Folr1
-
Official Full Name
folate receptor 1 (adult) -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the folate receptor family. Members of this gene family bind folic acid and its reduced derivatives, and transport 5-methyltetrahydrofolate into cells. This gene product is a secreted protein that either anchors to membranes via a glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol linkage or exists in a soluble form. Mutations in this gene have been associated with neurodegeneration due to cerebral folate transport deficiency. Due to the presence of two promoters, multiple transcription start sites, and alternative splicing, multiple transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009] -
Synonyms
FOLR1;folate receptor 1 (adult);FBP;FOLR;folate receptor alpha;FR-alpha;KB cells FBP;folate binding protein;folate receptor, adult;adult folate-binding protein;ovarian tumor-associated antigen MOv18
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Dog
- Rat
- Cynomolgus/Rhesus macaque
- Canine
- Rhesus macaque
- Chicken
- Cynomolgus/Rhesus
- HEK293
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cell
- Human Cell
- Mammalian cells
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- His&Avi
- Fc
- Twin Strep
- Non
- Fc&Avi
- His&Fc&Avi
- Strep
- GST
Background
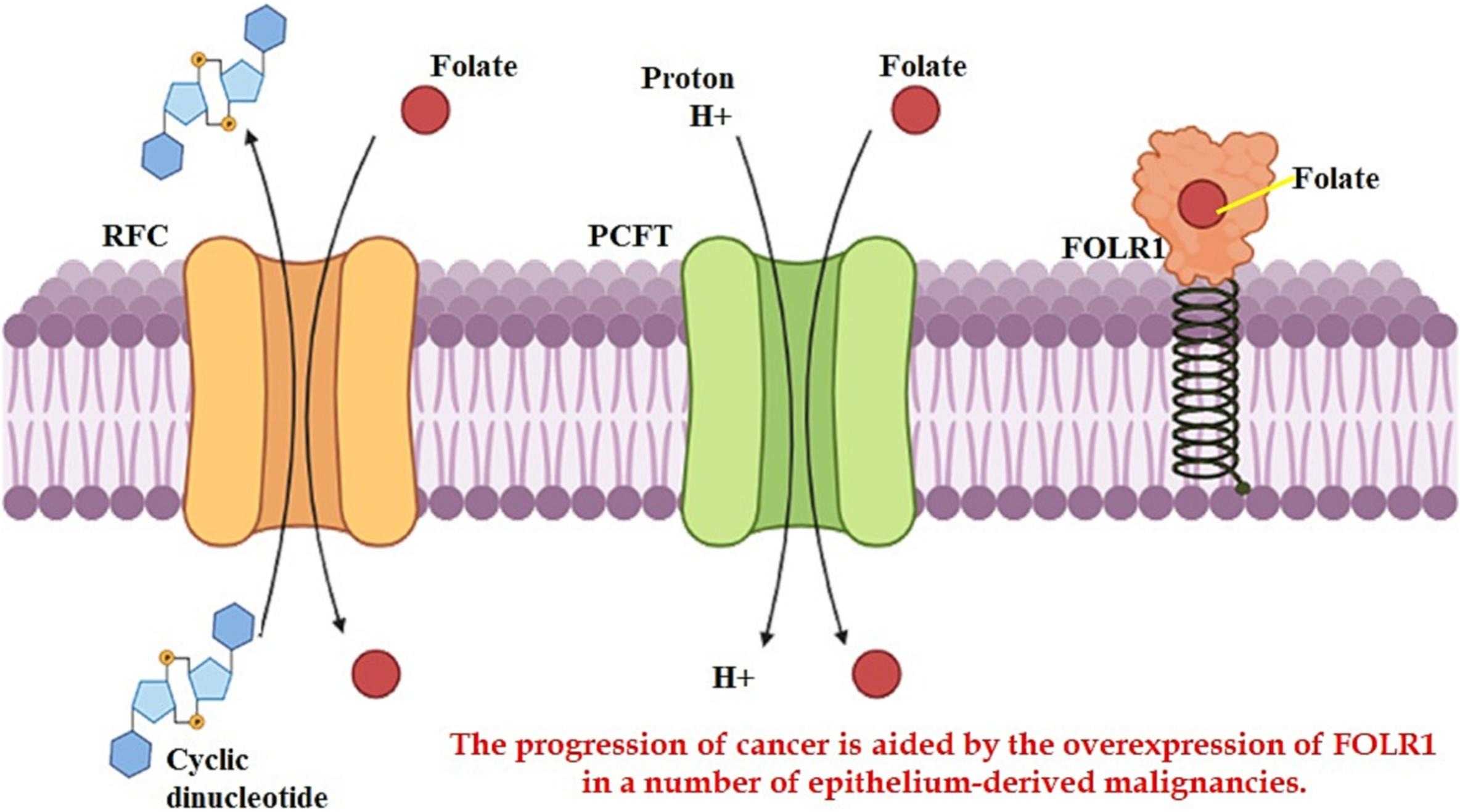
Fig1. FOLR1 plays a crucial role in the uptake and transport of folate, that is essential for cell growth and division. (Pavitra Varaganti, 2023)
What is FOLR1 protein?
FOLR1 gene (folate receptor alpha) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 11 at locus 11q13. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the folate receptor family. Members of this gene family bind folic acid and its reduced derivatives, and transport 5-methyltetrahydrofolate into cells. This gene product is a secreted protein that either anchors to membranes via a glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol linkage or exists in a soluble form. Mutations in this gene have been associated with neurodegeneration due to cerebral folate transport deficiency. The FOLR1 protein is consisted of 257 amino acids and FOLR1 molecular weight is approximately 29.8 kDa.
What is the function of FOLR1 protein?
