EIF6
-
Official Full Name
eukaryotic translation initiation factor 6 -
Overview
Eukaryotic initiation factor 6 (eIF6) is reqiured for the 60S ribosomal subunit assembly in the nucleolus. In the cytoplasm, this protein is bound to 60S ribosome subunits and prevents them from joining 40S ribosome subunits to form 80S ribosomes. eIF6 is -
Synonyms
EIF6;eukaryotic translation initiation factor 6;EIF3A, integrin beta 4 binding protein , ITGB4BP;b(2)gcn;p27BBP;B4 integrin interactor;p27 beta-4 integrin-binding protein;eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3A;CAB;EIF3A;eIF-6;ITGB4BP;p27
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Rat
- Chicken
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cell
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- HEK293T
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His
- T7
- Non
- His&Fc&Avi
- Myc&DDK
Background
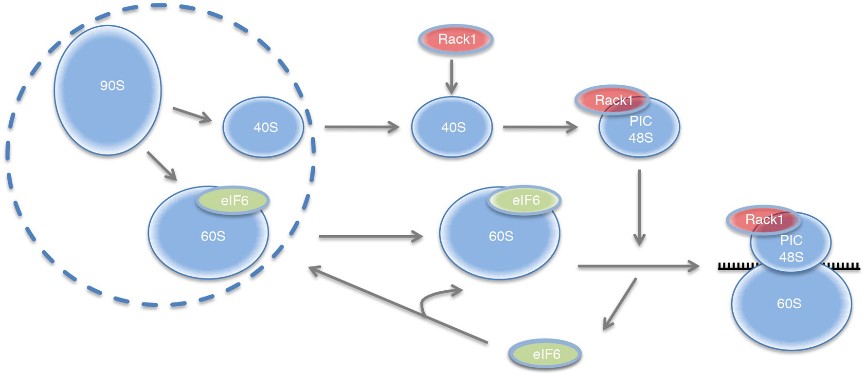
Fig1. eIF6 in ribosome biogenesis and translational control. (Daniela Brina, 2014)
What is EIF6 protein?
EIF6 (eukaryotic translation initiation factor 6) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 20 at locus 20q11. Hemidesmosomes are structures which link the basal lamina to the intermediate filament cytoskeleton. An important functional component of hemidesmosomes is the integrin beta-4 subunit (ITGB4), a protein containing two fibronectin type III domains. The protein encoded by this gene binds to the fibronectin type III domains of ITGB4 and may help link ITGB4 to the intermediate filament cytoskeleton. The encoded protein, which is insoluble and found both in the nucleus and in the cytoplasm, can function as a translation initiation factor and prevent the association of the 40S and 60S ribosomal subunits. The EIF6 protein is consisted of 245 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 26.6 kDa.
What is the function of EIF6 protein?
EIF6 is a protein that plays a role in eukaryotic translation initiation. The function of EIF6 is mainly involved in the regulation of ribosome biosynthesis and protein synthesis. It is involved in ribosome assembly by interacting with the 60S subunit, especially in eukaryotic cells, where EIF6 is essential for the correct folding and stability of the 60S subunit.
EIF6 Related Signaling Pathway
EIF6 protein is an important translational regulator, mainly involved in protein synthesis. It plays a role in the following two key signaling pathways: First, EIF6 can bind to the large subunit of ribosome and inhibit protein synthesis during cellular stress response, such as heat shock and oxidative stress. Second, in cell cycle regulation, EIF6 affects the cell cycle process by regulating the translation of specific genes. In addition, EIF6 may also be involved in other signaling pathways, such as apoptosis and growth factor signaling, but the specific mechanism needs to be further studied.
EIF6 Related Diseases
The abnormal expression of EIF6 protein is associated with many diseases, especially with the occurrence and development of tumors. EIF6 expression is increased in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and its high expression is associated with malignant progression of the tumor and can be used as an independent risk factor for prognosis in HCC patients. In addition, EIF6 expression levels have also been found to be abnormally elevated in cutaneous melanoma, which may serve as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker. EIF6 is also associated with malignant behavior in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), promoting tumor proliferation and invasion by activating the AKT signaling pathway. In gastric cancer, EIF6 is also a promising diagnostic and prognostic biomarker. Abnormalities in the EIF6 gene have also been linked to disorders such as Shwachman-Diamond syndrome and Bowen-Conradi syndrome. Abnormal functioning of EIF6 may also be associated with other types of cancer and pathological conditions, such as colorectal cancer, head and neck tumors, and malignant mesothelioma.
