CARM1
-
Official Full Name
coactivator-associated arginine methyltransferase 1 -
Overview
Protein arginine N-methyltransferases, such as CARM1, catalyze the transfer of a methyl group from;S-adenosyl-L-methionine to the side chain nitrogens of arginine residues within proteins to form methylated arginine;derivatives and S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine. Protein arginine methylation has been implicated in signal transduction,;metabolism of nascent pre-RNA, and transcriptional activation (Frankel et al., 2002 (PubMed 11724789)). -
Synonyms
CARM1;coactivator-associated arginine methyltransferase 1;histone-arginine methyltransferase CARM1;PRMT4;protein arginine N-methyltransferase 4
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Zebrafish
- Rat
- E.coli
- Insect Cell
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cell
- Free Style 293-F Cell
- Sf21 Insect Cell
- Sf9 Insect Cell
- HEK293
- Mammalian cells
- HEK293T
- GST
- FLAG
- His
- Non
- His&GST
- His&Fc&Avi
- Flag
- Myc&DDK
Background
What is CARM1 Protein?
CARM1, or PRMT4, acts like a protein modifier by sticking methyl groups onto them, which can shift their roles. It's particularly famous for jazzing up histone proteins with these methyl tags, significantly influencing gene expression by altering how DNA is packaged and accessed. But CARM1 doesn't stop there; it also modifies a range of other proteins, influencing transcription and various cell processes, including growth, proliferation, and differentiation. Its structure supports these activities, with parts designed for its catalytic actions and others for activating functions. Increased levels of CARM1 have been seen in several cancers, making it a target of interest for therapy. Additionally, CARM1 is involved in autophagy, a vital process for keeping cells healthy and defending against diseases. Overall, CARM1 is a versatile protein at the heart of many crucial cellular operations.
What is the Function of CARM1 Protein?
CARM1, or coactivator-associated arginine methyltransferase 1, plays a diverse role in the cell by adding methyl groups to specific proteins, which can shift their behavior and function. This tweaking is crucial, particularly when it comes to histone proteins, as it significantly influences how genes are expressed by altering the way DNA is packaged in the chromatin. But CARM1 doesn't stop at histones; it zeroes in on other proteins too, like those involved in controlling how genes get turned on and off, thereby playing a part in vital pathways related to cell growth, development, and even cell fate decisions. Its structural features, like the catalytic domain that executes these modifications, enable it to carry out various significant roles in the cell. Interestingly, CARM1 often pops up in discussions about cancer because it's frequently found in higher-than-normal levels in several types of cancer cells, suggesting it could be a key target for cancer treatment. Beyond this, CARM1 also has a hand in autophagy, which is the cell's way of clearing out damaged components to maintain health and stave off diseases.

Fig1. CARM1 controls autophagy, metabolism and redox homeostasis in tumors. (Zizhuo Xie, 2024)
CARM1 Related Signaling Pathway
CARM1, or Coactivator-associated Arginine Methyltransferase 1, is an enzyme that marks proteins with methyl groups, influencing their actions and interactions. It's spotlighted for its role in modifying histones, the proteins around which DNA winds, thereby shaping how genes get expressed by affecting the access to DNA instructions. Beyond histones, CARM1 also tweaks a variety of other proteins, playing a part in controlling how genes get turned on or off, and influencing vital cellular activities like growth, specialization, and response to stress. This enzyme's involvement doesn't end there; it ties into pathways related to cell division and survival, making its overexpression a commonality in various cancers, which pegs it as a promising target for therapy. On top of that, CARM1 plays a part in autophagy, a cleanup process that maintains cellular health by recycling parts and defending against disease. Through diverse roles across cellular landscapes, CARM1 emerges as a key player in maintaining balance and responding to cellular cues.