The FOLR1 protein, also known as folate receptor 1, plays a crucial role in neural tube formation by regulating the cellular processes involved in the morphogenesis of the neural tube, such as apical constriction of neural plate cells. It interacts with proteins like CD2AP to balance endocytosis and the turnover of adherens junctions, which is essential for proper neural tube development. Additionally, FOLR1 has been implicated in the regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation, and its expression has been associated with various types of cancer, suggesting its potential as a therapeutic target. Furthermore, FOLR1 is involved in the transport of folate into cells, which is vital for one-carbon metabolism and the synthesis of nucleotides and amino acids.
FOLR1 related signaling pathway
The FOLR1-related signaling pathway is primarily associated with the cellular uptake of folate, a vital nutrient required for DNA synthesis and repair. FOLR1, also known as folate receptor 1, binds to folate with high affinity and facilitates its internalization via endocytosis. This process is crucial for maintaining intracellular folate levels, which are essential for nucleotide biosynthesis, amino acid metabolism, and cell division. Dysregulation of this pathway can lead to folate deficiency, affecting cellular functions and contributing to conditions such as megaloblastic anemia and neural tube defects. Understanding the intricacies of FOLR1-mediated folate transport is important for developing targeted therapies in cancers that overexpress FOLR1, as well as for improving folate delivery in conditions of deficiency.
FOLR1 related diseases
The FOLR1-related diseases primarily encompass conditions arising from disruptions in folate uptake and utilization, which are crucial for DNA synthesis, repair, and cellular function. Overexpression of FOLR1 is associated with various cancers, including ovarian, lung, and kidney cancers, where it facilitates the increased uptake of folate to support rapid tumor cell proliferation. Conversely, mutations or deficiencies in FOLR1 can lead to impaired folate transport, resulting in megaloblastic anemia, a condition characterized by abnormally large red blood cells due to disrupted DNA synthesis. Additionally, insufficient folate levels during pregnancy can cause neural tube defects in the developing fetus. Thus, understanding the role of FOLR1 in these diseases is vital for developing targeted therapies and preventative measures.
