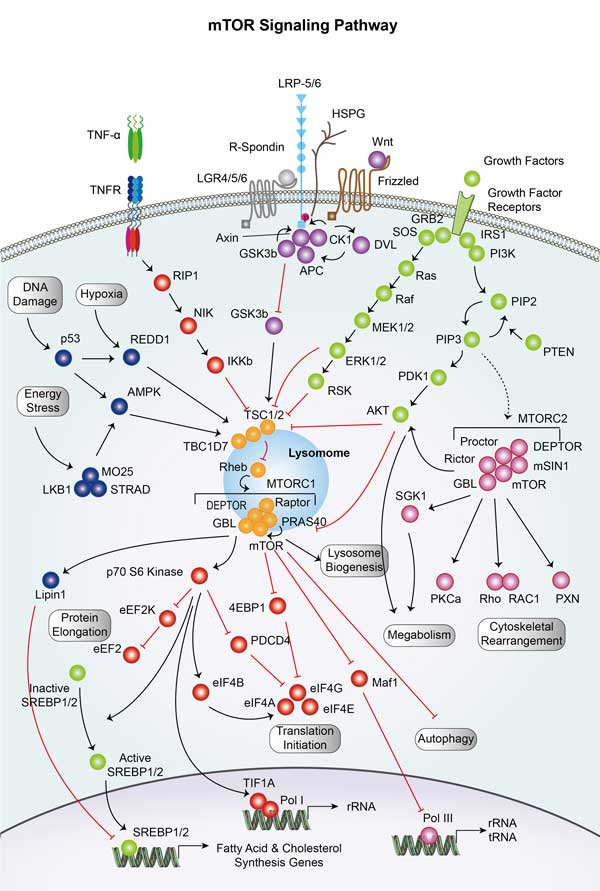
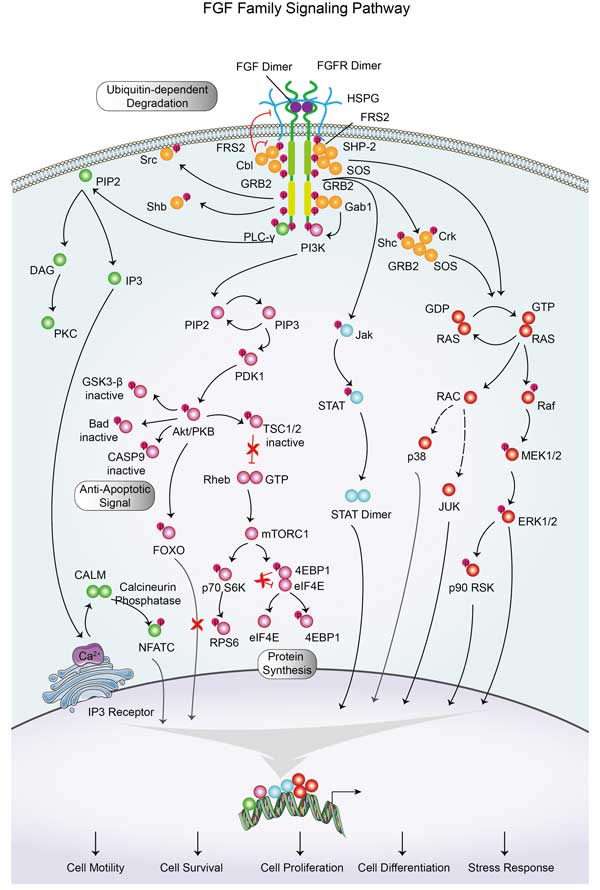
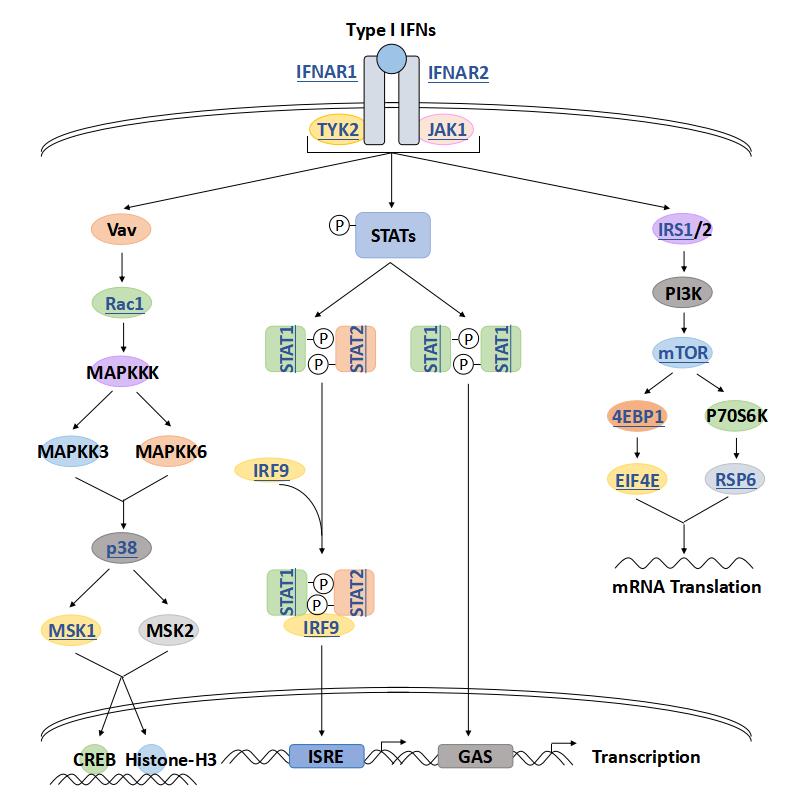
RAC1 related signaling pathway
Key pathways involving RAC1 include the regulation of the actin cytoskeleton, which controls cell shape, adhesion, and motility, as well as the promotion of cell survival and proliferation. RAC1 also plays a significant role in the reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton through the activation of downstream effectors like PAK1, which influences cell migration and invasion, processes particularly pertinent to cancer development and metastasis. Furthermore, RAC1 is implicated in the JNK/MAPK pathway, which is involved in stress response, and the regulation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, which is crucial for cellular differentiation and embryonic development. The activity of RAC1 is modulated by various upstream regulators such as guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs), GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs), and Rho GDP dissociation inhibitors (GDIs), making it a central node in a complex network of cellular signaling.
RAC1 related diseases
RAC1, a small GTPase, is central to numerous cellular functions and is implicated in a variety of diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, arthritis, and kidney diseases. In cancer, RAC1's role in cell migration and invasion makes it a promising target for therapy; its activity is associated with tumor progression and resistance to treatment. In cardiovascular diseases, RAC1 contributes to pathological processes like hypertrophy and atherosclerosis. In neurodegenerative diseases, RAC1 is involved in neuronal survival and protection against apoptosis. It also