What is GKN1 Protein?
Background and Discovery of GKN1 Protein
In the fascinating sphere of molecular biology, protein coding genes such as the Gastrokine 1 (GKN1) bear crucial implications for human health and disease.
The GKN1 protein, which gets its name from its production site - the stomach cells known as gastrokines, was discovered in 2002 during differential gene expression studies. Scientists were aiming to understand the unique protein expression patterns in diverse gastrointestinal tract tissues. GKN1 was singled out due to its high expression in normal gastric epithelium and starkly reduced expression in gastric cancer.
Gastrokine 1 is coded for by the GKN1 gene that is localized to the short arm of chromosome 2 at position 13, denoted as 2p13. This gene locus exerts significant influence on the structure of the GKN1 protein. The protein itself is small, with 175 amino acids, and its structure is yet to be fully delineated. However, preliminary reports suggest it contains an N-terminal BRICHOS domain, a feature associated with several human diseases like dementia and cancer.
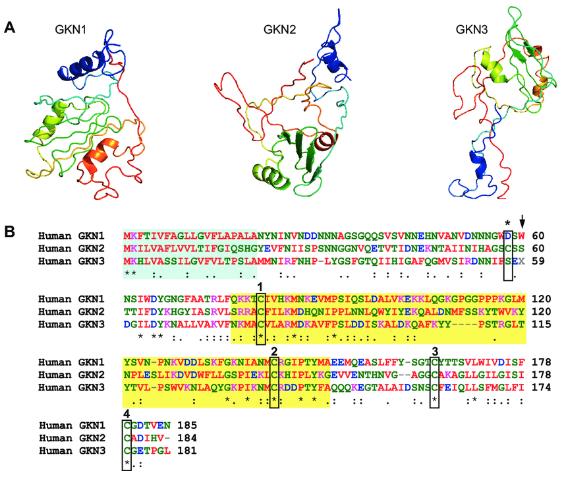
Fig1. GKN protein structures and sequence homology
What Is The Function of GKN1 Protein?
Functionally, GKN1 is implicated in maintaining gastric tissue homoeostasis. This protein plays a fundamental role in supporting the rapid self-renewal of gastric mucosal cells, healing of stress-induced gastric lesions, and protection against injury caused by infection with Helicobacter pylori, a bacterium found in the stomach. This protective function seemingly underscores the decreased presence of GKN1 in cases of stomach cancer.
GKN1 protein related signal pathway
On another level, the GKN1 protein is embedded in a web of complex signal pathways. In health, GKN1 stimulates the fibrinogen receptor, also known as integrin αMβ2, on the surface of Helicobacter pylori, leading to the activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signal pathway. This pathway regulates cellular activities such as growth, gene expression, differentiation, proliferation, and cell survival. In disease, the absence or downregulation of GKN1 means this protective signaling pathway is muted or subdued, predisposing to cancerous transformations.
GKN1 protein related diseases
As highlighted above, the relation between GKN1 protein and diseases is most notable in gastric cancer. The prevalent theory is that the loss of GKN1 expression, due to gene deletion or hypermethylation, initiates a susceptibility to gastric cancer, making it a potential tumour suppressor. Furthermore, GKN1 deficiency has been associated with Barrett's oesophagus and oesophageal adenocarcinoma, underscoring the protein's influence on gastrointestinal pathology.
Surprisingly, recent studies have also revealed GKN1 deficiency in non-gastrointestinal malignancies such as breast and kidney cancers, suggesting wider protective roles beyond the gastric tissue. Further research into the mechanistic link between GKN1 expression and these cancers will undoubtedly yield exciting insights.
GKN1 protein's applications in biomedical
Given the documented tumor-suppressive capacities of GKN1 protein, its applications in biomedical science are multitudinous. Notably, it can serve as a biomarker for early detection and monitoring of gastric cancer and other malignancies marked by GKN1 downregulation. Additionally, GKN1 supplementation could theoretically restore normal cell growth and differentiation in GKN1-deficient patients, potentially offering a therapeutic route for gastric cancer treatment. Moreover, understanding the pathways GKN1 participates may elucidate new drug targets, ushering new therapies.
In conclusion, GKN1 is an exciting candidate in the field of biomarker research and potential therapeutic interventions. Its role in maintaining the gastric mucosa's integrity is of fundamental importance, with its loss early in gastric carcinogenesis offering promising insights for early cancer detection and intervention. However, comprehending the molecular facets of GKN1 and its correlations with cancer remains an upward climb, necessitating committed research efforts.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GKN1-4942H | Recombinant Human GKN1 Protein, GST-tagged | Human | Wheat Germ | GST |
| GKN1-01H | Recombinant Human GKN1 Protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| GKN1-5305HF | Recombinant Full Length Human GKN1 Protein, GST-tagged | Human | In Vitro Cell Free System | GST |
| Gkn1-7830M | Recombinant Mouse Gkn1 protein, His-tagged | Mouse | E.coli | His |
| Gkn1-7832R | Recombinant Rat Gkn1 protein, His-tagged | Rat | E.coli | His |
Reference
- Menheniott, Treve & Kurklu, Bayzar & Giraud, Andrew. (2012). Gastrokines: Stomach-specific proteins with putative homeostatic and tumor suppressor roles. American journal of physiology. Gastrointestinal and liver physiology. 304. 10.1152/ajpgi.00374.2012.