CARM1 Related Diseases
CARM1, or PRMT4, has been tied to several diseases, largely due to its role in altering protein function through methylation. This enzyme's activity can impact gene expression, and its overexpression or aberrant function has been linked to various types of cancer, where it may drive unchecked cell growth by disrupting normal regulatory pathways. Besides cancer, CARM1's influence on immune responses and other cellular processes suggests it could be involved in inflammatory conditions and possibly neurodegenerative diseases, although research in these areas is still emerging. Its multifunctionality in pivotal pathways makes it a potential target for therapeutic interventions aiming to reinstate balance in affected systems.
Bioapplications of CARM1
Researchers have found multiple ways to tap into its functions across various bioapplications. This enzyme is fundamental in regulating gene expression as it modifies histones, which helps unpack or pack the DNA, influencing how genes get turned on or off. This action makes it a hot topic in epigenetics studies. Beyond that, CARM1 is explored for its relationship with certain diseases, especially cancers, where it's often overexpressed. So, scientists are interested in developing inhibitors that could serve as potential treatments. On the cellular level, CARM1 also gets involved in pathways related to growth, stress responses, and autophagy, playing roles that make it a significant focus in understanding cellular health and crafting interventions. Whether it's in drug development or fundamental research, CARM1's diverse functions make it a key enzyme worth keeping an eye on in the realms of both health and disease research.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Yiyang Wang, 2021
The E6 protein from human papillomavirus (HPV) enables the virus to manipulate host protein interactions, aiding infection. It works with the host's E3 ubiquitin ligase, E6AP, to hijack the ubiquitination process, driving infected cells toward cancerous changes. A proteomic screen using "orthogonal UB transfer (OUT)" identified over 200 E6AP targets affected by E6 of HPV-16, a high-risk type linked to cervical cancer. Notably, it causes E6AP to ubiquitinate and degrade proteins like KPNA1-3, PGAM5, and CARM1. This degradation impairs pathways like KPNA1-mediated nuclear transport, reducing phosphorylated STAT1 movement and dampening apoptosis triggered by interferon-γ in cervical cancer cells. The study showcases OUT's utility in exploring E6's impact on protein ubiquitination and unveils its role in inhibiting tumor suppressive signals through nuclear transport protein downregulation.
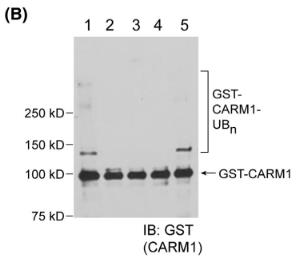
Fig1. Reactivity of the E6-E6AP pair was assayed with substrates identified by orthogonal UB transfer.

Fig2. Ubiquitination of the substrate proteins identified by the orthogonal UB transfer screen was confirmed with CARM1.
Case Study 2: Young Suk Yu, 2020
Autophagy is basically the body's way of cleaning out damaged cells and recycling parts, especially when under stress like starvation. Lately, researchers have found that transcriptional and epigenetic changes really keep this process humming along smoothly. In this context, CARM1, which is a methyltransferase, modifies Pontin, a chromatin-remodeling factor, when glucose is scarce. This modified Pontin then hooks up with FOXO3a, a transcription factor. Studies show that this interaction helps bring in Tip60, which enhances histone acetylation, and this, in turn, activates genes involved in autophagy. Interestingly, this CARM1-Pontin-FOXO3a pathway can activate autophagy genes even from a distance by turning on enhancers.

Fig3. CARM1-interacting proteins were purified from HEK293T cells stably expressing Flag-CARM1 by co-immunoprecipitation with Flag-M2 agarose.