Bioapplications of EIF6
Due to its abnormal expression in a variety of cancers, EIF6 has become an important biomarker for cancer diagnosis and prognosis assessment. For example, in cutaneous melanoma and hepatocellular carcinoma, high expression levels of EIF6 are associated with reduced survival in patients, so detection of EIF6 may help in early diagnosis of the disease and monitoring of treatment response. In addition, EIF6 is a potential target for cancer therapy, and drug development targeting EIF6 may be effective in inhibiting tumor growth and metastasis. In basic research, functional studies of EIF6 contribute to a deeper understanding of the molecular mechanisms of eukaryotic translation initiation, which may in turn reveal new regulatory networks and signaling pathways.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Courtney F Jungers, 2020
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 6 (eIF6) is essential for the synthesis of 60S ribosomal subunits and for regulating the association of 60S and 40S subunits. A mechanistic understanding of how eIF6 modulates translation in response to stress, specifically starvation-induced stress, is lacking. The researchers here show a novel mode of eIF6 regulation by glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) that is predominantly active in response to serum starvation. Both GSK3α and GSK3β phosphorylate human eIF6. Multiple residues in the C terminus of eIF6 are phosphorylated by GSK3 in a sequential manner. In response to serum starvation, eIF6 accumulates in the cytoplasm, and this altered localization depends on phosphorylation by GSK3. Disruption of eIF6 phosphorylation exacerbates the translation inhibitory response to serum starvation and stalls cell growth.
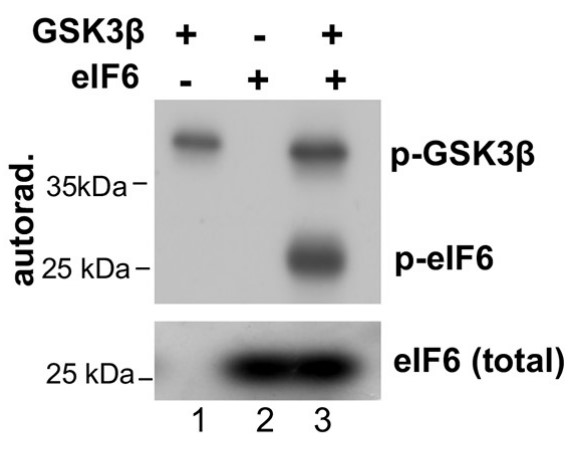
Fig1. In vitro kinase reactions were carried out in the presence and absence of recombinant full-length human eIF6 and GSK3β.
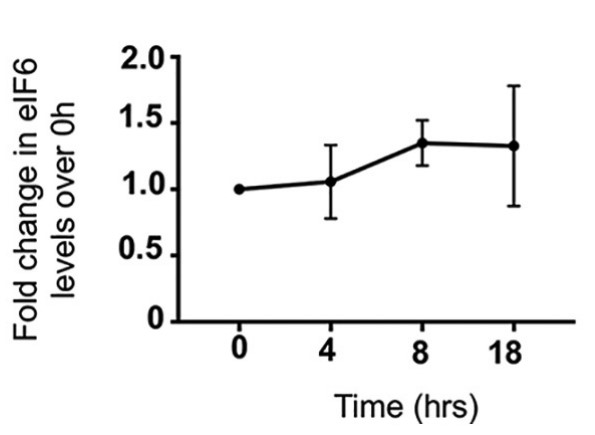
Fig2. Total eIF6 protein levels were quantitated.
Case Study 2: Elisa Pesce, 2020
Eukaryotic initiation factor 6 (eIF6) is necessary for the nucleolar biogenesis of 60S ribosomes. However, most of eIF6 resides in the cytoplasm, where it acts as an initiation factor. eIF6 is necessary for maximal protein synthesis downstream of growth factor stimulation. eIF6 is an antiassociation factor that binds 60S subunits, in turn preventing premature 40S joining and thus the formation of inactive 80S subunits. Here, the researchers exploited and improved our assay for eIF6 binding to ribosomes (iRIA) in order to screen for modulators of eIF6 binding to the 60S. Three compounds, eIFsixty-1 (clofazimine), eIFsixty-4, and eIFsixty-6 were identified and characterized. All three inhibit the binding of eIF6 to the 60S in the micromolar range. eIFsixty-4 robustly inhibits cell growth, whereas eIFsixty-1 and eIFsixty-6 might have dose- and cell-specific effects. Puromycin labeling shows that eIF6ixty-4 is a strong global translational inhibitor, whereas the other two are mild modulators. Polysome profiling and RT-qPCR show that all three inhibitors reduce the specific translation of well-known eIF6 targets. In contrast, none of them affect the nucleolar localization of eIF6.
