CDK5
-
Official Full Name
CDK5 cyclin-dependent kinase 5 -
Overview
Cyclin dependent kinase 5 (CdK5) is a member of the cyclindependent kinase family of serine/threonine kinases. It is present in numerous mammalian tissues including kidney, testes, and ovary. Its activity is detected almost exclusively in brain extracts. Neuronal and muscle cells contain the highest amount of this protein. Similar to other Cdks, monomeric Cdk5 displays no enzymatic activity, but Cdk5 is not activated by cyclins. Instead, the p35 protein, which is expressed solely in the brain, activates Cdk5. Cdk5 interacts with D1 and D3 type G1 cyclins and can phosphorylate histone H1, TAU, MAP2 and NF-H and NF-M. Cdk5 activity is involved in terminal differentiation of neurons and muscle cells. -
Synonyms
Cyclin cdk5;CDK5;cyclin-dependent kinase 5;PSSALRE;OTTHUMP00000212917;OTTHUMP00000212939;TPKII catalytic subunit;protein kinase CDK5 splicing;cell division protein kinase 5;serine/threonine-protein kinase PSSALRE;tau protein kinase II catalytic subunit;Cyclin dependent kinase 5
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Rhesus macaque
- Zebrafish
- E.coli
- Insect Cells
- Insect Cell
- Human
- Sf9 Insect Cell
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cell
- HEK293
- Mammalian cells
- Sf9 insect cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Insect (sf21)
- HEK293T
- Non
- GST
- gst
- His
- His&S
- Flag
- His&Fc&Avi
- His&SUMO
- Myc&DDK
Background
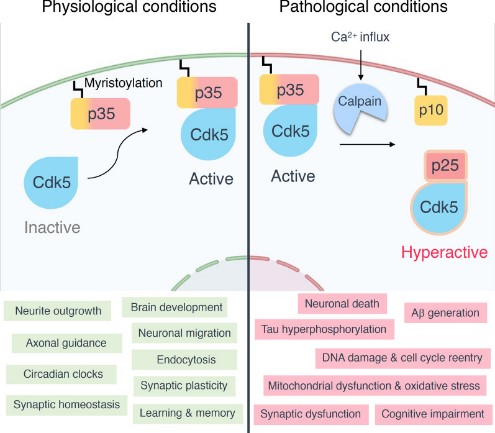
Fig1. Activation of Cdk5 and its functions under physiological or pathological conditions. (Ping-Chieh Pao, 2021)
What is CDK5 protein?
CDK5 (cyclin dependent kinase 5) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 7 at locus 7q36. This gene encodes a proline-directed serine/threonine kinase that is a member of the cyclin-dependent kinase family of proteins. Unlike other members of the family, the protein encoded by this gene does not directly control cell cycle regulation. Instead the protein, which is predominantly expressed at high levels in mammalian postmitotic central nervous system neurons, functions in diverse processes such as synaptic plasticity and neuronal migration through phosphorylation of proteins required for cytoskeletal organization, endocytosis and exocytosis, and apoptosis. The CDK5 protein is consisted of 292 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 33.3 kDa.
What is the function of CDK5 protein?
CDK5, or cyclin-dependent kinase 5, is an atypical member of the cyclin-dependent kinase family that plays significant roles in various cellular processes, particularly in neurons. CDK5 is considered neuron-specific and is crucial for neuronal development and function, including synaptic plasticity and neurotransmitter release. CDK5 is involved in regulating cell movement, which is essential for neuronal migration during brain development. CDK5 has been shown to play a role in the regulation of programmed cell death (apoptosis). It can be activated by cyclin I, leading to anti-apoptotic functions due to the increased expression of Bcl-2 family proteins. Although CDK5 is not traditionally associated with the cell cycle control like other CDKs, it does have a role in cell cycle progression in certain contexts. CDK5 is involved in the phosphorylation of various proteins, which can affect their activity and function in the cell.
CDK5 Related Signaling Pathway
CDK5 may also be involved in neuroinflammatory processes, as its activity can influence the behavior of microglia, the immune cells of the central nervous system. CDK5 activity is tightly regulated by its activators p35 and p25. The conversion of p35 to p25 can lead to hyperactivation of CDK5, which has been associated with neuronal death. CDK5 is involved in pathways associated with neurodegenerative diseases. Its dysregulation has been linked to Alzheimer's disease, and it may play a role in other neurodegenerative conditions as well. Although not traditionally associated with the cell cycle like other CDKs, CDK5 can influence cell cycle progression in specific cellular contexts.
