CD44
-
Official Full Name
CD44 molecule (Indian blood group) -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a cell-surface glycoprotein involved in cell-cell interactions, cell adhesion and migration. It is a receptor for hyaluronic acid (HA) and can also interact with other ligands, such as osteopontin, collagens, and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). This protein participates in a wide variety of cellular functions including lymphocyte activation, recirculation and homing, hematopoiesis, and tumor metastasis. Transcripts for this gene undergo complex alternative splicing that results in many functionally distinct isoforms, however, the full length nature of some of these variants has not been determined. Alternative splicing is the basis for the structural and functional diversity of this protein, and may be related to tumor metastasis. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
CD44;CD44 molecule (Indian blood group);IN;LHR;MC56;MDU2;MDU3;MIC4;Pgp1;CDW44;CSPG8;HCELL;HUTCH-I;ECMR-III;CD44 antigen;epican;Hermes antigen;hyaluronate receptor;phagocytic glycoprotein 1;heparan sulfate proteoglycan;cell surface glycoprotein CD44;extracellular matrix receptor III;chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 8;GP90 lymphocyte homing/adhesion receptor;hematopoietic cell E- and L-selectin ligand;homing function and Indian blood group system
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Mouse
- Cynomolgus
- Chicken
- Rabbit
- Cricetulus griseus
- Mus musculus
- Papio hamadryas (Hamadryas baboon)
- HEK293
- Mammalian cells
- CHO
- E. coli
- E.coli
- Human Cell
- C-hFc
- C-His
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cell
- HEK293T
- Human Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- HEK293F
- E.coli expression system
- His
- Fc
- GST
- Non
- Myc&DDK
- Flag
- His&Strep
- His&SUMO
- His&GST
- His&Fc&Avi
- N-His-SUMO&C-Myc
Background
What is CD44 protein?
CD44 (CD44 molecule (IN blood group)) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 11 at locus 11p13. The protein encoded by this gene is a cell-surface glycoprotein involved in cell-cell interactions, cell adhesion and migration. It is a receptor for hyaluronic acid (HA) and can also interact with other ligands, such as osteopontin, collagens, and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). Transcripts for this gene undergo complex alternative splicing that results in many functionally distinct isoforms, however, the full length nature of some of these variants has not been determined. Alternative splicing is the basis for the structural and functional diversity of this protein, and may be related to tumor metastasis. The CD44 protein is consisted of 742 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 81.5 kDa.
What is the function of CD44 protein?
CD44 antigen is a cell-surface glycoprotein involved in cell–cell interactions, cell adhesion and migration. CD44 is expressed in a large number of mammalian cell types. CD44 function is controlled by its posttranslational modifications. One critical modification involves discrete sialofucosylations rendering the selectin-binding glycoform of CD44 called HCELL (for Hematopoietic Cell E-selectin/L-selectin Ligand). CD44 participates in a wide variety of cellular functions including lymphocyte activation, recirculation and homing, hematopoiesis, and tumor metastasis.

Fig1. Schematic representation of CD44 expression in the context of epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity. (Mark Primeaux, 2022)
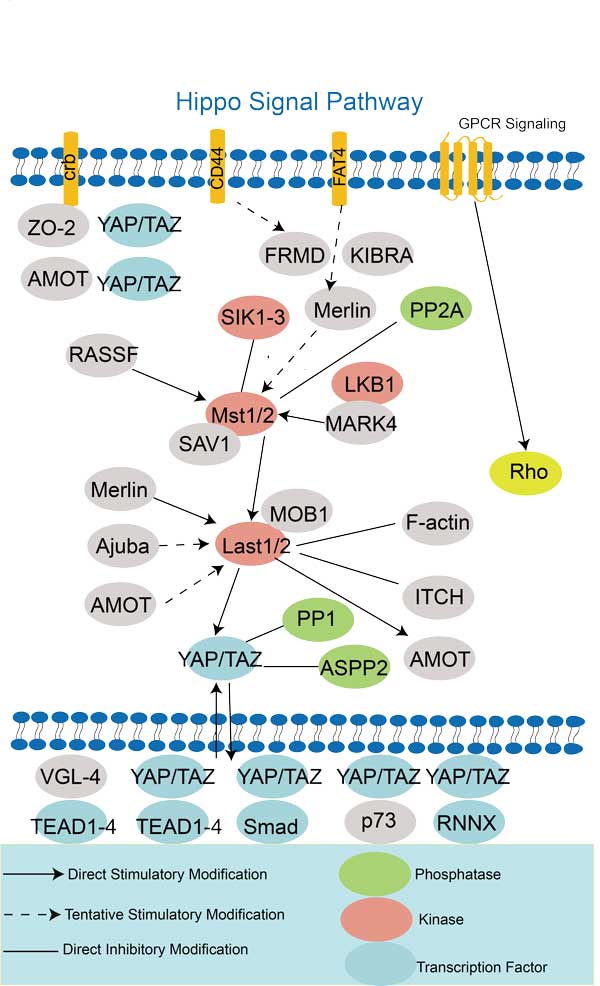
CD44 Related Signaling Pathway
CD44 can bind to Wnt ligands and activate Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, thereby regulating cell fate determination, tissue regeneration and cancer occurrence. The intracellular region of CD44 can bind to the PI3K subunit and activate the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Activation of CD44 can lead to the degradation of IκB and the activation of NF-κB, thereby promoting the inflammatory response of cells and inhibiting apoptosis. And other signaling pathways such as TGF-β signaling pathway, JAK/STAT signaling pathway, etc.

