Gad2
-
Official Full Name
glutamate decarboxylase 2 (pancreatic islets and brain, 65kDa) -
Overview
Adults express two forms of glutamate decarboxylase (GAD), GAD65 and GAD67, which are encoded by different independently regulated genes. Both are expressed in most GABA containing neurons. GAD65 appears to be targeted to the membrane and nerve endings; while GAD67 is more widely distributed throughout the cell. GAD65 preferentially synthesizes GABA for vesicular release and GAD67 preferentially synthesizes cytoplasmic GABA. GAD65 is predominantly expressed in pancreatic beta cells and autoantibodies to GAD65 are strongly associated with Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IMDM). -
Synonyms
GAD2;glutamate decarboxylase 2 (pancreatic islets and brain, 65kDa);glutamate decarboxylase 2 (pancreatic islets and brain, 65kD);glutamate decarboxylase 2;GAD65;GAD-65;65 kDa glutamic acid decarboxylase;Glutamate decarboxylase-2 (pancreas);glutamate decarboxylase 65 kDa isoform;MGC161605;MGC161607
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Zebrafish
- E.coli
- Insect Cells
- Mammalian Cell
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- Insect Cell
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- HEK293T
- Mammalian cells
- GST
- His&GST
- His
- Myc&DDK
- Non
- His&S
- His&Fc&Avi
- Flag
Background
What is GAD2 protein?
GAD2 gene (glutamate decarboxylase 2) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 10 at locus 10p12. This gene encodes one of several forms of glutamic acid decarboxylase, identified as a major autoantigen in insulin-dependent diabetes. The enzyme encoded is responsible for catalyzing the production of gamma-aminobutyric acid from L-glutamic acid. A pathogenic role for this enzyme has been identified in the human pancreas since it has been identified as an autoantibody and an autoreactive T cell target in insulin-dependent diabetes. This gene may also play a role in the stiff man syndrome. The GAD2 protein is consisted of 585 amino acids and GAD2 molecular weight is approximately 65.4 kDa.
What is the function of GAD2 protein?
GAD2 is an enzyme that catalyzes the production of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) from L-glutamate, playing a key role in the synthesis of the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian central nervous system. It is predominantly expressed in GABAergic neurons within the brain, where it helps maintain the balance between neuronal excitation and inhibition. Outside the nervous system, GAD2 is also present in pancreatic islet cells, contributing to insulin secretion. The protein's expression and function are relevant to certain neurological conditions, such as Stiff Person Syndrome, and it serves as a specific marker for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.
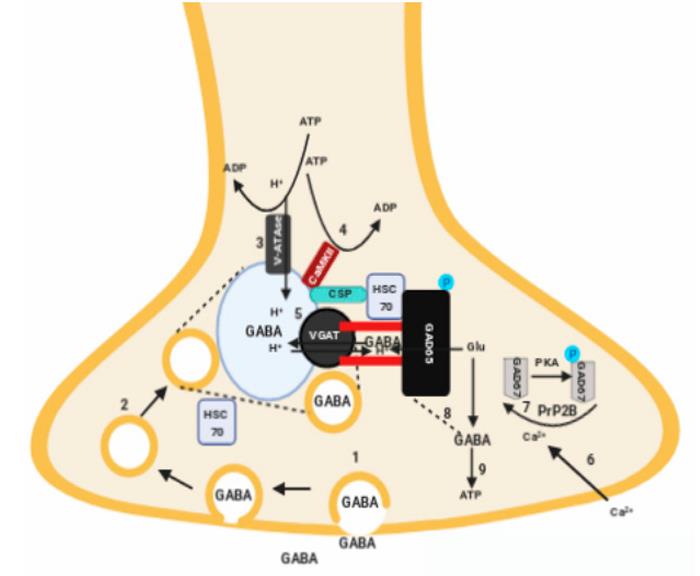
Fig1. The structural coupling between gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) synthesis and vesicular GABA transport into a synaptic vesicle (SV). (Maëlle Dade, 2020)
GAD2 related signaling pathway
GAD2 is a key enzyme in the synthesis of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. While GAD2 itself does not participate directly in signaling pathways, its activity and expression are modulated by various signaling mechanisms. For instance, calcium influx through voltage-gated calcium channels can activate GAD2, increasing GABA production and promoting inhibitory neurotransmission. Additionally, phosphorylation events and interactions with regulatory proteins can influence GAD2 stability and activity, impacting GABAergic tone. Dysregulation of these processes can lead to altered neuronal excitability and has been implicated in neurological disorders such as epilepsy and anxiety.
