FGF19
-
Official Full Name
fibroblast growth factor 19 -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family. FGF family members possess broad mitogenic and cell survival activities, and are involved in a variety of biological processes including embryonic development cell growth, morphogenesis, tissue repair, tumor growth and invasion. This growth factor is a high affinity, heparin dependent ligand for FGFR4. Expression of this gene was detected only in fetal but not adult brain tissue. Synergistic interaction of the chick homolog and Wnt-8c has been shown to be required for initiation of inner ear development. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
FGF19;fibroblast growth factor 19;FGF-19
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Chicken
- Rat
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cell
- HEK293T
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Mammalian cells
- Non
- His
- Flag
- Fc
- Myc&DDK
- GST
- His&Fc&Avi
Background
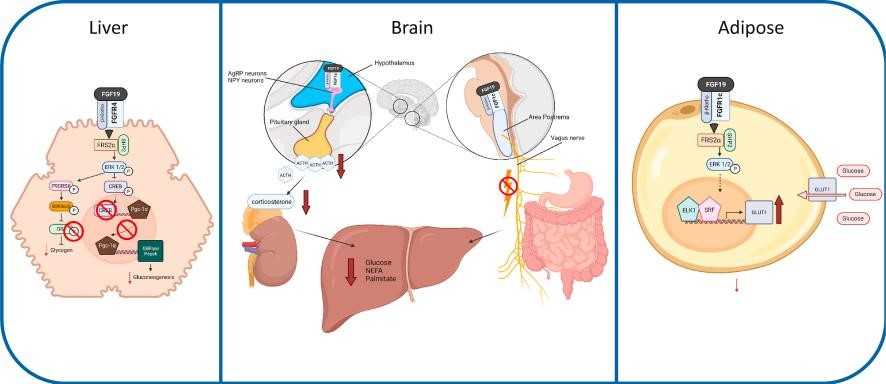
Fig1. FGF19 regulation of glucose homeostasis in the liver, brain, and adipose tissue. (Greg Guthrie, 2022)
What is FGF19 Protein?
FGF19 is a protein in humans encoded by the FGF19 gene, playing a key role in managing bile acid production and impacting glucose and lipid metabolism. It's part of the fibroblast growth factor family, known for supporting cell survival and growth. This protein functions a bit like a hormone, working mainly in the ileum in response to bile acid absorption and signaling through FGFR4 in the liver to keep bile acid synthesis under control. Although it's crucial for normal metabolic processes, its overactivity has been linked to cancer progression, showing up a lot in cancers like liver and colon cancer. So, while it has vital roles, a spike in FGF19 isn't always a good thing, especially in the context of cancer.
What is the Function of FGF19 Protein?
FGF19 is a protein that's like a metabolic helper in our bodies. It's a hormone regulating the production of bile acids, which are crucial for digesting fats, and it also affects how we manage glucose and lipids, playing a key role in maintaining our energy balance. FGF19 kicks in by signaling through a pathway involving FGFR4, usually after we've absorbed bile acids. This protein isn't just about digestion, though. It's also linked to a bunch of other processes like how we grow and develop and it even has a hand in some diseases. In certain cancers, FGF19 tends to be more active, which isn't always a good thing because it might make cancer cells grow.
