PUM1
-
Official Full Name
pumilio homolog 1 -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of the PUF family, evolutionarily conserved RNA-binding proteins related to the Pumilio proteins of Drosophila and the fem-3 mRNA binding factor proteins of C. elegans. The encoded protein contains a sequence-specific RNA binding domain comprised of eight repeats and N- and C-terminal flanking regions, and serves as a translational regulator of specific mRNAs by binding to their 3 untranslated regions. The evolutionarily conserved function of the encoded protein in invertebrates and lower vertebrates suggests that the human protein may be involved in translational regulation of embryogenesis, and cell development and differentiation. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described. -
Synonyms
PUM1;pumilio homolog 1 (Drosophila);pumilio (Drosophila) homolog 1;pumilio homolog 1;KIAA0099;PUMH1;pumilio-1;PUMH;HSPUM;PUML1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Chicken
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cell
- HEK293
- HEK293T
- E. coli
- Mammalian cells
- His
- Non
- His&Fc&Avi
- Myc&DDK
- GST
- Flag
Background
What is PUM1 protein?
PUM1 gene (pumilio RNA binding family member 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1p35. This gene encodes a member of the PUF family, evolutionarily conserved RNA-binding proteins related to the Pumilio proteins of Drosophila and the fem-3 mRNA binding factor proteins of C. elegans. The encoded protein contains a sequence-specific RNA binding domain comprised of eight repeats and N- and C-terminal flanking regions, and serves as a translational regulator of specific mRNAs by binding to their 3' untranslated regions. The evolutionarily conserved function of the encoded protein in invertebrates and lower vertebrates suggests that the human protein may be involved in translational regulation of embryogenesis, and cell development and differentiation. The PUM1 protein is consisted of 1186 amino acids and PUM1 molecular weight is approximately 126.5 kDa.
What is the function of PUM1 protein?
PUM1 protein is an RNA-binding protein that plays a key role in cell cycle, cell proliferation, DNA damage response, and tumorigenesis. It performs its function as a post-transcriptional suppressor by binding to a specific sequence on the 3' untranslated region (3'-UTR) of mRNA, the Pumilio response element (PRE). PUM1 is able to regulate the stability of target mRNA and the translation process through a variety of mechanisms, including direct recruitment of the CCR4-POP2-NOT deadenylate complex leading to translation inhibition and mRNA degradation, as well as promoting miRNA accessibility for inhibition independent of deadenylation. It is worth noting that the function of PUM1 is also affected by a series of regulatory factors, including miRNAs, lncRNAs and circRNAs, which affect the expression and activity of PUM1 through different mechanisms.
PUM1 Related Signaling Pathway
PUM1 affects the process of the cell cycle by regulating the expression of cell cycle related genes, especially in the G1/S phase transition. PUM1 is involved in molecular response to DNA damage and may maintain genomic stability by affecting the expression of genes associated with DNA repair and replication. In the testis, PUM1 acts as a post-transcriptional regulator and is involved in spermatogenesis by binding to the 3'-UTR of mRNA encoding the p53/TP53 regulatory protein. PUM1 is involved in the renewal of embryonic stem cells, accelerating the downregulation of naive pluripotent transcription factors at the beginning of differentiation by promoting withdrawal from the basal state.
PUM1 Related Diseases
Abnormal expression of PUM1 has been found in a variety of cancers, including pancreatic, ovarian, non-small cell lung, colorectal, stomach, prostate, and glioma. In these cancers, PUM1 typically acts as an oncogene to drive malignant progression of tumors by promoting tumor cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transformation (EMT). In addition, PUM1 is also involved in the occurrence and development of non-malignant diseases, such as diabetes, inflammation, pulmonary fibrosis and other diseases, PUM1 participates in the pathological process by regulating the expression of disease-related genes. In neurodegenerative diseases, PUM1 may be involved in the pathogenesis of the disease by affecting the stability and translation of specific MRnas.