CDK5 Related Diseases
CDK5 is known to hyperphosphorylate the tau protein, leading to the formation of neurofibrillary tangles, which are a characteristic feature of Alzheimer's disease. CDK5 plays a role in neuronal migration and differentiation, and its dysregulation can lead to neurodevelopmental disorders. CDK5 is involved in synaptic plasticity and cognitive functions. Dysregulation of CDK5 has been associated with cognitive decline and impairment. Menin, a protein that regulates CDK5, is a tumor suppressor. Mutations in menin can lead to various endocrine tumors, and its interaction with CDK5 may play a role in the development of these tumors. CDK5 is crucial for synaptic function, and its deregulation can lead to synaptic dysfunction, which is implicated in many neurological disorders.
Bioapplications of CDK5
The discovery of new regulatory mechanisms of CDK5, such as the role of menin in modulating CDK5 activation, opens up novel avenues for treatment approaches targeting the upstream regulators of CDK5 activity. CDK5 is a target for pharmacological research into drugs that affect neurotransmission and could potentially be used to develop new medications for neurological diseases. CDK5 is being explored as a therapeutic target for conditions involving abnormal neuronal function, including epilepsy and cognitive impairment.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Ping-Chieh Pao, 2023
Aberrant activity of cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk5) has been implicated in various neurodegenerative diseases. This deleterious effect is mediated by pathological cleavage of the Cdk5 activator p35 into the truncated product p25, leading to prolonged Cdk5 activation and altered substrate specificity. Elevated p25 levels have been reported in humans and rodents with neurodegeneration, and the benefit of genetically blocking p25 production has been demonstrated previously in rodent and human neurodegenerative models. Here, the researchers report a 12-amino-acid-long peptide fragment derived from Cdk5 (Cdk5i) that is considerably smaller than existing peptide inhibitors of Cdk5 (P5 and CIP) but shows high binding affinity toward the Cdk5/p25 complex, disrupts the interaction of Cdk5 with p25, and lowers Cdk5/p25 kinase activity. When tagged with a fluorophore (FITC) and the cell-penetrating transactivator of transcription (TAT) sequence, the Cdk5i-FT peptide exhibits cell- and brain-penetrant properties and confers protection against neurodegenerative phenotypes associated with Cdk5 hyperactivity in cell and mouse models of neurodegeneration, highlighting Cdk5i's therapeutic potential.

Fig1. Recombinant Cdk5/p25 proteins were incubated with Cdk5i or solvent control overnight and subjected to IP-linked Cdk5 kinase assay.

Fig2. Cell lysates from HEK293T cells cooverexpressing Cdk5-GFP, p25-GFP, and Cdk5i or scrambled peptide were used for IP with Cdk5 antibody.
Case Study 2: Xiao-Feng Zheng, 2019
Mitotic cells attenuate the DNA damage response (DDR) by phosphorylating 53BP1, a critical DDR mediator, to prevent its localization to damaged chromatin. Timely dephosphorylation of 53BP1 is critical for genome integrity, as premature recruitment of 53BP1 to DNA lesions impairs mitotic fidelity. Protein phosphatase 4 (PP4) dephosphorylates 53BP1 in late mitosis to allow its recruitment to DNA lesions in G1. How cells appropriately dephosphorylate 53BP1, thereby restoring DDR, is unclear. Here, the researchers elucidate the underlying mechanism of kinetic control of 53BP1 dephosphorylation in mitosis. They demonstrate that CDK5, a kinase primarily functional in post-mitotic neurons, is active in late mitotic phases in non-neuronal cells and directly phosphorylates PP4R3β, the PP4 regulatory subunit that recognizes 53BP1. Specific inhibition of CDK5 in mitosis abrogates PP4R3β phosphorylation and abolishes its recognition and dephosphorylation of 53BP1, ultimately preventing the localization of 53BP1 to damaged chromatin. The results establish CDK5 as a regulator of 53BP1 recruitment.
