CRK
-
Official Full Name
v-crk sarcoma virus CT10 oncogene homolog (avian) -
Overview
CrkII, a cellular homologue of v-Crk, belongs to a family of adaptor proteins with an SH2-SH3-SH3 domain structure that transmits signals from tyrosine kinases. The primary function of Crk is to recruit cytoplasmic proteins in the vicinity of tyrosine kin -
Synonyms
CRK;v-crk sarcoma virus CT10 oncogene homolog (avian);v crk avian sarcoma virus CT10 oncogene homolog;adapter molecule crk;proto-oncogene c-Crk;p38;CRKII;FLJ38130
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Rat
- Chicken
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cell
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- Mammalian cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- HEK293T
- GST
- His
- Non
- His&Fc&Avi
- Flag
- Myc&DDK
Background
What is CRK Protein?
CRK proteins are key intracellular adapters with SH2 and SH3 domains that play a crucial role in transmitting and modulating signal strength. The CRK family, which includes CrkI, CrkII, and CrkL, connects various signaling pathways affecting cell proliferation, adhesion, migration, endocytosis, apoptosis, and gene regulation through these domains. They serve as central players in both normal and pathological signaling, linking upstream tyrosine kinases and integrin-dependent signals to downstream effectors. In cancer, CRK proteins are heavily studied for their roles in tumor progression, driving research into their mechanisms in malignancy. Additionally, CRK proteins participate in plant immune responses, abiotic stress tolerance, and balancing growth under stress, reflecting their conservation as receptor-like kinases in plants. Thus, CRK proteins are pivotal in managing cellular and physiological processes.What is the Function of CRK Protein?
CRK proteins are key signaling adapters involved in various biological processes. They link multiple pathways through SH2 and SH3 domains, impacting cell proliferation, adhesion, migration, apoptosis, and gene regulation. Members like CrkI, CrkII, and CrkL, although lacking catalytic activity, interact with tyrosine kinases and integrin-dependent signals to connect them to downstream effectors. In cancer, CRK proteins play a role in cell transformation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), enhancing tumor cell spread and invasion. They also influence immune responses by regulating immune cell functions. In plants, CRK proteins are key components of receptor-like kinases (RLKs), contributing to development, stress responses, immunity, and symbiosis. Thus, CRK proteins are crucial in both physiological and pathological cellular regulation.
Fig1. Diagram of cancers in which Crk and CrkL are overexpressed. (Taeju Park, 2021)
CRK Related Signaling Pathway
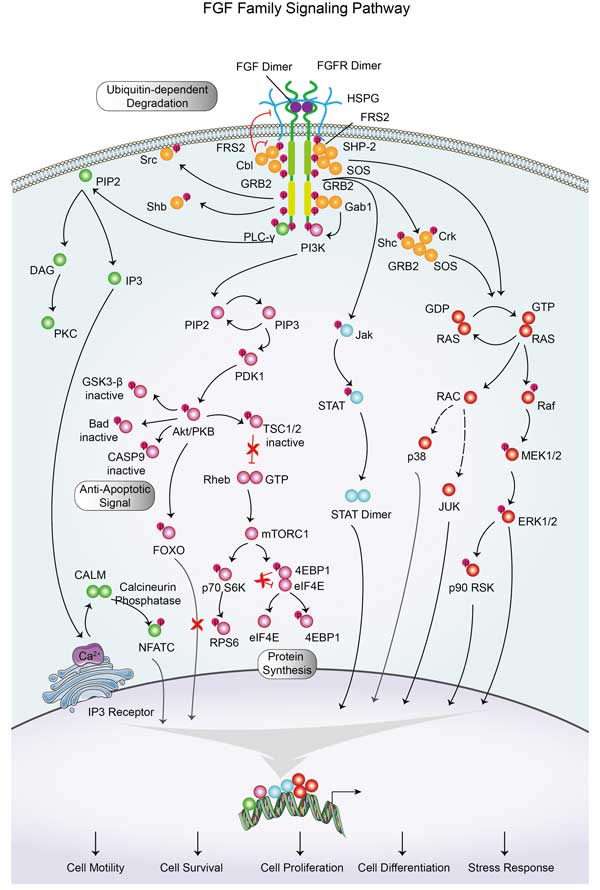
CRK proteins, vital in cellular signaling, have SH2 and SH3 domains to interact with various molecules, forming multiprotein complexes that connect signaling networks. Members like v-Crk, Crk II, Crk I, and CrkL respond to signals—growth factors, ECM molecules, apoptotic cells, immune complexes—via SH2 domain interactions, initiating signal transduction. They play roles in cell proliferation, adhesion, migration, phagocytosis, apoptosis, and gene regulation, by recognizing phosphorylated tyrosine through SH2 and proline-rich sequences through SH3, transferring signals from surface receptors to intracellular targets. Their adaptor function is essential in regulating physiological and pathological signals, dynamically modifying pathways for quick responses to changes.CRK Related Diseases
