H1F0
-
Official Full Name
H1 histone family, member 0 -
Overview
Histones are basic nuclear proteins that are responsible for the nucleosome structure of the chromosomal fiber in eukaryotes. Nucleosomes consist of approximately 146 bp of DNA wrapped around a histone octamer composed of pairs of each of the four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4). The chromatin fiber is further compacted through the interaction of a linker histone, H1, with the DNA between the nucleosomes to form higher order chromatin structures. This gene is intronless and encodes a member of the histone H1 family. -
Synonyms
H1F0;H1 histone family, member 0;H1FV;histone H1.0;H1.0;H1(0);H1 0;H10;H1 histone family member 0;Histone H1;Histone H10;Histone H5;MGC5241;histone H1(0);H1.0, H1(0), H1-0
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Chicken
- Mouse
- Zebrafish
- Bovine
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cell
- Wheat Germ
- Thymus
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His
- Non
- His&Fc&Avi
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1F0-13640H | Recombinant Human H1F0, GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | 1-194a.a. | |
| H1F0-6945H | Recombinant Human H1F0 protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Met1-Lys194 | |
| H1F0-100H | Recombinant Human H1F0 Protein | E.coli | Human | Non | 1-194 |
|
| H1F0-2132H | Recombinant Human H1 Histone Family, Member 0 | E.coli | Human | Non |
|
|
| H1F0-2773R | Recombinant Rat H1F0 Protein | Mammalian Cell | Rat | His |
|
|
| H1F0-3465C | Recombinant Chicken H1F0 | Mammalian Cell | Chicken | His |
|
|
| H1F0-4528H | Recombinant Human H1F0 Protein, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST |
|
|
| H1F0-7420M | Recombinant Mouse H1F0 Protein | Mammalian Cell | Mouse | His |
|
|
| H1F0-9956Z | Recombinant Zebrafish H1F0 | Mammalian Cell | Zebrafish | His |
|
|
| H1F0-2117HCL | Recombinant Human H1F0 cell lysate | Human | Non |
|
||
| H1F0-01B | Native Bovine H1F0 Protein | Thymus | Bovine | 1-213 (H1.2), 1-221 (H1.3), and 1-219 (H1.4) |
|
|
| H1F0-2427R | Recombinant Rat H1F0 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Rat | His&Fc&Avi |
|
|
| H1F0-2427R-B | Recombinant Rat H1F0 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Rat |
|
||
| H1F0-2578H | Recombinant Human H1F0 protein(31-160 aa), C-His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 31-160 aa |
|
| H1F0-2579H | Recombinant Human H1F0 protein(21-120 aa), C-His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 21-120 aa |
|
| H1F0-3395HF | Recombinant Full Length Human H1F0 Protein, GST-tagged | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | GST | Full L. 194 amino acids |
|
| H1F0-4035M | Recombinant Mouse H1F0 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | His&Fc&Avi |
|
|
| H1F0-4035M-B | Recombinant Mouse H1F0 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
Background
What is H1F0 protein?
H1F0 also known as H1-0. H1-0 gene (H1.0 linker histone) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 22 at locus 22q13. Histones are basic nuclear proteins that are responsible for the nucleosome structure of the chromosomal fiber in eukaryotes. Nucleosomes consist of approximately 146 bp of DNA wrapped around a histone octamer composed of pairs of each of the four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4). The chromatin fiber is further compacted through the interaction of a linker histone, H1, with the DNA between the nucleosomes to form higher order chromatin structures. This gene is intronless and encodes a replication-independent histone that is a member of the histone H1 family. The H1F0 protein is consisted of 194 amino acids and H1F0 molecular weight is approximately 20.9 kDa.
What is the function of H1F0 protein?
It is a member of the histone H1 family and is involved in DNA binding, which is essential for the nucleosome structure of chromosomal fiber in eukaryotes. The H1.0 protein has distinct nuclear expression across various tissues and is particularly enhanced in bone marrow. Furthermore, H1F0 has been implicated in the response to mechanical stress within cells, where it can adaptively respond to changes in extracellular tension, thereby influencing chromatin compaction and gene expression. This protein is also involved in the regulation of cellular mechanical behaviors, including contractile force generation, cytoskeletal regulation, motility, and extracellular matrix deposition.