Bioapplications of FOLR1
The bioapplications of FOLR1 are primarily focused on its role in targeted cancer therapy and as a biomarker for certain malignancies. Given its high affinity for folate, FOLR1 is exploited in drug delivery systems to selectively target and treat cancer cells that overexpress this receptor. Conjugates of FOLR1-targeting ligands with cytotoxic drugs or imaging agents enhance the specificity and efficacy of cancer treatments while minimizing off-target effects. Additionally, FOLR1 expression levels serve as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in various cancers, aiding in the early detection and monitoring of disease progression. These applications highlight the therapeutic potential of manipulating FOLR1 pathways for improved cancer management outcomes.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Olga A Balashova, 2024
Folate receptor 1 (FOLR1) is essential for neural tube formation, as its knockdown leads to neural tube defects (NTDs) in both human neural organoids and Xenopus laevis embryos, while folate signaling and interaction with CD2-associated protein regulate apical endocytosis and C-cadherin turnover, highlighting a non-metabolic mechanism of folate's action in preventing NTDs.

Fig1. FOLR1 localizes to the apical surface of neural cells surrounding the neural tube-like structure lumen.

Fig2. Neural plate stage Xenopus laevis embryos were processed for co-immunoprecipitation (IP) assays.
Case Study 2: Hailong Liu. Loh, 2017
Medulloblastoma, the most common malignant brain tumor in children, shows upregulated Folr1 expression, which correlates with Ki-67 and MMP9 levels, pathological subtypes, and serum Folr1 levels. Serum Folr1 can predict histological subgroups with sensitivity and specificity, and its high expression is an independent prognostic factor. Targeted Folr1 therapy shows potential in reducing tumor growth and metastasis in medulloblastoma.

Fig3. Immunoblotting analysis of the Folr1 levels in human MB specimens (up) and tumor cells (down).

Fig4. Tumor volume curve showed that the xenograft in Folr1-Ara-C group progressed slowly.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (FOLR1-4419H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (FOLR1-241H)
Involved Pathway
Folr1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Folr1 participated on our site, such as Endocytosis, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Folr1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Endocytosis | ASAP2B,RHOAD,PSD,CXCR4A,FGFR3,RAB35B,CHMP4B,RHOAA,FGFR2,NEDD4 |
Protein Function
Folr1 has several biochemical functions, for example, drug binding,folic acid binding,folic acid transporter activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Folr1 itself. We selected most functions Folr1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Folr1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| folic acid transporter activity | SLC25A32,SLC46A1,DAAM2,SLC19A2,FOLR2,SLC19A1 |
| methotrexate binding | DAAM2,FOLR2,DHFR |
| drug binding | PDXK,DRD2,CHRNB3,DHFR,P2RX2,SRP54A,CHRNB4,MT2A,GPR30,MT3 |
| receptor activity | MED30,TNFRSF11A,CD93,SLC20A2,MED24,TNFRSF6B,CSF3R,NLGN2A,ABP1,UBXN6 |
| folic acid binding | FOLR2,MTHFS,TYMS,GNMT,DHFR,FOLR3,DMGDH,SLC46A1,FTCD,DAAM2 |
Interacting Protein
Folr1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Folr1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Folr1.
ganglioside_gm1;Cdk1;Cbx1;Cep76;Cep192;Trim69;Poc1b;Dync1h1;CUL3;NCAPH2;IRAK3;cona_canen
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Wen, YF; Graybill, WS; et al. Immunotherapy Targeting Folate Receptor Induces Cell Death Associated with Autophagy in Ovarian Cancer. CLINICAL CANCER RESEARCH 21:448-459(2015).
- Kabel, M; Madore, J; et al. Evidence for a time-dependent association between FOLR1 expression and survival from ovarian carcinoma: implications for clinical testing. An Ovarian Tumour Tissue Analysis consortium study. BRITISH JOURNAL OF CANCER 111:2297-2307(2014).


