FOXA2
-
Official Full Name
forkhead box A2 -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of the forkhead class of DNA-binding proteins. These hepatocyte nuclear factors are transcriptional activators for liver-specific genes such as albumin and transthyretin, and they also interact with chromatin. Similar family members in mice have roles in the regulation of metabolism and in the differentiation of the pancreas and liver. This gene has been linked to sporadic cases of maturity-onset diabetes of the young. Transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008] -
Synonyms
FOXA2;forkhead box A2;HNF3B;TCF3B;hepatocyte nuclear factor 3-beta;HNF-3B;TCF-3B;HNF-3-beta;forkhead box protein A2;transcription factor 3B;hepatic nuclear factor-3-beta;hepatocyte nuclear factor 3, beta
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Zebrafish
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cell
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Non
- His
- His&Fc&Avi
- GST
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FOXA2-127H | Recombinant Human FOXA2 | E.coli | Human | Non |
|
|
| FOXA2-2383R | Recombinant Rat FOXA2 Protein | Mammalian Cell | Rat | His |
|
|
| FOXA2-28944TH | Recombinant Human FOXA2 | E.coli | Human | Non | Full L. 1-457 a.a. |
|
| FOXA2-5976M | Recombinant Mouse FOXA2 Protein | Mammalian Cell | Mouse | His |
|
|
| FOXA2-6334C | Recombinant Chicken FOXA2 | Mammalian Cell | Chicken | His |
|
|
| FOXA2-8588Z | Recombinant Zebrafish FOXA2 | Mammalian Cell | Zebrafish | His |
|
|
| FOXA2-6163HCL | Recombinant Human FOXA2 293 Cell Lysate | HEK293 | Human | Non |
|
|
| Foxa2-1510M | Recombinant Mouse Foxa2 Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Mouse | His | Met1-Ser459 |
|
| FOXA2-2039R | Recombinant Rat FOXA2 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Rat | His&Fc&Avi |
|
|
| FOXA2-2039R-B | Recombinant Rat FOXA2 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Rat |
|
||
| FOXA2-3314M | Recombinant Mouse FOXA2 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | His&Fc&Avi |
|
|
| FOXA2-3314M-B | Recombinant Mouse FOXA2 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
||
| FOXA2-4433H | Recombinant Human FOXA2 Protein, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST |
|
|
| FOXA2-5046HF | Recombinant Full Length Human FOXA2 Protein, GST-tagged | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | GST | Full L. 457 amino acids |
|
Background
What is FOXA2 protein?
FOXA2 gene (forkhead box A2) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 20 at locus 20p11. This gene encodes a member of the forkhead class of DNA-binding proteins. These hepatocyte nuclear factors are transcriptional activators for liver-specific genes such as albumin and transthyretin, and they also interact with chromatin. Similar family members in mice have roles in the regulation of metabolism and in the differentiation of the pancreas and liver. This gene has been linked to sporadic cases of maturity-onset diabetes of the young. The FOXA2 protein is consisted of 457 amino acids and FOXA2 molecular weight is approximately 48.3 kDa.
What is the function of FOXA2 protein?
FOXA2 is crucial for embryonic development, particularly in the formation of the notochord and the development of multiple endoderm-derived organ systems such as the liver, pancreas, and lungs. FOXA2 acts as a 'pioneer' factor, opening the compacted chromatin for other proteins through interactions with nucleosomal core histones, thereby replacing linker histones at target enhancer and/or promoter sites. It is involved in glucose homeostasis by regulating the expression of genes important for glucose sensing in pancreatic beta-cells. FOXA2 plays a role in the regulation of fat metabolism and binds to the fibrinogen beta promoter, contributing to IL6-induced fibrinogen beta transcriptional activation.
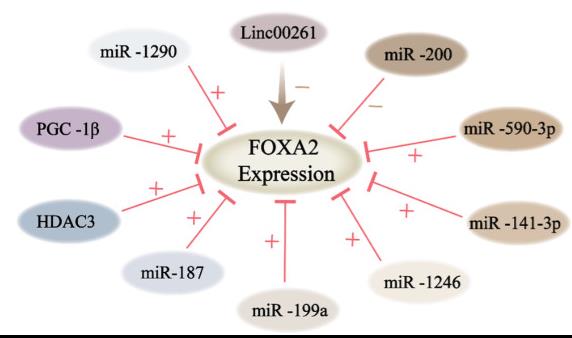
Fig1. Schematic representation of targeting upstream regulators of FOXA2 for cancer therapy. (Na Liu, 2024)
FOXA2 Related Signaling Pathway
FOXA2 controls glucose and lipid metabolism by regulating multiple target genes in the liver, pancreas, and adipose tissue, playing a role in glucose homeostasis. FOXA2 is implicated in the regulation of cell proliferation and migration, which are important for processes like organ development and tumor progression. FOXA2 is thought to act as a 'pioneer' factor, opening compacted chromatin to allow other transcription factors access, thereby regulating gene expression. FOXA2 is involved in the regulation of genes important for glucose sensing in pancreatic beta cells. FOXA2 interacts with nuclear receptors like the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ) and androgen receptor (AR) to modulate hormone signaling pathways.