GAD2 related diseases
GAD2 is an enzyme crucial for the synthesis of GABA, an inhibitory neurotransmitter. Dysregulation or mutations in GAD2 can lead to various neurological disorders. For instance, reduced GAD2 activity is associated with epilepsy, characterized by excessive neuronal excitability and seizures. Conversely, increased GAD2 expression has been linked to anxiety disorders, where elevated GABA levels may contribute to heightened inhibitory tone. Additionally, GAD2 autoantibodies are implicated in stiff-person syndrome and other autoimmune neurological conditions, leading to muscle rigidity and spasms. These associations highlight the importance of GAD2 in maintaining neurotransmitter balance and neural function.
Bioapplications of GAD2
GAD2 has significant bioapplications, primarily in the diagnosis and research of neurological disorders. As a key enzyme in GABA production, it serves as a marker for GABAergic neurons, aiding in the study of brain functions and the development of treatments for related disorders. The detection of GAD2 autoantibodies is particularly useful for diagnosing conditions like Stiff Person Syndrome and insulin-dependent diabetes, where these antibodies can emerge. Moreover, GAD2 is a specific marker for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors, assisting in their identification and differentiation from other tumor types. Its role in GABA synthesis also makes it a subject of interest in research on neurodegenerative diseases and mental health disorders, highlighting its importance in both clinical practice and scientific inquiry.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Sarah H Hayes, 2024
It's widely accepted that hearing loss induces central auditory pathway plasticity, potentially contributing to conditions like tinnitus and hyperacusis. Recent studies also indicate that it could affect higher cognitive areas like the prefrontal cortex, possibly linking hearing loss to cognitive decline. The previous work using the 40-Hz auditory steady-state response revealed that noise-induced hearing loss impairs gamma phase coherence in the prefrontal cortex, not the auditory cortex. Further investigation with Golgi-Cox staining and Western blotting showed that this coherence impairment is paired with changes in dendritic morphology of pyramidal cells and reduced expression of GABAergic (GAD65) and glutamatergic (NR2B) synaptic proteins in the prefrontal cortex. In contrast, the auditory cortex exhibited increased NR2B and higher synaptic protein levels (PSD95 and synaptophysin), indicating increased excitability post-hearing loss.

Fig1. Western blot of synaptophysin, PSD-95, NR2B, GAD65 and β-tubulin in the auditory cortex of sham- and noise-exposed animals.

Fig2. Western blot of synaptophysin, PSD-95, NR2B, GAD65 and β-actin in the prefrontal cortex of sham- and noise-exposed animals.
Case Study 2: Chunmei Zeng, 2023
The study aimed to investigate the role of parvalbumin-expressing neurons in seizure termination by manipulating the parvalbumin gene in PC12 cells. Using lentiviral technology, researchers overexpressed or silenced the parvalbumin gene and examined its impact on the glutamate and GABA metabolic pathway. Immunofluorescence confirmed the neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells induced by NGF, while Western blotting and qRT-PCR validated the lentiviral-mediated modulation of parvalbumin. Here parvalbumin's expression correlates with GAD65 and GAD67, with its overexpression enhancing GAD65 and GAD67 levels, elevating GABA, and reducing glutamate. Conversely, silencing parvalbumin had the opposite effects, indicating that parvalbumin regulates the glutamate and GABA pathway by influencing GAD65 and GAD67 expression.

Fig3. Levels of GAD65 protein were analyzed after PV overexpression or silencing.
