DCAF7
-
Official Full Name
DDB1 and CUL4 associated factor 7 -
Overview
Involved in craniofacial development. Acts upstream of the EDN1 pathway and is required for formation of the upper jaw equivalent, the palatoquadrate. The activity required for EDN1 pathway function differs between the first and second arches (By similarity). Associates with DIAPH1 and controls GLI1 transcriptional activity. Could be involved in normal and disease skin development. May function as a substrate receptor for CUL4-DDB1 E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex. -
Synonyms
DCAF7;DDB1 and CUL4 associated factor 7;WD repeat domain 68 , WDR68;DDB1- and CUL4-associated factor 7;HAN11;human anthocyanin;seven WD repeat protein of the AN11 family 1;SWAN 1;AN11;DCAF7_HUMAN;WD repeat domain 68;WD repeat protein An11 homolog;WD repeat-containing protein 68;WD repeat-containing protein An11 homolog;WDR68;WD-repeat protein;seven-WD-repeat protein of the AN11 family-1;SWAN-1
Recombinant Proteins
- Zebrafish
- Human
- Chicken
- Mammalian Cell
- E.coli
- Human
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- Insect Cell
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- T7
- GST
- Non
- His&Strep
- His&SUMO
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCAF7-10423Z | Recombinant Zebrafish DCAF7 | Mammalian Cell | Zebrafish | His |
|
|
| DCAF7-3012H | Recombinant Human DDB1 And CUL4 Associated Factor 7, T7-tagged | E.coli | Human | T7 |
|
|
| DCAF7-30698TH | Recombinant Human DCAF7, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 277 amino acids |
|
| DCAF7-3543C | Recombinant Chicken DCAF7 | Mammalian Cell | Chicken | His |
|
|
| DCAF7-3624H | Recombinant Human DCAF7, His-tagged | Human | Human | His |
|
|
| DCAF7-4565H | Recombinant Human DCAF7 Protein, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST |
|
|
| DCAF7-7055HCL | Recombinant Human DCAF7 293 Cell Lysate | HEK293 | Human | Non |
|
|
| DCAF7-0582H | Recombinant Human DCAF7 Protein (S2-V342), Tag Free | Insect Cell | Human | Non | S2-V342 |
|
| DCAF7-0583H | Recombinant Human DCAF7 Protein (S2-V342), His/Strep tagged | Insect Cell | Human | His&Strep | S2-V342 |
|
| DCAF7-3456HF | Recombinant Full Length Human DCAF7 Protein, GST-tagged | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | GST | Full L. 342 amino acids |
|
| DCAF7-3761H | Recombinant Human DCAF7 protein, His-SUMO-tagged | E.coli | Human | His&SUMO | 1-342aa |
|
| DCAF7-4210H | Recombinant Human DCAF7 protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 1-342aa |
|
Background
What is DCAF7 Protein?
DCAF7 gene (DDB1 and CUL4 associated factor 7) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 17 at locus 17q23. This gene encodes a protein with multiple WD40 repeats which facilitate protein-protein interactions and thereby enable the assembly of multiprotein complexes. This protein has been shown to function as a scaffold protein for protein complexes involved in kinase signaling. This highly conserved gene is present in eukaryotic plants, fungi, and animals. The ortholog of this gene was first identified in plants as a key regulator of anthocyanin biosynthesis and flower pigmentation. The DCAF7 protein is consisted of 342 amino acids and DCAF7 molecular weight is approximately 38.9 kDa.
What is the Function of DCAF7 Protein?
The DCAF7 protein, also known as DDB1 and CUL4-associated factor 7, is a multifunctional cellular adaptation protein that contains a single WD40 repeat domain, is typically involved in protein-protein interactions, and plays multiple roles within the cell. As an aptamer, DCAF7 can interact with a variety of protein kinases, including DYRK1A and HIPK2. The binding of DCAF7 to DYRK1A is achieved through a specific 12-amino acid motif in its n-terminal region that is conserved in Class 1 DYRK kinases. DCAF7 also interacts with HIPK2, and this interaction is important for DYRK1A and HIPK2 signaling. The function of DCAF7 is not limited to its interaction with kinases, it is also involved in the regulation of the cell cycle and cell proliferation.

