DRD2
-
Official Full Name
dopamine receptor D2 -
Overview
This gene encodes the D2 subtype of the dopamine receptor. This G-protein coupled receptor inhibits adenylyl cyclase activity. A missense mutation in this gene causes myoclonus dystonia; other mutations have been associated with schizophrenia. Alternative splicing of this gene results in two transcript variants encoding different isoforms. A third variant has been described, but it has not been determined whether this form is normal or due to aberrant splicing. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
DRD2;dopamine receptor D2;D2R;D2DR;D(2) dopamine receptor;dopamine D2 receptor;dopamine receptor D2 isoform;seven transmembrane helix receptor
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Chicken
- Mouse
- Pan troglodytes
- Meleagris gallopavo (Wild turkey)
- Mus musculus
- Bovine
- Chlorocebus Aethiops
- Dog
- Mustela putorius furo (European domestic ferret) (Mustela furo)
- E.coli
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- Non
- T7
- DDK
- Myc
- Flag
- Strep
- Avi
- Fc
- GST
Background
What is DRD2 protein?
DRD2 gene (dopamine receptor D2) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 11 at locus 11q23. The DRD2 protein is a G-protein-coupled receptor that is mainly expressed in the brain and is especially abundant in the basal ganglia. By binding to dopamine, an endogenous neurotransmitter, it activates G protein and inhibits the activity of adenylate cyclase. This inhibition affects intracellular cAMP levels, which regulate a variety of physiological functions, including mood, cognition, attention, motor control, and more. The DRD2 protein is consisted of 443 amino acids and DRD2 molecular weight is approximately 50.6 kDa.
What is the function of DRD2 protein?
By binding with dopamine, DRD2 regulates neuronal excitability and affects neurotransmitter release and signal transmission. DRD2 plays a role in the emotional and reward centers of the brain, and is associated with emotional regulation, feelings of pleasure, and addictive behaviors. DRD2 is involved in regulating cognitive processes, including memory, attention, and learning. In the basal ganglia, DRD2 plays an important role in motor control, and its dysfunction may be related to motor disorders such as Parkinson's disease. DRD2 is expressed on some immune cells and may be involved in inflammatory response and regulation of immune cell function. Polymorphisms in the DRD2 gene affect an individual's response to drugs and are associated with individual differences in drug efficacy and side effects.
DRD2 Related Signaling Pathway
As a G protein-coupled receptor, DRD2 inhibits the activity of adenylate cyclase by coupling with Gi/o proteins, thereby reducing the generation of cAMP and affecting intracellular signal transduction. DRD2 plays a role in synaptic pruning during development, and changes in its expression levels are associated with behaviors such as anxiety and depression. The structural characteristics of DRD2 determine its selective recognition of ligands and coupling to specific G proteins, which in turn affect intracellular signaling pathways. The activation of DRD2 may have a protective effect on neurons, preventing apoptosis, and its dysfunction may be related to the occurrence and development of some neurodegenerative diseases.
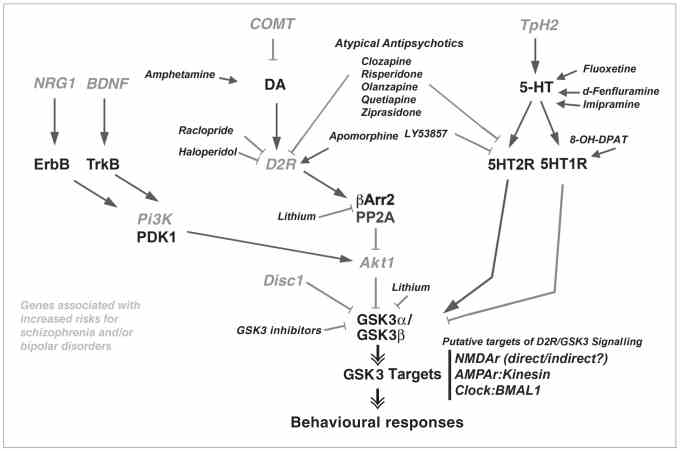
Fig1. Regulation of Akt–GSK3 signalling by psychoactive drugs and gene products associated with mental disorders. (Jean-Martin Beaulieu, 2012)
DRD2 Related Diseases
DRD2 plays an important role in the pathological mechanism of schizophrenia, and its abnormal expression in the brain is associated with the symptom presentation of the disease. DRD2 signaling is associated with motor symptom regulation in Parkinson's disease, and drugs such as bromocriptine reduce symptoms by activating DRD2. The dopamine system, including DRD2, is involved in reward and addictive behavior, and its role in addictive diseases is an important target for drug development. Although ADHD is primarily associated with dopamine transporters and DRD4, DRD2 may also play a role in regulating attention and behavior. In multiple sclerosis, elevated levels of DRD2 expression in astrocytes may promote neuroinflammation through a specific signaling pathway.