CRK proteins are linked to many diseases, especially in cancer and infectious diseases. They’re crucial in cancers like sarcomas, chronic myeloid leukemia, stomach, and ovarian cancer, affecting how cancer cells grow, die, move, and invade. Abnormal CRK protein levels are often tied to cancer’s aggressive traits, making them a possible marker for tumor prognosis. They also play a role in bacterial pathogenicity, possibly influencing bacterial entry into host cells or acting as bacterial toxin targets. CRK proteins are related to congenital disorders and cardiovascular diseases, including Miller-Dieker syndrome, DiGeorge syndrome, Tetralogy of Fallot, and double outlet right ventricle. Hence, CRK proteins are potential targets for therapeutic intervention due to their critical role in various pathological processes.Bioapplications of CRK
Recombinant CRK protein is key in research, industrial production, and medical studies. Researchers use it to explore its role in signal transduction networks, especially regarding cell functions in various conditions. In the industrial arena, it’s instrumental in developing specific antibodies and screening drugs to identify compounds that affect CRK protein function. In medical research, the protein’s connection to cancer opens up avenues to investigate cancer mechanisms and new therapies. Notably, studies on non-small cell lung cancer show how recombinant CRK protein can boost autophagy through the ERK pathway, hinting at fresh cancer treatment paths. Overall, it’s pivotal for a deeper understanding of disease roles and crafting innovative diagnostic and treatment approaches.Case Study
Case Study 1: Kakemura B. et al. Commun Biol. 2024
Targeting cancer cells without harming normal cells is crucial for effective cancer treatment. In a Drosophila model, researchers identified potential anti-cancer targets by utilizing RNAi screens to inhibit tumor growth. Specifically, knockdown of Crk, the fly equivalent of human CRK adapter proteins, significantly reduced tumor growth by promoting apoptosis via JNK signaling. Importantly, this knockdown didn’t affect normal cell growth. The mechanism involves blocking Yorkie/YAP activity, crucial in cancer development, by disrupting F-actin accumulation. These findings suggest a promising anti-cancer approach targeting YAP-activated pathways, beneficial in treating human cancers where similar pathways are active.-
 Fig1. Eye disc bearing eyFLP-induced MARCM clones and Crk::GFP heterozygously.
Fig1. Eye disc bearing eyFLP-induced MARCM clones and Crk::GFP heterozygously. -
 Fig2. Eye disc bearing eyFLP-induced MARCM clones of RasV12+ scrib−/−+ Crk-I cells.
Fig2. Eye disc bearing eyFLP-induced MARCM clones of RasV12+ scrib−/−+ Crk-I cells.
Case Study 2: Rodríguez-Blázquez A. et al. Cell Commun Signal. 2023
C3G is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor that activates Rap1, essential for cell adhesion. Inactive C3G becomes active when tyrosine kinases trigger it, often through phosphorylation and Crk adaptor protein interaction—proteins known to be overexpressed in many cancers. We’ve used various methods to understand how C3G gets activated. Our findings show Crk proteins bind four specific sites on C3G, with initial binding helping guide C3G to the cell membrane. Although phosphorylation alone only slightly activates C3G, it makes C3G more receptive to Crk protein binding, boosting activity. Notably, maximum activation also needs CrkL to connect with phosphorylated C3G.-
 Fig3. Dose-dependent analysis of the activation of C3G (1 µM) by CrkII and the CrkII-CrkL chimeric proteins.