Fig4. Co-immunoprecipitation assay was performed to detect the interaction between FOXO3a and Pontin in MEFs under glucose starvation after treating with CARM1-specific inhibitors.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CARM1-0402H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CARM1-003H)
Involved Pathway
CARM1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CARM1 participated on our site, such as Activation of gene expression by SREBF (SREBP),Androgen receptor signaling pathway,BMAL1:CLOCK,NPAS2 activates circadian gene expression, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CARM1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Androgen receptor signaling pathway | RHOB,HMGB2A,SMAD3B,RAD54L2,NCOA2,EGFR,HTATIP,RNF14,EFCAB6,DSTN |
| Coregulation of Androgen receptor activity | ZMIZ1,TGFB1I1,PATZ1,PIAS3,CMTM2A,SNURF,TCF4,KDM3A,MAK,SVIL |
| BMAL1:CLOCK,NPAS2 activates circadian gene expression | NCOA2,CRY2,NAMPT,NRIP1,CREBBP,DBP,HELZ2,CRY1 |
| Activation of gene expression by SREBF (SREBP) | DHCR7,NCOA2,MTF1,CREBBP,HELZ2,NFYBB,PMVK,CYP51A1,NFYBA,NFYAL |
| Chromatin organization | ZZZ3,SUZ12A,KIAA1267,PADI1,PHF8,KDM5C,MTA2,MBIP,SUDS3,SETD3 |
| Circadian Clock | CPT1A,HELZ2,CSNK1E,NRIP1,NAMPT,DBP,CRY2,CRY1,RAI1 |
| Chromatin modifying enzymes | PADI4,BRD1,ARID2,BRPF1,ZZZ3,CSRP2BP,MBD3,KDM6AL,KDM7AB,KDM5D |
| Developmental Biology | EPHA2,EGR2,DPYSL2B,MED10,EFNB1,KDR,FRS2B,CDON,CFC1,AP2S1 |
Protein Function
CARM1 has several biochemical functions, for example, beta-catenin binding,histone methyltransferase activity,histone methyltransferase activity (H3-R17 specific). Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CARM1 itself. We selected most functions CARM1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CARM1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| histone-arginine N-methyltransferase activity | PRMT2,PRMT3,PRMT6,PRMT5,PRMT7,PRMT8 |
| transcription coactivator activity | MED7,PMF1,SETD3,GATA3,MAGED1,FHL2,PRMT2,JUPA,RAP2C,HINFP |
| protein-arginine omega-N asymmetric methyltransferase activity | PRMT7,PRMT8B,PRMT6,PRMT8,PRMT1,PRMT3,PRMT2 |
| beta-catenin binding | GRIP1,TRPC4,PTPRK,TCF7L2,AXIN1,SHROOM2,BCL9,CXADR,GLI3,SMAD7 |
| protein binding | BMP1A,KIR2DL1,FAM154A,TTLL6,DPEP3,TMEM183A,STX19,ATP6V1F,CABP1,SMC2 |
| lysine-acetylated histone binding | PHIP,ATAD2B,BRD3,SMARCA4,BRD2,PSME4B,BAZ2A,BRDT,TRIM24,TAF1L |
| protein-arginine N-methyltransferase activity | METTL7B,PRMT5,PRMT3,PRDM12,FBLL1,DIMT1,NDUFAF5,PRDM11,PRMT2,METTL21A |
| transcription regulatory region DNA binding | SALL1A,HIVEP2,TCF7L1B,TNF,HHEX,SMAD3,HMGB2,MZF1,TFAP4,NKX3 |
| protein methyltransferase activity | NDUFAF5,PRDM13,FBLL1,METTL21A,NTMT1,METTL11A,TRMT10C,METTL8,N6AMT1,HEMK1 |
Interacting Protein
CARM1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CARM1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CARM1.
SMARCC1;CEBPB;CEBPB;NUDT21;DNAJA3;QKI;ORF;NRIP1;HNRNPK;UBE2I
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Zeng, H; Wu, JC; et al. A TR-FRET-Based Functional Assay for Screening Activators of CARM1. CHEMBIOCHEM 14:827-835(2013).
- Sakabe, K; Hart, GW; et al. O-GlcNAc Transferase Regulates Mitotic Chromatin Dynamics. JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY 285:34460-34468(2010).



