LMAN1
-
Official Full Name
lectin, mannose-binding, 1 -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a type I integral membrane protein localized in the intermediate region between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi, presumably recycling between the two compartments. The protein is a mannose-specific lectin and is a member of a novel family of plant lectin homologs in the secretory pathway of animal cells. Mutations in the gene are associated with a coagulation defect. Using positional cloning, the gene was identified as the disease gene leading to combined factor V-factor VIII deficiency, a rare, autosomal recessive disorder in which both coagulation factors V and VIII are diminished. -
Synonyms
LMAN1;lectin, mannose-binding, 1;coagulation factor V factor VIII combined deficiency , F5F8D;protein ERGIC-53;endoplasmic reticulum golgi intermediate compartment protein 53;ERGIC 53;ERGIC53;FMFD1;gp58;MCFD1;MR60;intracellular mannose specific
Recombinant Proteins
- Rhesus macaque
- Chicken
- Rat
- Human
- Mouse
- Mammalian Cell
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Mammalian cells
- HEK293T
- E.coli expression system
- His
- Non
- His&Fc&Avi
- Flag
- Myc&DDK
Background
What is LMAN1 protein?
LMAN1 gene (lectin, mannose binding 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 18 at locus 18q21. The protein encoded by this gene is a membrane mannose-specific lectin that cycles between the endoplasmic reticulum, endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment, and cis-Golgi, functioning as a cargo receptor for glycoprotein transport. The protein has an N-terminal signal sequence, a calcium-dependent and pH-sensitive carbohydrate recognition domain, a stalk region that functions in oligomerization, a transmembrane domain, and a short cytoplasmic domain required for organelle targeting. The LMAN1 protein is consisted of 510 amino acids and LMAN1 molecular weight is approximately 57.5 kDa.
What is the function of LMAN1 protein?
LMAN1 is a type I transmembrane protein that plays a crucial role in the transport of glycoproteins from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to the Golgi apparatus. It functions as a cargo receptor, selectively transporting its cargo proteins and is involved in the maintenance of photoreceptor homeostasis in the retina, as well as potentially serving as a prognostic biomarker and molecular therapeutic target for glioma. Additionally, research indicates that high expression of LMAN1 is associated with shorter overall survival and poor clinical prognostic variables in glioma, suggesting its role as a potential therapeutic target.
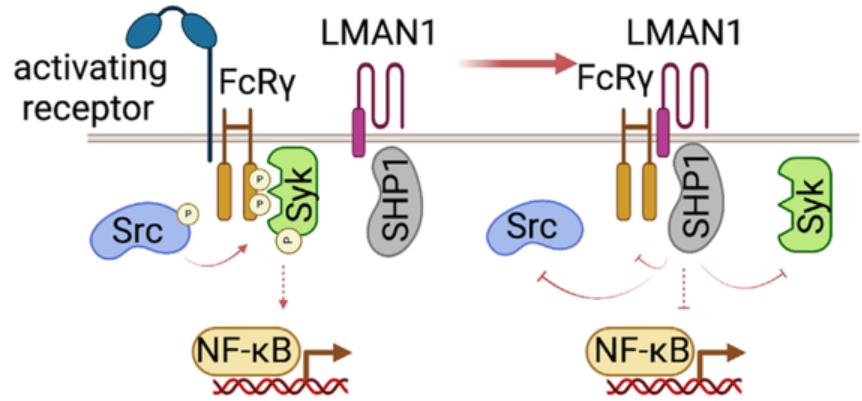
Fig1. Engagement of LMAN1 by HDM restrains inflammatory responses. (Madelyn H Miller, 2023)
LMAN1 Related Signaling Pathway
The biological functions of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) are mainly focused on immune responses, suggesting that LMAN1 may be involved in the regulation of immune-related signaling pathways. LMAN1 protein forms a complex with MCFD2 and is involved in the transport process from ER to Golgi as a cargo receptor. The expression of LMAN1 protein is related to the proliferation and invasion ability of glioma cells, which may involve a variety of signaling pathways related to cell proliferation and invasion. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) has shown that many cancer-related pathways are associated with high LMAN1 phenotype. The interactions between LMAN1 and MCFD2, F8 and TMED10 may involve specific signal transduction processes.
LMAN1 Related Diseases
The expression of LMAN1 in gliomas is associated with tumor proliferation, invasion and poor prognosis. High expression of LMAN1 is associated with higher WHO grade, IDH status, and 1p/19q co-deletion, as well as reduced overall survival in glioma patients. LMAN1 is involved in protein transport of photoreceptors in the retina and maintenance of retinal structure, and its abnormal function may lead to retinal diseases. LMAN1 is associated with deficiencies in coagulation factors V and VIII, which affect the blood clotting process. Because LMAN1 plays a role in the transport of neurotransmitter receptors, its abnormalities may be associated with the development of certain neurodegenerative diseases.
Bioapplications of LMAN1
As a drug target, LMAN1 has potential in the development of anti-tumor drugs and other therapeutic areas. LMAN1 can be used as a biomarker for disease diagnosis and treatment monitoring, especially in the diagnosis and prognosis assessment of glioma. LMAN1 is related to the proliferation, migration and invasion ability of glioma cells, which provides an important index for the study of tumor biological behavior. LMAN1 is involved in the study of immune response related pathways, which contributes to the in-depth understanding of the molecular mechanism of immune-related diseases. LMAN1 has been identified as a receptor for house dust mite allergens, providing a new target for the study and treatment of allergic reactions.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Madelyn H Miller, 2023
Development of therapies with the potential to change the allergic asthmatic disease course will require the discovery of targets that play a central role during the initiation of an allergic response, such as those involved in the process of allergen recognition. Researchers use a receptor glycocapture technique to screen for house dust mite (HDM) receptors and identify LMAN1 as a candidate. They verify the ability of LMAN1 to directly bind HDM allergens and demonstrate that LMAN1 is expressed on the surface of dendritic cells (DCs) and airway epithelial cells (AECs) in vivo. Overexpression of LMAN1 downregulates NF-κB signaling in response to inflammatory cytokines or HDM. HDM promotes binding of LMAN1 to the FcRγ and recruitment of SHP1. Last, peripheral DCs of asthmatic individuals show a significant reduction in the expression of LMAN1 compared with healthy controls.