Fig1. Histone-based malignant transformation, tumour heterogeneity and selection of aggressive characters. (Tao Wang, 2019)
H1F0 Related Signaling Pathway
H1F0, as a linker histone, plays a role in the compaction of chromatin. Chromatin remodeling is essential for various cellular processes, including gene expression, DNA repair, and replication. The modulation of chromatin structure by H1F0 could also be involved in the DNA damage response pathway, where the accessibility of DNA repair proteins to damaged sites is crucial. H1F0 may be involved in epigenetic regulation by affecting the accessibility of DNA to methyltransferases and other modifiers, which can alter gene expression without changing the DNA sequence. As H1F0 is involved in the regulation of gene expression, it could potentially influence inflammatory and immune response pathways by modulating the expression of cytokines and other immune-related genes.
H1F0 Related Diseases
The gene has been implicated in cancer, where its expression patterns can influence the behavior of cancer cells. Its re-expression in cancer cells has been shown to halt disease maintenance and relapse, suggesting a significant role in cancer progression. Additionally, H1F0 is involved in epigenetic regulation, which can affect cellular processes like self-renewal and differentiation. The gene has also been linked to primary hyperoxaluria. Furthermore, H1F0's involvement in chromatin structure makes it a candidate gene for studies on developmental disorders and other conditions influenced by gene expression and regulation.
Bioapplications of H1F0
The restoration of H1F0 levels in cancer cells has been demonstrated as an effective approach to impair tumor maintenance, making it a promising target for cancer therapy. Certain HDAC inhibitors (HDACi), such as Quisinostat, have been shown to induce the re-expression of H1F0 in various cancer cell lines and patient-derived xenografts (PDXs), indicating a potential use in selectively inhibiting cancer cell self-renewal without affecting normal stem cells. Furthermore, H1F0's role in chromatin compaction and gene regulation suggests its involvement in epigenetic mechanisms, which is another key area of bioapplication in understanding and potentially manipulating cellular processes.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Nathaniel L Burge, 2022
The linker histone H1 is a highly prevalent protein that compacts chromatin and regulates DNA accessibility and transcription. However, the mechanisms behind H1 regulation of transcription factor (TF) binding within nucleosomes are not well understood. Using in vitro fluorescence assays, researchers positioned fluorophores throughout human H1 and the nucleosome, then monitored the distance changes between H1 and the histone octamer, H1 and nucleosomal DNA, or nucleosomal DNA and the histone octamer to monitor the H1 movement during TF binding. They found that H1 remains bound to the nucleosome dyad, while the C terminal domain (CTD) releases the linker DNA during nucleosome partial unwrapping and TF binding. In addition, mutational studies revealed that a small 16 amino acid region at the beginning of the H1 CTD is largely responsible for altering nucleosome wrapping and regulating TF binding within nucleosomes.
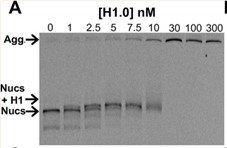
Fig1. EMSA of full length H1.0 binding to DNA-OctFRET nucleosomes.

Fig2. FRET efficiency of nucleosomes with increasing amounts of H1.0.
Case Study 2: Yabin Huang, 2024
Here, researchers disclose the critical role of interferon-related developmental regulator 1 (IFRD1) in the adaptive survival of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells during glutamine starvation. IFRD1 is induced under glutamine starvation to inhibit autophagy by promoting the proteasomal degradation of the key autophagy regulator ATG14 in a TRIM21-dependent manner. Conversely, targeting IFRD1 in the glutamine-deprived state increases autophagy flux, triggering cancer cell exhaustive death. This effect largely results from the nucleophilic degradation of histone H1.0 and the ensuing unchecked increases in ribosome and protein biosynthesis associated with globally enhanced chromatin accessibility.
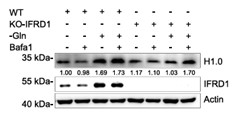
Fig3. Representative immunoblots of H1.0.

Fig4. Protein synthesis in cells expressing Flag or Flag-H1.0.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (H1F0-4528H)
Involved Pathway
H1F0 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways H1F0 participated on our site, such as Activation of DNA fragmentation factor,Apoptosis,Apoptosis induced DNA fragmentation, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with H1F0 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence | HMGA1B,HIST1H1C,HIRA,RAD50,HTATIP,TINF2,HIST1H1B,TERF1,CABIN1,POT1A |
| Formation of Senescence-Associated Heterochromatin Foci (SAHF) | ASF1A,HMGA1B,HIST1H1C,HIST1H1E,HMGA1-RS1,HIST1H1A,UBN1,EP400,HIRA,HIST1H1B |
| Activation of DNA fragmentation factor | HIST1H1C,DFFA,HIST1H1A,HMGB2,HIST1H1E,HMGB2A,HIST1H1D,HIST1H1B |
| Apoptosis | IKBKG,DBNLB,HIST1H1A,CAPN1,Casp3,HIST1H1C,TNFRSF10D,DSG1,CAPN2B,PPP3R2 |
| Apoptotic execution phase | PKP1,HIST1H1C,DBNLA,VIML,CASP6L2,ADD1,CASP8L1,HMGB2A,DBNLB,CLSPN |
| Apoptosis induced DNA fragmentation | HIST1H1C,HIST1H1D,HIST1H1B,HMGB2,HIST1H1E,DFFA,HIST1H1A,HMGB2A |
| Cellular responses to stress | WDR45L,SUZ12,ST13,EGLN2,ATG101,RNF2,DNAJC2,HSBP1A,ASF1A,KDM6B |
| Cellular Senescence | HIST3H2BB,TXN,ACD,HMGA1-RS1,BMI1B,HIST2H3C,RBBP4,TERF2,SCMH1,CDKN2D |
Protein Function
H1F0 has several biochemical functions, for example, chromatin DNA binding,poly(A) RNA binding,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by H1F0 itself. We selected most functions H1F0 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with H1F0. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| poly(A) RNA binding | CSTF2T,DDX46,SERBP1,DHX38,MRPL3,HDLBP,PARN,GLRX3,GFM1,RPL10 |
| chromatin DNA binding | NOTCH1,RELA,ACTN4,FOXO3,FOXC2,MYOD1,VAX2,PRDM14,RXRA,SMAD3 |
| protein binding | LRRC8C,ARHGEF10,SYCE3,MKNK1,ESYT2,GALR1,PYGL,MLLT1,MX1,BLM |
Interacting Protein
H1F0 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with H1F0 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of H1F0.
RAD51B;E1;par;IKBKG;lt_sv40;GRB2;NOA1;2_aha_camp;ssrna_cg
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Wade, MG; Kawata, A; et al. Methoxyacetic acid-induced spermatocyte death is associated with histone hyperacetylation in rats. BIOLOGY OF REPRODUCTION 78:822-831(2008).