plays a role in inflammatory responses in conditions like arthritis and kidney disorders. Targeting RAC1 signaling pathways could offer therapeutic benefits, but the development of effective RAC1 inhibitors that can distinguish between protective and detrimental roles of RAC1 is an ongoing challenge.
Bioapplications of RAC1
RAC1 protein plays a significant role in various cellular processes, including cell migration, adhesion, and the regulation of the actin cytoskeleton. It is particularly noted for its impact on cancer cell invasion and metastasis, making it a potential target for cancer therapy. Additionally, RAC1's involvement in immune responses and its regulatory effects on gene transcription suggest possible applications in treating autoimmune diseases and modulating inflammatory reactions. Understanding and targeting RAC1's activity could lead to novel therapeutic strategies in these areas.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Jun Sun, 2021
RAC1, a Rho family GTPase, is crucial for normal cell functions but becomes dysregulated in various cancers, including breast cancer (BC). The findings show that RAC1's activity is vital for estrogen receptor alpha (ER) stability and transcription in ER-positive BC cells, which are more sensitive to RAC1 inhibition than ER-negative ones. By reducing RAC1 activity with siRNA or EHT 1864, an Rac inhibitor, we observed rapid ER degradation. RAC1's interaction with ER and its role in RNA Pol II function on ER target genes suggest that targeting RAC1 could be a promising therapeutic strategy for ER-positive BC.
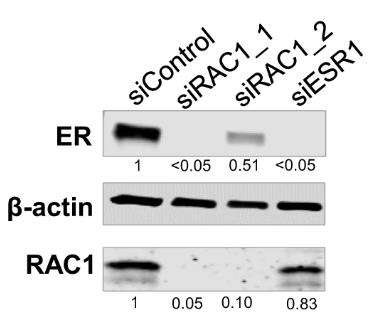
Fig1. The Western blot analyses for changes in RAC1 or ER protein levels three days after MCF-7 cells were transfected with siRNA oligos.