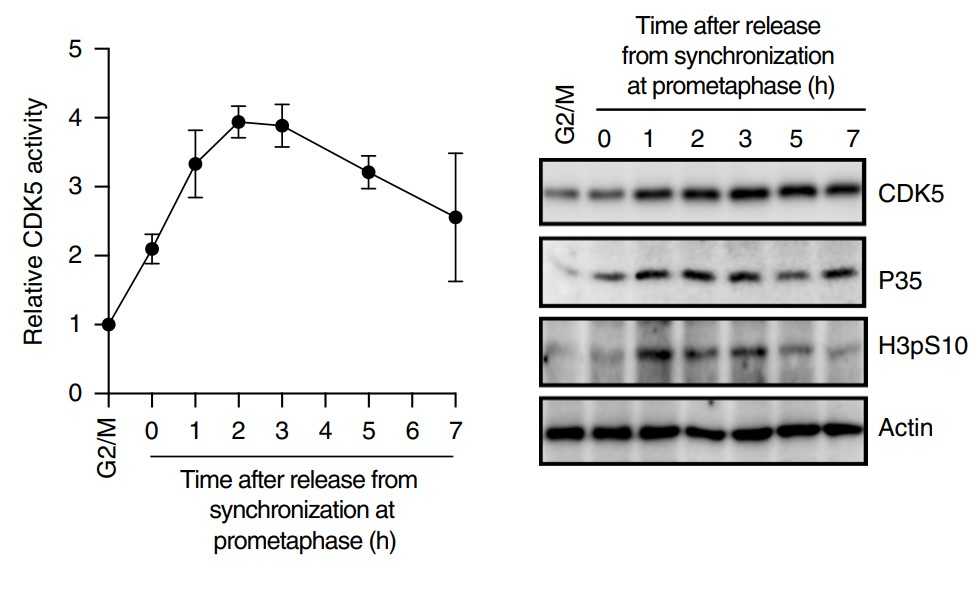
Fig3. Kinase activity levels of CDK5 in mitosis and G1.

Fig4. Effect of CDK5 inhibition on radiosensitivity.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CDK5-382H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CDK5-236H)
Involved Pathway
CDK5 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CDK5 participated on our site, such as Alzheimers disease,Axon guidance,BDNF signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CDK5 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Axon guidance | AGRN,PAK4,CFL2,GDNF,GPC1B,EPHA7,ARHGEF12,CXCL12,ACTR2B,PPP3CC |
| DARPP-32 events | PRKAR1AA |
| DNA damage response | DDB2,RAD9A,CHEK2,RAD1,HUS1B,GADD45A,RAD17,GADD45G,TLK2 |
| Cocaine addiction | PRKACG,CREB3L4,CREB3L2,GRIN2D,NFKB1,BDNF,DRD1A,GNAI3,SLC18A2,DRD1 |
| BDNF signaling pathway | IGF2BP1,EGR2,YBX1,GNB2L1,BCL2L11,DPYSL2,FRS2,EIF4E,LINGO1,KCNN2 |
| CRMPs in Sema3A signaling | SEMA3AB,DPYSL4,DPYSL5A,CDK5R1B,SEMA3A,DPYSL5B,DPYSL3,DPYSL2B,SEMA3AA,CRMP1 |
| Alzheimers disease | CASP7,NDUFA8,ATP2A3,NDUFA5,PLCB2,UQCRFS1,NDUFA4,COX7A1,UQCRH,NDUFS5 |
Protein Function
CDK5 has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,ErbB-2 class receptor binding,ErbB-3 class receptor binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CDK5 itself. We selected most functions CDK5 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CDK5. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | ATP2A2,TMEM242,RFX3,OSTC,PEX3,MCPH1,GSN,ADORA1,PIK3C3,ATG9A |
| ErbB-2 class receptor binding | MUC4,NRG1 |
| ephrin receptor binding | EFNA1A,EPHA7,GRB2,EFNA4,SHC1,EFNA1,EFNA2A,PTPN1,EFNB2A,EFNA5 |
| p53 binding | MDM2,SETD8,DUSP26,SMARCB1,DAXX,ZFP385C,TRP53,HSPD1,AAAS,TP73 |
| protein kinase binding | RPS6KA3,ITGB1BP1,FAM83A,TSKS,SKAP1,EEF1A2,PAX6,TELO2,SLC12A5,GYS1 |
| ErbB-3 class receptor binding | ERBB2,PIK3R1,NRG1 |
| protein kinase activity | SLKA,DYRK1AA,STK38A,STK24B,MAP2K4,FASTKD1,AURKA,IKBKB,IGF1RB,PHKG1B |
| cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity | CDK19,CDK1,CDK18,CDKL3,CDK14,CDK3,CDK2,CCND3,CDK12,ICK |
| tau-protein kinase activity | PHKG2,PRKAA1,MARK4,MARK2,GSK3B,PHKG1,CSNK1D,MARK1,GSK3A |
Interacting Protein
CDK5 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CDK5 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CDK5.
CDKN1B;CCND2;CABLES1;CDKN1A
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Olah, Z; Kalman, J; et al. Proteomic Analysis of Cerebrospinal Fluid in Alzheimer's Disease: Wanted Dead or Alive. JOURNAL OF ALZHEIMERS DISEASE 44:1303-1312(2015).
- Vazquez-Rosa, E; Rodriguez-Cruz, EN; et al. Cdk5 phosphorylation of EFhd2 at S74 affects its calcium binding activity. PROTEIN SCIENCE 23:1197-1207(2014).
Reviews
Q&As
The CDK5 is expressed from HEK293 host, which is a mammalian cells system.