Bioapplications of DRD2
DRD2 is a key target for drugs used to treat schizophrenia, Parkinson's disease, depression, and other neuropsychiatric disorders, and its agonists, or antagonists, can regulate dopamine signaling and improve symptoms. The study of the structure and function of DRD2 provides a structural template and molecular mechanism understanding for the development of novel dopamine receptor drugs, and helps to design more effective and selective drugs. The role of DRD2 in synaptic pruning and functional regulation contributes to the understanding of the molecular mechanisms of learning and memory, and provides important information for the study of cognitive function. The potential role of DRD2 in addictive behaviors provides a research basis for the development of interventions targeting addiction.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Yiqing Tan, 2021
Advanced BrCa is considered as incurable, which still lack effective treatment strategies. Identifying and characterizing new tumor suppression genes is important to establish effective prognostic biomarkers or therapeutic targets for late-stage BrCa. Through analyzing differentially expressed genes, DRD2 was selected for further analysis. And expression and promoter methylation status of DRD2 were also determined. DRD2 functions were analyzed by various cell biology assays in vitro. Subcutaneous tumor model was used to explore DRD2 effects in vivo. A co-cultivated system was constructed to investigate interactions of DRD2 and macrophages in vitro. The results showed that Higher expression of DRD2 positively correlated with longer survival times especially in HER2-positive patients. DRD2 also promoted BrCa cells sensitivity to Paclitaxel. Ectopic expression of DRD2 significantly inhibited BrCa tumorigenesis. DRD2 also induced apoptosis as well as necroptosis in vitro and in vivo. DRD2 restricted NF-κB signaling pathway activation through interacting with β-arrestin2, DDX5 and eEF1A2.

Fig1. Measurement of proliferation in Vector- and DRD2-transfected BrCa cells by CCK8 assay.

Fig2. IB was sued to determine the binding of TAB1, TAK1, and β-arrestin2 in Vector- and DRD2-expressed MDA-MB231.
Case Study 2: Seamus P Caragher, 2019
The complex relationship between GBM and the brain microenvironment contributes to this malignant phenotype. However, the interaction between GBM and neurotransmitters, signaling molecules involved in neuronal communication, remains incompletely understood. Here researchers examined, using human patient-derived xenograft lines, how the monoamine dopamine influences GBM cells. They demonstrate that GBM cells express dopamine receptor 2 (DRD2), with elevated expression in the glioma-initiating cell (GIC) population. Stimulation of DRD2 caused a neuron-like hyperpolarization exclusively in GICs. In addition, long-term activation of DRD2 heightened the sphere-forming capacity of GBM cells, as well as tumor engraftment efficiency in both male and female mice. Mechanistic investigation revealed that DRD2 signaling activates the hypoxia response and functionally alters metabolism. Finally, GBM cells synthesize and secrete dopamine themselves, suggesting a potential autocrine mechanism.
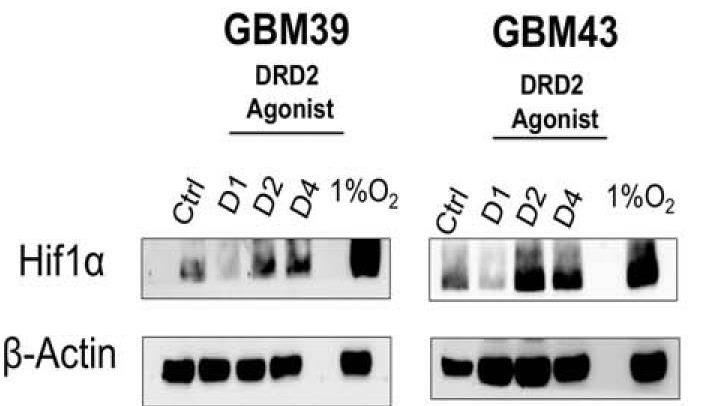
Fig3. PDX GBM cells were treated with DRD2 agonist and then probed for expression of HIF1α by immunoblot analysis.