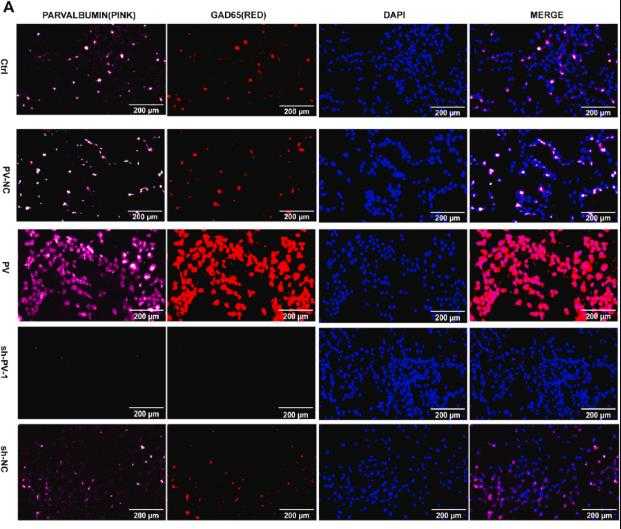
Fig4. Double immunofluorescence labelling for parvalbumin (PV) and GAD65.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (GAD2-9169H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (GAD2-6734H)
Involved Pathway
Gad2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Gad2 participated on our site, such as Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism,beta-Alanine metabolism,Taurine and hypotaurine metabolism, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Gad2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism | GLULA,ASS1,GLS2,GPT2L,RIMKLB,GOT2A,ALDH5A1,GFPT2,NAT8L,CAD |
| Taurine and hypotaurine metabolism | GAD1B,BAAT,CSAD,ADOB,CDO1,GGT5A,GGT1,ADO,GAD1,GGT5 |
| Metabolic pathways | NDUFB10,ST3GAL2,CYP2C37,GART,GBGT1L4,PI4KAA,C1GALT1B,AKR1C4,PCK1,DAO1 |
| Butanoate metabolism | ACAT2,ACSM1,OXCT2A,HADHA,BDH2,EHHADH,HMGCL,HMGCLL1,OXCT1,ACSM2 |
| GABAergic synapse | SLC38A5,GAD1,Adcy4,GNG13,GABRR1,SLC38A3,GLS2,GNG11,GNG4,GABRA4 |
| beta-Alanine metabolism | CARNS1,ALDH3A2,SMOX,ALDH1B1,SRM,ACADM,HADHAA,ALDH9A1B,GAD1,ALDH1A3 |
| Type I diabetes mellitus | IL1B,IL12B,HLA-DQB1,INS1,Il2,Fasl,IL12A,HLA-DRB3,HLA-DOB,H2-AA |
Protein Function
Gad2 has several biochemical functions, for example, glutamate binding,glutamate decarboxylase activity,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Gad2 itself. We selected most functions Gad2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Gad2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| pyridoxal phosphate binding | ACCSL,CTH,PDXDC2P,OAT,HINT2,SRR,ACCS,SPTLC3,CBSA,AGXT2L1 |
| glutamate binding | SLC1A1,GRIN2A,SLC1A3,GRIK1,CPS1,GRM7,GLUL,GCLC,GRIN1 |
| protein heterodimerization activity | HEXA,SOX5,BCL2L10,TYRO3,P4HB,TCF3A,GM5506,CREB3L3,IL12A,BCL2 |
| glutamate decarboxylase activity | GAD1B,GLUL,GAD1 |
| protein binding | TUBA3D,FAM192A,MYF5,RNF216,C4BP,HSPB1,PHF20L1,RASSF3,C18orf56,MSI2 |
Interacting Protein
Gad2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Gad2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Gad2.
ARL6IP1;AGTRAP;MAL2;TMEM159;CMTM5
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Werner, C; Haselmann, H; et al. Stiff person-syndrome IgG affects presynaptic GABAergic release mechanisms. JOURNAL OF NEURAL TRANSMISSION 122:357-362(2015).
- Zhubi, A; Chen, Y; et al. Increased binding of MeCP2 to the GAD1 and RELN promoters may be mediated by an enrichment of 5-hmC in autism spectrum disorder (ASD) cerebellum. TRANSLATIONAL PSYCHIATRY 4:-(2014).