Fig3. Dose-dependent analysis of the activation of C3G (1 µM) by CrkII and the CrkII-CrkL chimeric proteins. -
 Fig4. Pull-down (PD) analysis of the binding of GST-CrkL, wild type and mutants, to C3G and pC3G.
Fig4. Pull-down (PD) analysis of the binding of GST-CrkL, wild type and mutants, to C3G and pC3G.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CRK-1886H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CRK-1886H)
-
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CRK-5279H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CRK-5279H)
Involved Pathway
CRK involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CRK participated on our site, such as ARMS-mediated activation,Angiopoietin receptor Tie2-mediated signaling,B Cell Receptor Signaling Pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CRK were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| CXCR4-mediated signaling events | ARR3,GNA13,GNB2L1,BLK,DNM1,MAPKAP1,JAK2,CSK,PAG1,CFL1 |
| Cytokine Signaling in Immune system | NEFLB,TRIM5,TRIM48,XAF1,SPNA2,NRG3,DUSP6,IFITM3,IL17RD,DUSP10 |
| Angiopoietin receptor Tie2-mediated signaling | CDKN1A,AGTR1,ELF2,GRB14,GRB7,ELF1,DOK2,BMX |
| Bacterial invasion of epithelial cells | CTTN,WASF2,CAV2,RAC1,DNM2,VCL,ELMO2,FN1,ITGB1,ACTB |
| Chronic myeloid leukemia | CBLB,GAB2,BRAF,CBLC,HDAC2,SHC4,STAT5B,PIK3CA,CRKL,HDAC1 |
| Chemokine signaling pathway | VAV1,GNB3,Cxcl15,PRKCD,CXCL6,Ccl12,RAF1,CCL16,XCL1,XCL2 |
| ARMS-mediated activation | PSME3,DAB2IPB,DUSP4,SPRED3,SPTB,SPRED1,DUSP7,PTPRA,FGF18B,FGF20A |
| B Cell Receptor Signaling Pathway | BLNK,HDAC5,DOK1B,PPP3R1,GSK3B,DOK3,GSK3AB,NFKBIE,CD22,PPP3CA |
-
 Fig1. A model for tumor suppression caused by targeting Crk family proteins. (Bungo Kakemura, 2024)
Fig1. A model for tumor suppression caused by targeting Crk family proteins. (Bungo Kakemura, 2024) -
 Fig2. Regulation of CRK-RAC1 activity by the miR-1/206/133 miRNA family is essential for neuromuscular junction function. (Ina Klockner, 2022)
Fig2. Regulation of CRK-RAC1 activity by the miR-1/206/133 miRNA family is essential for neuromuscular junction function. (Ina Klockner, 2022)
Protein Function
CRK has several biochemical functions, for example, SH2 domain binding,SH3/SH2 adaptor activity,ephrin receptor binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CRK itself. We selected most functions CRK had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CRK. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| SH2 domain binding | PAG1,NLK,DAG1,ARHGAP5,INPPL1,NUP62,JAK2,DLC1,SYNGR3,LAT2 |
| ephrin receptor binding | CHN1,EFNA1A,GRB2,SHC1,EFNA5,CDK5R1,PTPN1,NTRK3,EFNB3,EFNA1 |
| SH3/SH2 adaptor activity | SH2B2,RUSC1,ITSN2,PTPN11,PAG1,CHN1,SH2D3A,GRB7,NCK1,GAB1 |
| protein binding | BCLAF1,VEGFB,NME4,RFPL3,SERP1,MAL,EEA1,SETBP1,NABP1,NAV2 |
| protein phosphorylated amino acid binding | BTRC,ARRB1 |
Interacting Protein
CRK has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CRK here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CRK.
CBL;BCAR1;PDGFRA;ABL2
CRK Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Li, J; Chen, S; et al. Histone deacetylase 8 regulates cortactin deacetylation and contraction in smooth muscle tissues. AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PHYSIOLOGY-CELL PHYSIOLOGY 307:C288-C295(2014).
- Aten, TM; Redmond, MM; et al. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the orphan receptor ESDN/DCBLD2 serves as a scaffold for the signaling adaptor CrkL. FEBS LETTERS 587:2313-2318(2013).