FOXA2 Related Diseases
In the field of cancer, FOXA2 is closely related to the progression, metastasis and prognosis of malignant tumors such as prostate cancer, breast cancer and liver cancer, and it plays an important role in the proliferation, invasion and metabolism of tumor cells. In addition, the function of FOXA2 is critical in the regulation of insulin secretion in diabetes, and its abnormality may lead to an imbalance in blood sugar control. In neurodegenerative diseases, changes in FOXA2 expression may be associated with dysfunction of dopaminergic neurons, involving conditions such as Parkinson's disease. FOXA2 is also involved in immune regulatory processes in autoimmune diseases and plays an important role in liver development and function, which may play a central role in the pathogenesis of liver disease. In terms of rare diseases, FOXA2 has been linked to endocrine disorders such as hypopituitarism.
Bioapplications of FOXA2
FOXA2's role in regulating insulin secretion and glucose metabolism makes it a potential target for diabetes treatment. By regulating FOXA2 activity, it may help improve the function of islet beta cells, thereby controlling blood sugar levels. The regulatory mechanisms of FOXA2 provide new directions for drug development, especially in the development of drugs that can interfere with FOXA2 function to treat related diseases. Variations in FOXA2 expression levels in certain diseases make it a potential biomarker for disease diagnosis, prognostic assessment, and therapeutic response monitoring. FOXA2's role in cell fate determination and transdifferentiation provides an important transcription factor for cell reprogramming and tissue engineering, helping to generate the cell types needed to repair or replace damaged tissue.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Julio Cesar Aguila, 2014
Inductive differentiation protocols can generate midbrain dopamine neurons but result in heterogeneous cell mixtures. Therefore, selection strategies are necessary to obtain uniform dopamine cell populations. Here, researchers developed a selection approach using lentivirus vectors to express green fluorescent protein under the promoter region of FOXA2. They first validated the specificity of the vectors in human cell lines against a promoterless construct. And then selected FOXA2-positive neural progenitors from several human pluripotent stem cell lines, which demonstrated a gene expression profile typical for the ventral domain of the midbrain and floor plate, but failed to enrich for dopamine neurons. To investigate whether this was due to the selection approach, they overexpressed FOXA2 in neural progenitors derived from human pluripotent stem cell lines. FOXA2 forced expression resulted in an increased expression of floor plate but not mature neuronal markers. Furthermore, selection of the FOXA2 overexpressing fraction also failed to enrich for dopamine neurons.
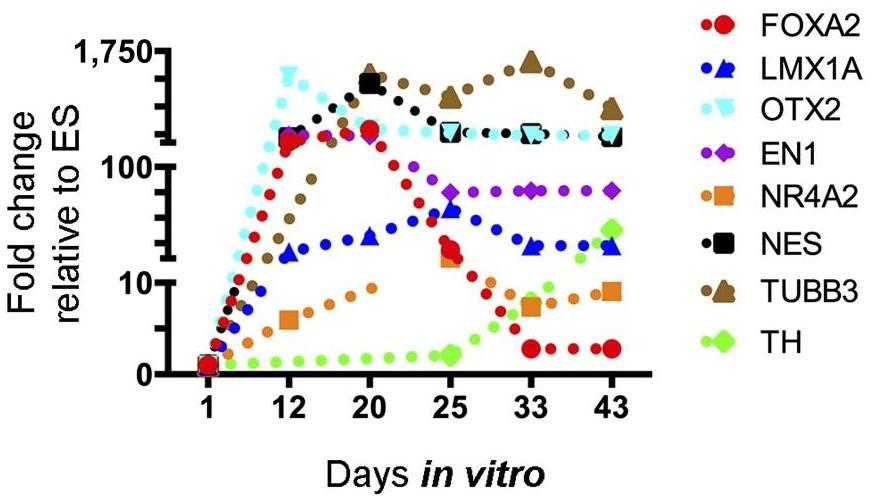
Fig1. Transcriptional profile by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction shows early induction of FOXA2 and the region-specific transcription factors En1 and OTX2.
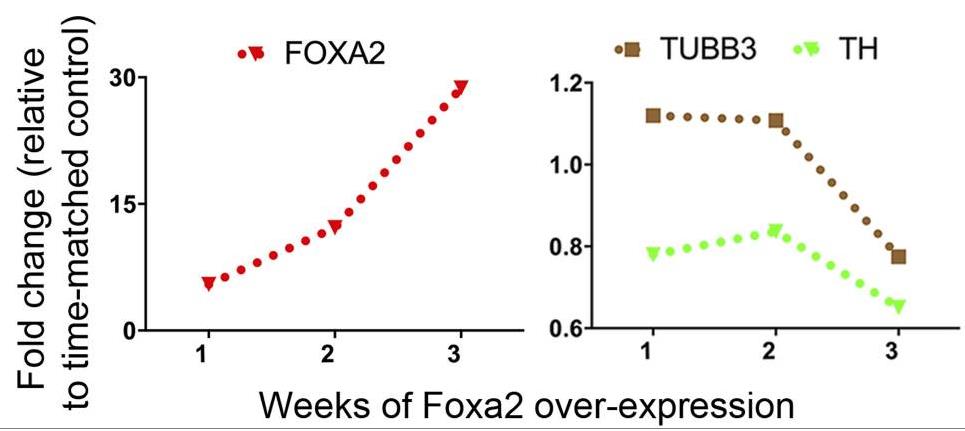
Fig2. qPCR analysis showed a persistent increase of FOXA2 and a concomitant decline in TH and TUBB3.