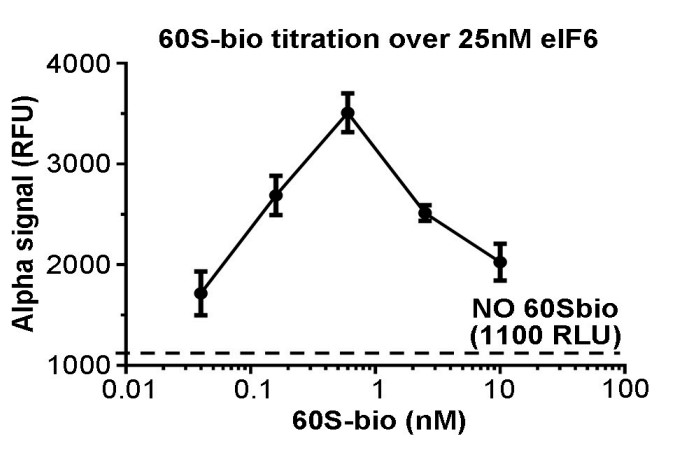
Fig3. Optimization of the 60S-bio signal against a fixed concentration of eIF6.
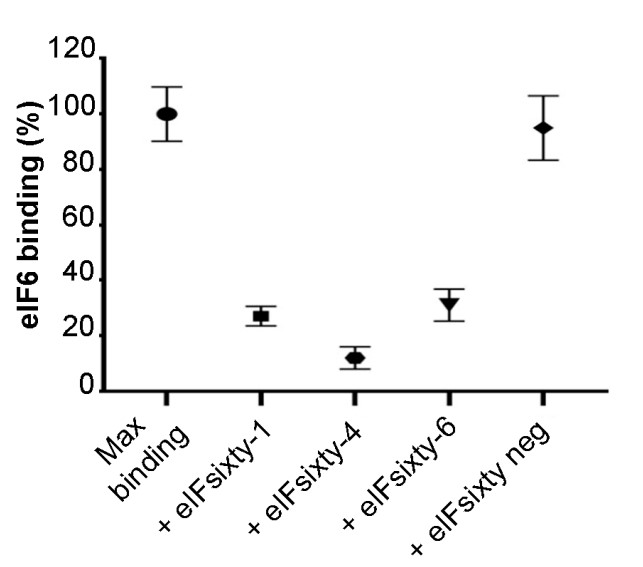
Fig4. Relative eIF6–60S binding upon eIFsixty-i compounds (eIFsixty-1, eIFsixty-4, and eIFsixty-6) addition.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (EIF6-671H)
Involved Pathway
EIF6 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways EIF6 participated on our site, such as Ribosome biogenesis in eukaryotes, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with EIF6 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Ribosome biogenesis in eukaryotes | NHP2,NOP56,GTPBP4,SBDS,UTP6,WDR43,CSNK2A2A,PWP2,GAR1,cka1 |
Protein Function
EIF6 has several biochemical functions, for example, protein binding,ribosomal large subunit binding,ribosome binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by EIF6 itself. We selected most functions EIF6 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with EIF6. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| ribosome binding | ETF1,SEC61B,BAG6,NAA16,CPEB1,ERI1,CPEB2,EIF2S1B,RPSA,WIBG |
| ribosomal large subunit binding | CPEB2,NMD3,MALSU1,OLA1,MRRF,RBM3,NPM1 |
| translation initiation factor activity | EIF3F,EIF3HA,EIF4A1,EIF1AX,EIF4B,EIF2S3Y,EIF4E3,EIF3S10,EIF4H,BRF1A |
| protein binding | MOB3C,DUSP23,RFFL,FAM20A,NAIF1,FAM83A,PPCDC,BLMH,MATN2,SMURF1 |
Interacting Protein
EIF6 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with EIF6 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of EIF6.
NREP;EIF2AK2;DHX58;OAS3;Prkcb;q96nr0_human
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Vreugde, S; Ferrai, C; et al. Nuclear myosin VI enhances RNA polymerase II-dependent transcription. MOLECULAR CELL 23:749-755(2006).
- Si, K; Chaudhuri, J; et al. Molecular cloning and functional expression of a human cDNA encoding translation initiation factor 6. PROCEEDINGS OF THE NATIONAL ACADEMY OF SCIENCES OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA 94:14285-14290(1997).