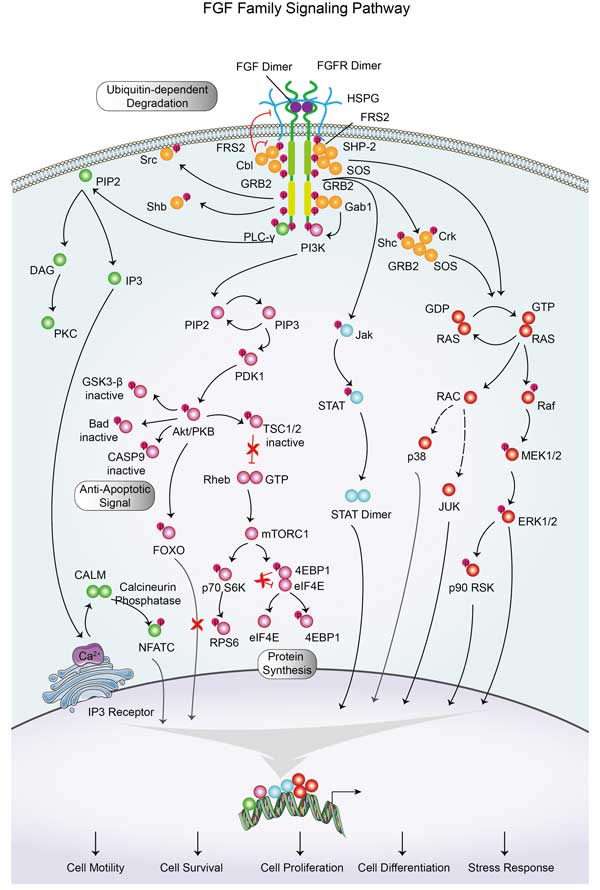
FGF19 Related Signaling Pathway
FGF19 is pretty crucial when it comes to signaling in the body. It interacts mainly with the FGFR4 receptor and the Klotho-β protein in the liver. This interaction plays a key role in controlling bile acid levels by kicking in the suppression of CYP7A1, a major enzyme in bile acid synthesis. Aside from managing bile, FGF19 signaling gets involved in glucose and lipid metabolism, contributing to overall energy management. Moreover, FGF19's signaling pathway has been linked to cancer progression in several studies, especially in liver cancer, where it seems to promote tumor growth when present in excess.
FGF19 Related Diseases
FGF19 is linked to several health issues. When it's not at the right level, it can lead to chronic diarrhea due to excessive bile acids, especially when absorption is messed up like after certain intestinal surgeries. Low levels are often seen in those with metabolic problems like non-alcoholic fatty liver disease or insulin resistance. On the flip side, when there's too much FGF19 activity, it's associated with the growth of tumors in various cancers such as liver, breast, and lung cancer. This dual role makes it a focus for research into both metabolic disorders and cancer therapy.
Bioapplications of FGF19
Recombinant FGF19 protein is quite versatile and finds its way into various fields like research and industrial production. In scientific research, it's used to explore its role in metabolism, especially how it regulates bile acids, glucose, and lipids. This helps in studying diseases like liver disorders and metabolic syndromes. On the industrial side, it's tapped into drug development, particularly for creating therapies targeting its pathway or effects. Plus, it can be part of cosmetic formulations, aiming to influence skin health and vitality. Overall, recombinant FGF19 is a handy tool in both understanding biological processes and developing new products.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Hao Chen, 2023
Fibroblast growth factor 19, or FGF19, is becoming a key player in tackling metabolic bone issues, but we're still figuring out how it affects cell growth in the skeletal system. We found that FGF19 can slow down chondrocyte (those are cartilage cells) growth by halting them in the G2 phase of the cell cycle. It works its magic through an accessory protein called β-Klotho, which helps FGF19 hook up with its receptor. This stalling process involves tweaking some key molecules like cdk1/cyclinb1, chk1, and gadd45a. Turns out, the FGFR4 receptor is crucial here—FGF19 needs it to pause cell cycling. It's all about the p38/MAPK signaling pathway; when FGFR4's blocked, p38 signaling takes a hit, even if FGF19 is around. Blocking p38 also cuts down FGF19's hold on the cell cycle, letting cdk1 and cyclinb1 bounce back and dialing down chk1 and gadd45a expressions that FGF19 otherwise cranks up in chondrocytes.

Fig1. CCK-8 assay showing the changes in cell viability of chondrocytes induced by 200 ng/ml FGF19.