Fig1. Proposed model of the DYRK1A-DCAF7-E1A complex. (Florian Glenewinkel, 2016)
DCAF7 Related Signaling Pathway
DCAF7 interacts with IRS1 in the insulin /IGF1 signaling pathway, regulates IRS1-FOXO1 signaling, and affects cell proliferation. DCAF7 interacts with ERCC1-XPF heterodimers and maintains the cellular level of ERCC1-XPF through its binding to XPF, which is critical for the nucleotide excision repair (NER) pathway. As a substrate receptor of the CRL4 E3 ubiquitin ligase complex, DCAF7 is involved in protein ubiquitination and subsequent proteasome degradation, affecting the stability of multiple proteins and cell signaling. As an aptamer protein, DCAF7 mediates the interaction of adenovirus E1A oncoprotein with protein kinases DYRK1A and HIPK2, which has a negative effect on E1A-induced carcinogenic transformation.
DCAF7 Related Diseases
Mutations in DCAF7, a substrate receptor for the CRL4 E3 ubiquitin ligase complex, have been detected in patients with Down syndrome-associated myeloid leukemia, affecting hematopoietic stem cell function and possibly contributing to the development of leukemia. DCAF7 is associated with embryonic development and tissue maturation, and its loss or abnormality may be associated with developmental abnormalities, such as DCAF7-deficient mice showing a reduced birth ratio and a reduced number of mature cells. DCAF7 plays a key role in maintaining homeostasis of hematopoietic stem cells and pluripotent stem cells, and its abnormal function may lead to decreased tissue regeneration ability. DCAF7 affects cell proliferation by regulating IRS1-FOXO1 signaling, and its abnormal expression or function may lead to cell cycle dysregulation, which is associated with tumor development and resistance to chemotherapy drugs.
Bioapplications of DCAF7
Because DCAF7 is expressed at elevated levels in some cancers and is associated with tumor cell proliferation and survival, it could be a target for cancer therapy. By developing inhibitors or targeted therapeutic strategies against DCAF7, it may be helpful to inhibit tumor growth. DCAF7's interaction with ERCC1-XPF is crucial for maintaining genome stability, and its role in DNA repair pathways makes it an important protein for studying DNA damage and repair mechanisms. Based on the function of DCAF7 in cell cycle regulation and signaling, small molecule drugs that regulate DCAF7 activity can be developed for the treatment of related diseases. The abnormal expression of DCAF7 may be related to the occurrence and development of the disease, and the change of its expression level can be used as a biomarker for disease diagnosis and monitoring.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Scott Frendo-Cumbo, 2022
Cell proliferation is dependent on growth factors insulin and IGF1. Researchers sought to identify interactors of IRS1, the most proximal mediator of insulin/IGF1 signaling, that regulate cell proliferation. Using proximity-dependent biotin identification (BioID), they detected 40 proteins displaying proximal interactions with IRS1, including DCAF7 and its interacting partners DYRK1A and DYRK1B. In HepG2 cells, DCAF7 knockdown attenuated cell proliferation by inducing cell cycle arrest at G2. DCAF7 expression was required for insulin-stimulated AKT phosphorylation, and its absence promoted nuclear localization of the transcription factor FOXO1. DCAF7 knockdown induced expression of FOXO1-target genes implicated in G2 cell cycle inhibition, correlating with G2 cell cycle arrest. In Drosophila melanogaster, wing-specific knockdown of DCAF7/wap caused smaller wing size and lower wing cell number; the latter recovered upon double knockdown of wap and dfoxo.
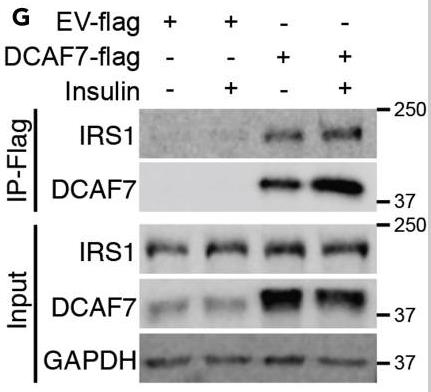
Fig1. Coimmunoprecipitation of DCAF7-Flag with endogenous IRS1, in the presence or absence of insulin, in HepG2 cells.

Fig2. Media LDH activity assay was performed to assess cellular viability in NC and DCAF7 siRNA treated cells.
Case Study 2: Dan Yu, 2019
The general transcription factor P-TEFb, a master regulator of RNA polymerase (Pol) II elongation, phosphorylates the C-terminal domain (CTD) of Pol II and negative elongation factors to release Pol II from promoter-proximal pausing. Here, P-TEFb surprisingly inhibits the myoblast differentiation into myotubes, and that P-TEFb and its two positive complexes are eliminated in this process. In contrast, DYRK1A, another CTD kinase known to control transcription of a subset of genes important for development and tissue homeostasis, is found to activate transcription of key myogenic genes. And active DYRK1A exists in a complex with the WD40-repeat protein DCAF7 that stabilizes and tethers DYRK1A to Pol II, so that DYRK1A-DCAF7 can co-migrate with and phosphorylate Pol II along the myogenic gene loci.

Fig3. Recombinant GST-DYRK1A (Life Technologies) was incubated with or without F-DCAF7.

Fig4. ChIP-qPCR analyses were conducted to assess the occupancy of DCAF7.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (DCAF7-4565H)
Involved Pathway
DCAF7 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways DCAF7 participated on our site, such as TNF-alpha/NF-kB Signaling Pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with DCAF7 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| TNF-alpha/NF-kB Signaling Pathway | CRADD,CAPN3,CSNK2A1P,TIFA,UNC5CL,DDX3X,PEG3,COPS3,KPNA6,RNF216 |
Protein Function
DCAF7 has several biochemical functions, for example, protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by DCAF7 itself. We selected most functions DCAF7 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with DCAF7. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | CALR,MPPE1,ANXA4,GREM1,SETMAR,MC2R,RD3,Car8,ACMSD,CCDC151 |
Interacting Protein
DCAF7 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with DCAF7 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of DCAF7.
MAP3K1;HIPK2;DYRK1A
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