Case Study 2: Sang-Hoon Yi, 2014
Understanding how dopamine (DA) phenotypes are acquired in midbrain DA (mDA) neuron development is important for bioassays and cell replacement therapy for mDA neuron-associated disorders. Here, researchers demonstrate a feed-forward mechanism of mDA neuron development involving Nurr1 and Foxa2. Nurr1 acts as a transcription factor for DA phenotype gene expression. However, Nurr1-mediated DA gene expression was inactivated by forming a protein complex with CoREST, and then recruiting histone deacetylase 1 (Hdac1), an enzyme catalyzing histone deacetylation, to DA gene promoters. Co-expression of Nurr1 and Foxa2 was established in mDA neuron precursor cells by a positive cross-regulatory loop. In the presence of Foxa2, the Nurr1-CoREST interaction was diminished (by competitive formation of the Nurr1-Foxa2 activator complex), and CoREST-Hdac1 proteins were less enriched in DA gene promoters.
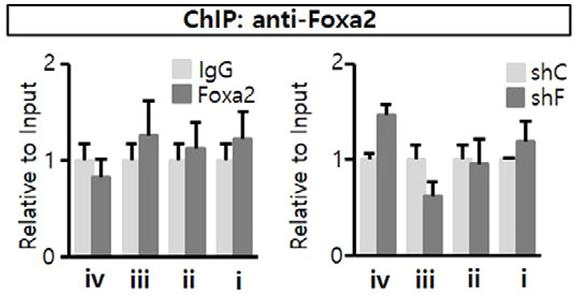
Fig3. ChIP analyses for Foxa2 protein enrichment in the Nurr1 promoter region.

Fig4. IP assays for physical interactions between Foxa2 and Nurr1 proteins.
Quality Guarantee
.
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (FOXA2-4433H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (Foxa2-1510M)
Involved Pathway
FOXA2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways FOXA2 participated on our site, such as Maturity onset diabetes of the young, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with FOXA2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Maturity onset diabetes of the young | NKX6-1,NEUROD1,FOXA3,NKX6,PDX1,INS2,SLC2A2,PAX6,HES1,RFX6 |
Protein Function
FOXA2 has several biochemical functions, for example, DNA binding,RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific DNA binding,RNA polymerase II transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by FOXA2 itself. We selected most functions FOXA2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with FOXA2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| RNA polymerase II transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | FOXE3,FOXJ1A,FLI1A,ATF4,FOXN2B,GATA6,TFDP1A,ATF5A,SP3A,ETV6 |
| DNA binding | ZNF43,AHRRB,RFX5,ARID1A,HIF1AL,EBF4,HIST1H2B8,ZNF434,H2AFVA,POU2F1B |
| RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific DNA binding | ATF7,HIST2H3A,JUNBA,ZNF257,MEF2B,FEZF2,ARID3B,RELA,NCOA2,ZNF718 |
| transcription factor binding | NFATC4,MDFIC,TCF3,LCOR,NFATC2,CHCHD2,ARNT,WWP2,HES2,E2F2 |
| transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | NFIA,SOX1,RFX2,FLI1A,HLFB,MTA3,FOXA3,EGR2A,NKX2-5,NR2F1B |
| protein domain specific binding | WNT3,HSPA5,STX1A,GABRR2,ZBTB16,CNTLN,NFASC,NEFL,YWHAE1,PRKCI |
| transcription regulatory region DNA binding | CITED1,ARRB1,CTCF,TP53,TRP63,ZNF174,MZF1,TBL1X,ERBB4,PAX8 |
Interacting Protein
FOXA2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with FOXA2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of FOXA2.
FOXA1
Resources
Research Area
Hepatic Progenitor Cell Transcription FactorsHepatic and Pancreatic Progenitor Cell Transcription Factors
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Liang, S; Li, HC; et al. Pulmonary endoderm, second heart field and the morphogenesis of distal outflow tract in mouse embryonic heart. DEVELOPMENT GROWTH & DIFFERENTIATION 56:276-292(2014).
- Reers, S; Pfannerstill, AC; et al. Stem cell profiling in head and neck cancer reveals an Oct-4 expressing subpopulation with properties of chemoresistance. ORAL ONCOLOGY 50:155-162(2014).