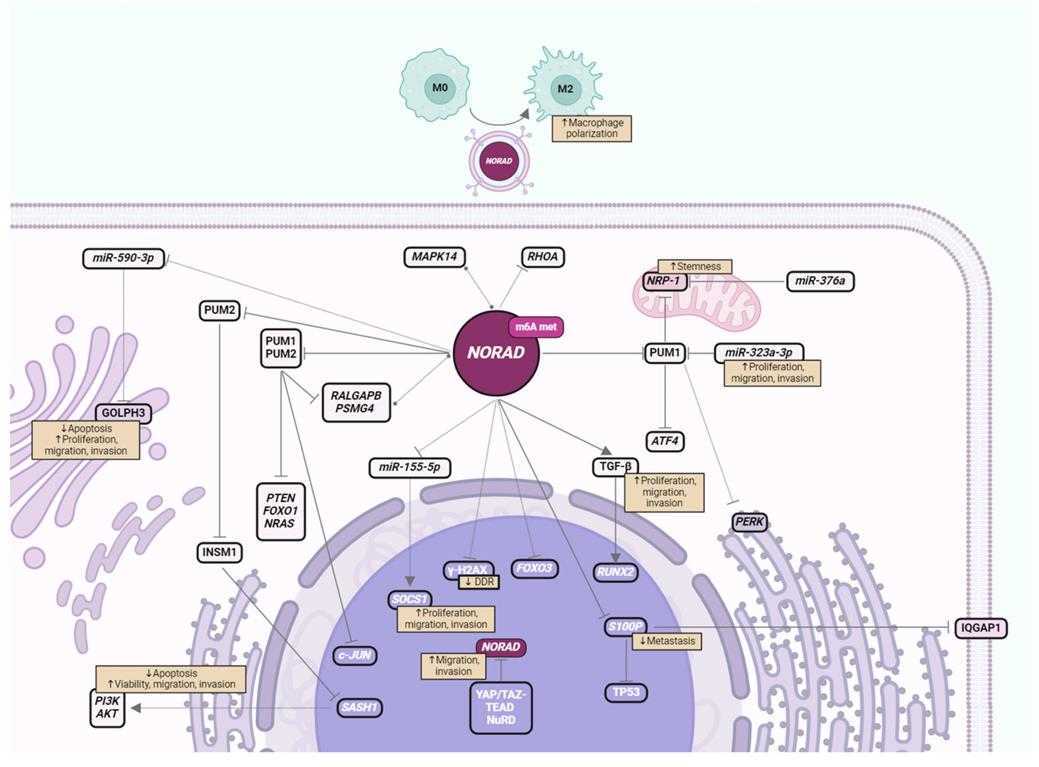
Fig1. Schematic of NORAD molecular interacting partners in BC, emphasizing cellular localization, and impact on cancer progression. (Ana Maria Capela, 2024)
Bioapplications of PUM1
The high expression levels of PUM1 in a variety of cancers make it an attractive therapeutic target. Reducing the expression or activity of PUM1 through drugs or other interventions may inhibit the proliferation and metastasis of tumor cells. The expression level of PUM1 is closely related to the progression of various cancers and the prognosis of patients, and can be used as an important biomarker for cancer diagnosis and prognosis evaluation. Drug development for PUM1 is ongoing with the aim of discovering small molecule compounds or biologics that can regulate PUM1 activity, providing new strategies for cancer treatment. PUM1 plays a role in the self-renewal and differentiation of stem cells, and its use in stem cell research could help develop stem cell-based therapeutic strategies.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Yuexin Zhang, 2024
It is reported that exosome circular RNA (circRNA) is involved in the gastric cancer (GC) progression. However, the function and potential mechanism of circGMPS in GC remains unclear and needs further exploration. In this study, researchers isolated and identified exosomes from serum by TEM, NTA analysis and Western blot. RNA expression was evaluated by qRT-PCR. Western blot was employed to examine protein expression. Cell proliferation was measured using CCK-8. Transwell assay was adopted to analyze cell migration and invasion. It is found that circGMPS was elevated in GC exosomes, tissues and cells. Poor prognosis of GC patients was related to high circGMPS expression. Mechanically, circGMPS sponged miR-144-3p to regulate PUM1. Inhibition of PUM1 or miR-144-3p overexpression inhibited the malignant GC cell progression.
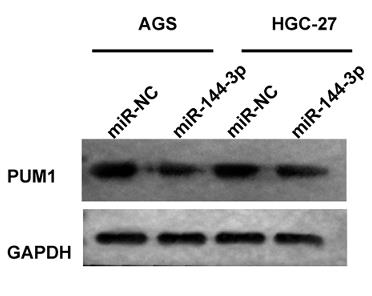
Fig1. Western blot was applied to check PUM1 protein in GC cells transfected with miR-144-3p mimic.
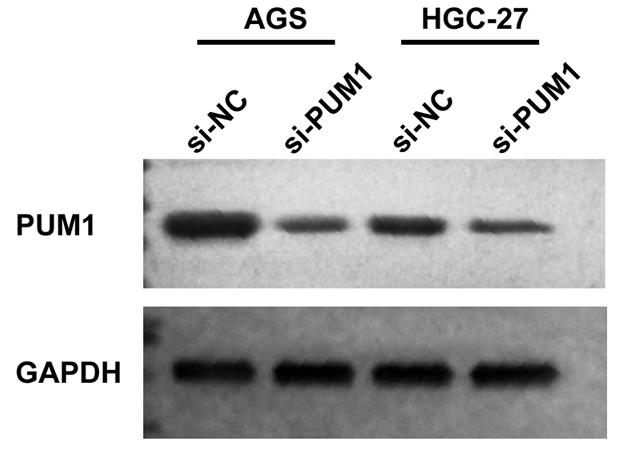
Fig2. PUM1 protein was checked using Western blot after PUM1 knockdown.