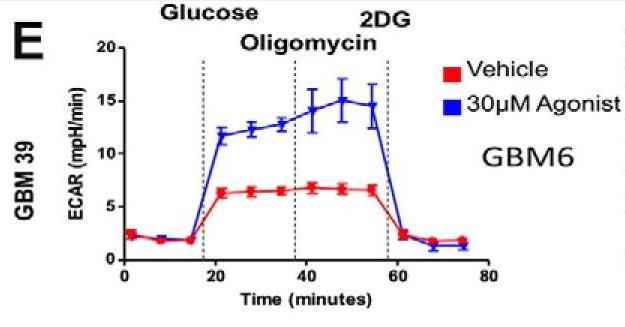
Fig4. GBM39, which responds to DRD2 activation with increased sphere-formation.
Quality Guarantee
.
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (DRD2-16H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (DRD2-1785H)
Involved Pathway
DRD2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways DRD2 participated on our site, such as Alcoholism,Amine ligand-binding receptors,Class A/1 (Rhodopsin-like receptors), which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with DRD2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Dopaminergic synapse | SLC18A1,MAPK9,KIF5C,CREB5,GNB3,GNAL,PRKCA,PPP1CA,GNB1,CLOCK |
| Cocaine addiction | CREB3,DRD1A,RGS9,GRM3,MAOB,CREB3L3,GPSM1,GRIN3A,GRIN2A,GRIN1 |
| Class A/1 (Rhodopsin-like receptors) | GPR37L1,APLN,GPR68,CXCR6,CXCR7B,CGA,LPAR2B,OPN1LW,TRH,CHRM5 |
| Alcoholism | HIST1H4G,HIST1H2AP,MAOB,HIST1H2BQ,GM14482,HIST3H3,CREB3L3,GNAI3,HIST1H4I,GNG4 |
| GPCR downstream signaling | S1PR1,PMCH,PROK1,ARHGEF1B,RAMP2,NPB,S1PR3,CRHB,PENK,OPN1LW1 |
| Amine ligand-binding receptors | ADRA1D,CHRM3,CHRM1,DRD1,DRD4,ADRa1A,ADRA1B,TAAR1,ADRA2A,CHRM4 |
| G alpha (i) signalling events | PYYA,ADRA2B,SSTR5,OXGR1A.1,S1PR1,CCR3,HEBP1,CASR,RGS4,CHRM4 |
| Dopamine receptors | DRD4,DRD5,DRD3,DRD1 |
Protein Function
DRD2 has several biochemical functions, for example, NOT adrenergic receptor activity,dopamine binding,dopamine neurotransmitter receptor activity, coupled via Gi/Go. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by DRD2 itself. We selected most functions DRD2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with DRD2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| drug binding | DRD3,TLR8,ACE,P2RX2,SFRP1,SRP54B,PPARG,SRP54A,DRD1,CHRNB2 |
| dopamine neurotransmitter receptor activity, coupled via Gi/Go | DRD4,DRD4-RS,DRD4A,DRD2A,DRD3,DRD2L,DRD2B,DRD4B |
| NOT adrenergic receptor activity | DRD2A,DRD2L,DRD2B |
| identical protein binding | GRB7,PACSIN2,MIEF1,SMAD3,CHMP4A,PFKL,CSK,SETX,NOXO1,AGXT2 |
| potassium channel regulator activity | DPP6,ADRB2,DPP10,KCNMB3,SGK2,LRRC26,PIAS3,SGK3,AMIGO1,YWHAE |
| protein homodimerization activity | IGJ,DGAT2,PVRL1,SRF,PTPRO,GRPEL2,HARS2,EFR3A,FAM109B,PCYT1A |
| protein heterodimerization activity | H2AFB3,ADRA2C,IKZF2,H2AFB1,NOTCH1,NR2C2,TENM3,MID2,H3F3A,CASP8 |
| protein binding | CTCF,CALCOCO2,LSM11,TNFAIP8L1,CCDC25,C5,CELSR1,UBA7,EIF4G1,DMAP1 |
| ionotropic glutamate receptor binding | DLG3,CACNG2,DLG1L,DLG4,CANX,SHANK2,NETO1,DLG2,SHANK1,FLOT2 |
Interacting Protein
DRD2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with DRD2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of DRD2.
SLC6A3;ADORA2A;CALM1;butaclamol;spiperone;PPP1R9B
Resources
Research Area
Parkinson's Disease Related MoleculesNeurotransmitter G Protein-Coupled Receptors
Dopamine Receptors
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Qu, BX; Gong, YH; et al. Beta-amyloid auto-antibodies are reduced in Alzheimer's disease. JOURNAL OF NEUROIMMUNOLOGY 274:168-173(2014).
- Prast, JM; Schardl, A; et al. Reacquisition of cocaine conditioned place preference and its inhibition by previous social interaction preferentially affect D1-medium spiny neurons in the accumbens corridor. FRONTIERS IN BEHAVIORAL NEUROSCIENCE 8:-(2014).