Fig1. Ligand-receptor capture (LRC)-Tri-CEPs platform identifies LMAN1 as a candidate receptor for HDM.

Fig2. FLAG-tagged human LMAN1 was purified using an affinity resin.
Case Study 2: Tyler Duellman, 2015
Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) is a secreted glycoprotein with a major role in shaping the extracellular matrix and a detailed understanding of the secretory mechanism could help identify methods to correct diseases resulting from dysregulation of secretion. MMP-9 appears to follow a canonical secretory pathway through a quality control cycle in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) before transport of the properly folded protein to the Golgi apparatus and beyond for secretion. Through a complementation assay, we determined that LMAN1, a well-studied lectin-carrier protein, interacts with a secretion-competent N-glycosylated MMP-9 in the ER while N-glycosylation-deficient secretion-compromised MMP-9 does not. In contrast, co-immunoprecipitation demonstrated protein interaction between LMAN1 and secretion-compromised N-glycosylation-deficient MMP-9. MMP-9 secretion was reduced in the LMAN1 knockout cell line compared to control cells confirming the functional role of LMAN1.
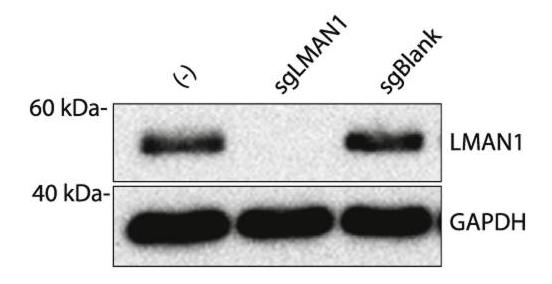
Fig3. Western blot of endogenous LMAN1 expression in HEK293 cells.

Fig4. Effects of chemical crosslinking on co-IP between LMAN1.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (LMAN1-7896H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (LMAN1-224HFL)
Involved Pathway
LMAN1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways LMAN1 participated on our site, such as Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with LMAN1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum | UGGT1,PLAA,DNAJC5,BAK1,ATXN3,ERLEC1,FBXO6,SAR1AB,SSR4,MAPK8A |
Protein Function
LMAN1 has several biochemical functions, for example, mannose binding,metal ion binding,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by LMAN1 itself. We selected most functions LMAN1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with LMAN1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| mannose binding | MRC1,CD209C,MANBA,MBL2,M6PR,COLEC10,BSG,CLN5,Acr,CD209A |
| protein binding | KRTAP19-7,PLP2,KDRL,KCNA2,CCER1,SLU7,PRKAR2AA,UBE2U,EMP2,STX8 |
| metal ion binding | RYBPB,ZFP667,PLEKHF1,REST,KLF6,ITGB7,SMPD2,FTH1B,ATF7B,HRG |
| unfolded protein binding | CRYAB,HSPA9,DNAJB2,DNAJB4,HSP90AA1.2,PFDN4,DNAJA2,PDRG1,SRSF12,TCP1 |
Interacting Protein
LMAN1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with LMAN1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of LMAN1.
SURF4;env;env;ERP44;MCFD2;VHL;q81wb2_bacan;P;PTPN2;TMED5;SNX9
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Yamada, T; Fujimori, Y; et al. A novel missense mutation causing abnormal LMAN1 in a Japanese patient with combined deficiency of factor V and factor VIII. AMERICAN JOURNAL OF HEMATOLOGY 84:738-742(2009).