Case Study 2: Han Wang, 2024
Previously, Pumilio 1 (PUM1), a RBP, was reported to regulate glycolysis metabolism and promote the progression of gastric cancer (GC). However, the role of PUM1 in tumor immune regulation remains largely elusive. In this study, researchers report that PUM1 induces immune escape through posttranscriptional regulation of PD-L1 in GC. They used multiplexed immunohistochemistry to analyze the correlation between PUM1 expression and immune microenvironment in GC. The effect of PUM1 deficiency on tumor killing of T cells was examined in vitro and in vivo. The molecular mechanism of PUM1 was evaluated via RNA immunoprecipitation, chromatin immunoprecipitation, Western blot, co-immunoprecipitation, and RNA stability assays. Mechanistically, PUM1 directly binds to nucleophosmin/nucleoplasmin 3 (NPM3) mRNA and stabilizes NPM3. NPM3 interacts with NPM1 to promote NPM1 translocation into the nucleus and increase the transcription of PD-L1. PUM1 inhibits the anti-tumor activity of T cells through the PUM1/NPM3/PD-L1 axis.

Fig3. PD-L1 expression analyzed by flow cytometry with shPUM1.
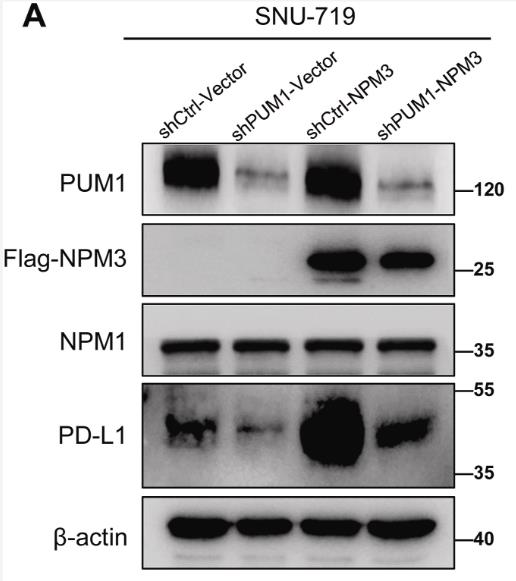
Fig4. Western blotting of Flag-NPM3, NPM1 and PD-L1 in PUM1 knockdown cells.
Quality Guarantee
.
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PUM1-2883H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (PUM1-930HFL)
Involved Pathway
PUM1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PUM1 participated on our site, such as Clathrin derived vesicle budding,Golgi Associated Vesicle Biogenesis,Membrane Trafficking, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PUM1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Clathrin derived vesicle budding | APPB,BLOC1S3,SNX9,TFR1B,TPD52L1,FTH1A,APPA,PICALMA,CPD,TBC1D8B |
| Membrane Trafficking | TMED10,TRAPPC2L,STAM2,CNIH,SNF8,GJB7,CTAGE5,TCEAL4,COPE,MCFD2 |
| Vesicle-mediated transport | COPZ1,GJB3,TRAPPC2L,CTAGE5,AP1S3A,RALAB,SEC16B,TPD52L1,AP4B1,CLVS1 |
| Golgi Associated Vesicle Biogenesis | SNAPIN,TPD52L1,PLDN,SNX9,AP4B1,AP1B1,FTH1B,PICALM,AP1G1,BLOC1S4 |
| trans-Golgi Network Vesicle Budding | BLOC1S6,HIP1RB,SNX9,TPD52,TPD52L1,AP4B1,AP3S1,YIPF6,DTNBP1B,SNX9B |
Protein Function
PUM1 has several biochemical functions, for example, mRNA 3-UTR binding,poly(A) RNA binding,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PUM1 itself. We selected most functions PUM1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PUM1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| mRNA 3-UTR binding | ELAVL2,ZNF385A,CARHSP1,RBM38,TUT1,PPP1R2P9,TES,RBMS3,RBM24,FXR1 |
| poly(A) RNA binding | RPS17L,RPL10L,PRRC2A,PEF1,ATP5A1,ARHGEF1,SRPK1,FTSJ3,NOVA2,RPL3 |
| protein binding | NEK8,ZMYND11,ABI2,WWC1,GLYCTK,CSNK2B,C16orf48,MCL1,NUP62,IL12A |
Interacting Protein
PUM1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PUM1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PUM1.
ATXN1;EIF5;SMAD1;ppc;mutS;PRR12;PTBP3;VCAM1;YWHAB;ORF7;CDC5L;SAV1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