Fig2. Summary of carcinogenic mechanisms and signalling pathways induced by CD44, as well as CD44 regulators, ligands, prognostic value and possible targeting strategies. (Malak Hassn Mesrati, 2021)
CD44 Related Diseases
CD44 is a cell surface receptor that is involved in a variety of biological processes, including cell adhesion, migration, proliferation, and apoptosis. Abnormal expression or mutation of CD44 is associated with a variety of diseases, the following are some common CD44-related diseases: cancer such as breast cancer, colon cancer, lung cancer, etc.; CD44 is involved in the adhesion and migration of blood system cells and is associated with blood system diseases such as leukemia and lymphoma. And immune diseases and inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, enteritis and so on. At the same time, CD44 is involved in the adhesion and proliferation of stem cells and is associated with tissue repair and regeneration, such as liver regeneration and nervous system regeneration.
Bioapplications of CD44
CD44 is abnormally expressed in a variety of cancers, and as a therapeutic target, there are already some drugs and therapies targeting CD44 under study, such as antibody drugs (Bivatuzumab), small molecule inhibitors. CD44 can promote cell adhesion and migration, and researchers can regulate the expression of CD44 to control cell behavior and tissue formation, or interfere with the function of CD44 to study the development and function of neurons.
Case Study
Case study 1: Mahboobeh Rezaeeyazdi, 2018
Polymeric scaffolds such as hydrogels can be engineered to restore, maintain, or improve impaired tissues and organs. However, most hydrogels require surgical implantation that can cause several complications such as infection and damage to adjacent tissues. Therefore, developing minimally invasive strategies is of critical importance for these purposes.
Herein, this team developed several injectable cryogels made out of hyaluronic acid and gelatin for tissue-engineering applications. The physical characteristics of pure gelatin cryogels, such as mechanics and injectability, were enhanced once copolymerized with hyaluronic acid. And in vitro studies revealed that copolymerizing gelatin with hyaluronic acid did not significantly alter their respective intrinsic biological properties. The data indicates that the chemically modified and crosslinked HA has unchanged biological behavior and is able to bind strongly to CD44 protein. These findings suggest that hyaluronic acid-co-gelatin cryogels combined the favorable inherent properties of each biopolymer, providing a mechanically robust, cell-responsive, macroporous, and injectable platform for tissue-engineering applications.

Fig1. Evaluation of biological properties of cryogels.

Case study 2: Yu-Wei Hsiao, 2022
Due to the heterogeneity and high frequency of genome mutations in cancer cells, targeting vital protumour factors found in stromal cells in the tumour microenvironment may represent an ideal strategy in cancer therapy. However, the regulation and mechanisms of potential targetable therapeutic candidates need to be investigated. An in vivo study demonstrated that stromal PTX3 expression correlates with adverse prognostic features and is associated with worse survival outcomes in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). And following PTX3 stimulation, CD44, a PTX3 receptor, activates the downstream ERK1/2, AKT and NF-κB pathways to specifically contribute to the metastasis/invasion and stemness of TNBC MDA-MB-231 cells.
Two types of PTX3 inhibitors were developed to disrupt the PTX3/CD44 interaction and they showed a significant effect on attenuating growth and restricting the metastasis/invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells, suggesting that targeting the PTX3/CD44 interaction could be a new strategy for future TNBC therapies.

Fig3. Harvested MDA-MB-231 cell membrane proteins were incubated with or without recombinant PTX3 protein, and then co-immunoprecipitation was performed with the membrane proteins and PTX3 antibody or CD44 antibody.