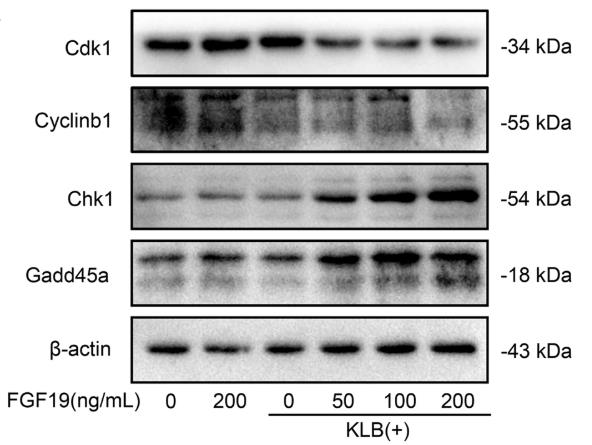
Fig2. Western blot showing the expression change of cdk1, cylinb1, chk1 and gadd45a in chondrocytes stimulated with 0, 50, 100 and 200 ng/ml FGF19.
Case Study 2: Yingcheng Wei, 2024
Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is tough to treat and usually has a poor outcome. While lenvatinib is known to work well on various solid tumors, its impact on CCA is less explored. Studies in lab settings showed lenvatinib slowing CCA cell growth, spread, and triggering cell death by targeting FGF19 and blocking the PI3K/AKT pathway. Decreasing FGF19 made lenvatinib work better, while increasing it did the opposite. Adding an AKT inhibitor further helped lenvatinib block CCA. Tests on mice confirmed lenvatinib curbed CCA growth by reducing certain protein markers.

Fig3. The expression levels of FGF19 were examined by western blotting.

Fig4. The expression levels of p-PI3K and p-AKT in CCA cells with combined OE-FGF19/si-FGF19 and lenvatinib treatment were examined by western blotting
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (FGF19-238H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (FGF19-3206H)
Involved Pathway
FGF19 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways FGF19 participated on our site, such as MAPK signaling pathway,Ras signaling pathway,Rap signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with FGF19 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Rap signaling pathway | ITGAL,Kitl,APBB1IP,VAV2,ITGB2,AKT2,PLCB2,GRIN1,PRKD2,PRKCI |
| PIK-Akt signaling pathway | Pdgfa&Pdgfb,FGFR2,LPAR5,PKN1,Kitl,RELA,ITGB8,PDGFRB,FLT4,IFNA16 |
| Pathways in cancer | PLD1,EP300,FZD10,CCDC6,CCNE2,LPAR2,MSH3,Kitl,MMP1A,FZD1 |
| MAPK signaling pathway | Fgf15,FGF1,MAP3K3,MAP2K3,FGF7,PLA2G4F,TGFB2,FGF1A,CACNA2D1,NGF |
| Ras signaling pathway | SOS1,KITLG,PLCE1,GNG8,SHC3,BCL2L1,SHC1,FGF12,PLA2G4C,PGF |
| Regulation of Actin Cytoskeleton | ITGA3B,LIMK2,PDGFRB,CYFIP1,FGF16,ARPC5LB,ACTN2,PPP1R12B,PAK1,ITGB8 |
| Melanoma | Fgf15,BRAF,PIK3R2,FGF7,FGF1,NRAS,MAPK3,FGF6,FGF5,IGF1R |
Protein Function
FGF19 has several biochemical functions, for example, protein binding,protein kinase binding,protein phosphatase binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by FGF19 itself. We selected most functions FGF19 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with FGF19. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein phosphatase binding | AP3B1,JUP,PIK3R2,ANAPC5,CTNNB1,SHOC2,MAP3K5,RPA2,ERBB2,DLG3 |
| protein binding | MASP1,CASK,POMP,MRPS27,LDHA,SRRT,DYSFIP1,PNRC2,RAB33A,FEZ1 |
| protein kinase binding | CCNT2B,PDCD10,TOM1L1,BCAR1,SV2A,ADAM10,BCL2L1,CNPPD1,CALM,PPP1R12A |
Interacting Protein
FGF19 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with FGF19 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of FGF19.
FGF19 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Walters, JRF; et al. Bile acid diarrhoea and FGF19: new views on diagnosis, pathogenesis and therapy. NATURE REVIEWS GASTROENTEROLOGY & HEPATOLOGY 11:426-434(2014).
- Kong, B; Guo, GL; et al. Soluble Expression of Disulfide Bond Containing Proteins FGF15 and FGF19 in the Cytoplasm of Escherichia coli. PLOS ONE 9:-(2014).