Fig2. The cell extract was fractionated into different portions and analyzed by Western blotting with the indicated antibodies.
Case Study 2: Natalia Ruiz-Lafuente, 2021
The HeLa cell line model has demonstrated that DOCK10 activates Rho GTPases Cdc42 and Rac1, inducing filopodia and plasma membrane ruffles. Both active and dominant-negative mutants of Cdc42 and Rac1 were found to promote these protrusions. Specifically, active Cdc42 and Rac1 enhance filopodia and ruffles, respectively, with DOCK10 intensifying these effects. This study clarifies the distinct roles of Cdc42 and Rac1 in membrane protrusion regulation and suggests that the HeLa model is a valuable tool for further investigating the mechanisms of plasma membrane dynamics.

Fig3. Generation of HeLa cell clones with stable inducible expression of Rho GTPases Cdc42 and Rac1.

Fig4. Proliferation of HeLa cell clones with stable inducible expression of the Rho GTPases Cdc42 and Rac1 in WT and DN conformations, alone or co-expressed with their GEF DOCK10.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (RAC1-1105HFL)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (RAC1-5665H)
Involved Pathway
RAC1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways RAC1 participated on our site, such as MAPK signaling pathway,Ras signaling pathway,Rap signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with RAC1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Focal adhesion | CAV1,ITGB6,PAK1,MAPK8,PXN,RAP1AB,DOCK1,VCL,ITGA3B,CAV2 |
| Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis | AKT1,PTPRC,FCGR1A,PRKCE,ARPC5L,PLCG1,SPHK2,cgr2b,PLA2G4F,PLD2 |
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | CCL5,IL-8,STAT1A,IKBKE,NFKB1,CD80,TRAF6,MAPK13,TAB2,IRF7 |
| Sphingolipid signaling pathway | PPP2R5D,CERS5,TNF,PLD1,PPP2R5A,PLCB2,LOC100328615,PTEN,MAP2K1,BDKRB2 |
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | IRS1,AKT2,SOS1,SHC3,PSEN2,RAF1,CALM3,ZFP110,PIK3R5,CALM2 |
| Pancreatic cancer | RB1,TGFBR1,RAF1,PIK3CB,RELA,SMAD2,CDC42,RALGDS,NFKB1,BCL2L1 |
| MAPK signaling pathway | HSPA2,MAP4K2,PPP5C,CDC42,CACNG8,MECOM,MYCB,NR4A1,PPM1BA,FGF18 |
| B Cell Receptor Signaling Pathway | PILRB,CTNNB2,CSK,PDPK1A,CDK6,CD19,INPP5D,RAC2,PTPN18,VAV1 |
| Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection | JAM2,ATP6V1G3,ATP6V0B,IKBKG,ATP6V1A,ATP6V1F,ATP6V0D2,PTPN11,MAPK9,CCL5 |
Protein Function
RAC1 has several biochemical functions, for example, GTP binding,GTPase activity,Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by RAC1 itself. We selected most functions RAC1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with RAC1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| thioesterase binding | TRAF1,TRAF3,CDC42,TRAF5,TRAF4,TRAF6,CALM2,ADRA2A,CALM,TRAF2 |
| GTPase activity | MXA,RAP1GAP,GBP6,GNAO1B,TUBA1B,MSTO1,GTPBP1L,TUBB4A,GTPBP1,RAB40AL |
| GTP binding | GTPBP2,TUBB2B,ARL16,ARF3B,TUBA1L2,SEPT9,GCH2,RAB2B,AK3,RAB1B |
| protein binding | CENPJ,DFFA,TMIGD2,OGG1,SPG21,EIF6,CD200R4,CD82,GSDMA2,CTLA2B |
| enzyme binding | MAT2B,PEBP1,KDM1A,MSH2,A2M,PLCE1,UGT1A6,NPC2,PCBP2,LAMP2 |
| Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor binding | RHOA |
Interacting Protein
RAC1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with RAC1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of RAC1.
PAK1
RAC1 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Yu, CH; Zhang, S; et al. Rac1 signaling regulates neutrophil-dependent tissue damage in experimental colitis. EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY 741:90-96(2014).
- Kenny, HA; Chiang, CY; et al. Mesothelial cells promote early ovarian cancer metastasis through fibronectin secretion. JOURNAL OF CLINICAL INVESTIGATION 124:4614-4628(2014).