Quality Guarantee
High Purity

Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CD44-3961H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.

Fig2. Activity Data. (CD44-3961H)
Involved Pathway
CD44 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CD44 participated on our site, such as ECM-receptor interaction,Hematopoietic cell lineage,Shigellosis, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CD44 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| MicroRNAs in cancer | ITGA5,PDGFRB,MARCKS,HMGA2,GLS2,IRS1,MAP2K2,PIK3CA,SPRY2,ABCB1 |
| Epstein-Barr virus infection | HLA-A,PIK3CB,GTF2B,POLR2I,PIK3R3,YWHAE,CD40,HLA-DQB1,HLA-DPA1,TRAF6 |
| ECM-receptor interaction | ITGA2B,ITGA10,THBS2,Itga10&Itgb1,LAMC1,Npnt,ITGB1A,LAMA3,COL4A4,ITGA1 |
| Proteoglycans in cancer | MET,PIK3CB,VTN,RRAS,CAMK2B,PLCE1,CAV2,FASLG,FGFR1,WNT8B |
| Shigellosis | FBXW11,ELMO3,MAPK12,ATG5,VCL,RAC1,WASL,RIPK2,NFKBIB,U2AF1L4 |
| Hematopoietic cell lineage | HLA-DRA,GM13305,TFRC,CD1D2,ITGA6,IL7R,ITGA1,IL4R,FCGR1, B2M |

Fig1. A highly simplified diagram of the PTX3/CD44 signalling pathway. (Yu-Wei Hsiao, 2022)

Fig2. P falciparum exploits CD44 as a coreceptor during invasion of human erythrocytes, stimulating CD44-dependent phosphorylation of host cytoskeletal proteins that alter host cell deformability and facilitate parasite entry. (Barbara Baro, 2023)
Protein Function
CD44 has several biochemical functions, for example, collagen binding,contributes_to cytokine receptor activity,hyaluronic acid binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CD44 itself. We selected most functions CD44 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CD44. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| hyaluronic acid binding | HAPLN1,IMPG2,TNFAIP6,LAYN,HAPLN4,HMMR,C1QBP,HAPLN3,KIAA1199,HAPLN1A |
| hyalurononglucosaminidase activity | KIAA1199,HYAL6,HYAL4,MGEA5,HYAL3,HYAL2,HYAL1,SPAM1 |
| protein binding | MAU2,RBP5,TRIM16,PYDC1,TAOK3,TMEM19,NR2F2,PPP1R15A,CDC37,AGTR1A |
| collagen binding | ADAM9,ITGA2,CTSL1,PDGFB,SRGN,ITGA1,CTSB,SMAD4,PCOLCE,ITGA9 |
| contributes_to cytokine receptor activity | IL28RA,IRX1 |
Interacting Protein
CD44 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CD44 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CD44.
ipaB;SPP1;ganglioside_gm1;SLC7A11;MSN
CD44 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Research Area
Myeloid Lineage MarkersChondrogenesis Markers
Osteoclast Markers
Granulocyte Markers
Neurotransmitter G Protein-Coupled Receptors
Peptide Hormone G Protein-Coupled Receptors
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Markers
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Markers
Osteoblast and Osteoclast Markers
Hyaluronan (HA) binding Proteins
Basophils
Glial Lineage Markers
Adipose-derived Stem Cell Markers
Natural Killer T (NKT) Cells
CD Antigen (Granulocyte Markers)
Colon Cancer Stem Cell Markers
Gastric Cancer Stem Cell Markers
Head and Neck Cancer Stem Cell Markers
Leukemia Cancer Stem Cell Markers
Osteosarcoma Cancer Stem Cell Markers
Ovarian Cancer Stem Cell Markers
Prostate Cancer Stem Cell Markers
Bladder Cancer Stem Cell Markers
Breast Cancer Stem Cell Markers
Glioma/Medulloblastoma Cancer Stem Cell Markers
Pancreatic Cancer Stem Cell Markers
Mesodermal Lineage Markers
Dendritic Cell Adhesion and Migration
MDSC Phenotyping - Positive Markers
Glioma Biomarkers
Melanoma Biomarkers
Osteosarcoma Biomarkers
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Gu, JJ; Fang, XL; et al. Reversal of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance by CD44 antibody-targeted nanocomplexes for short hairpin RNA-encoding plasmid DNA delivery. BIOMATERIALS 45:99-114(2015).
- Kaneko, K; Higuchi, C; et al. Hyaluronan inhibits BMP-induced osteoblast differentiation. FEBS LETTERS 589:447-454(2015).