LAIR Family
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
Background
About LAIR Family
The LAIR (Leukocyte-associated immunoglobulin-like receptor) family is a group of cell surface receptors that belong to the immunoglobulin superfamily. These receptors are primarily expressed on various immune cells, including subsets of lymphocytes, myeloid cells, and natural killer (NK) cells. The LAIR family receptors play important roles in immune regulation, modulation of cellular functions, and interactions with extracellular matrix components.
Key features of the LAIR family include:
Structure: LAIR family receptors are characterized by their extracellular immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domains, which are involved in ligand binding and receptor interactions. They typically possess one or two Ig-like domains in their extracellular regions, followed by a short cytoplasmic tail.
Ligands: The LAIR family receptors recognize and interact with various ligands, including collagen and collagens-related peptides. Specifically, LAIR-1 (also known as CD305) has been extensively studied for its binding to collagens and its inhibitory effects on immune cell activation.
Inhibitory Function: LAIR family receptors are generally associated with inhibitory signaling pathways. Upon ligand binding, they can deliver inhibitory signals that regulate immune cell activation, cytokine production, and cellular functions. These inhibitory signals can modulate immune responses and contribute to immune tolerance.
Expression and Cell Types: LAIR family receptors are expressed on a range of immune cells, including subsets of T cells, B cells, NK cells, monocytes, and dendritic cells. Their expression patterns may vary depending on cell type and activation status. For example, LAIR-1 is expressed on multiple immune cell subsets, while LAIR-2 is primarily expressed in skin and mucosal tissues.
Role in Disease: Dysregulated expression or function of LAIR family receptors has been associated with various diseases. Their involvement has been reported in autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus, as well as cancer progression and metastasis.
The LAIR family of receptors represents an important component of immune regulation and immunomodulation. Further research is needed to unravel their precise mechanisms of action, identify additional ligands, and understand their roles in different cellular contexts and disease settings.
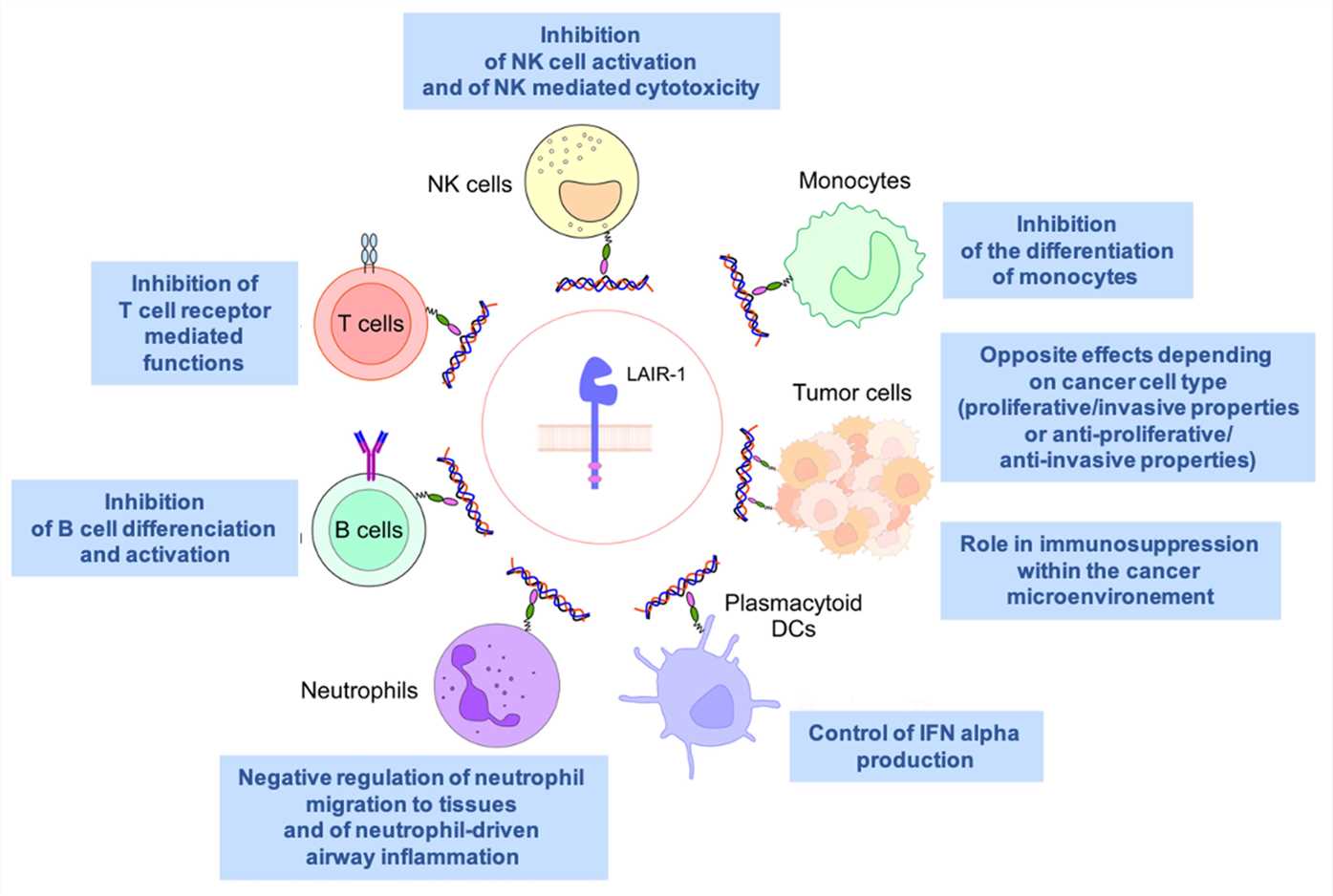 Fig.1 Summary of LAIR1 expression and functions in normal leucocytes, plasmacytoid dendritic (pDCs) cells, and tumor cells. (Van Laethem F, et al., 2022)
Fig.1 Summary of LAIR1 expression and functions in normal leucocytes, plasmacytoid dendritic (pDCs) cells, and tumor cells. (Van Laethem F, et al., 2022)Interactions and Potential Modulatory Roles of LAIR Family
The LAIR family primarily functions as an inhibitory receptor, transmitting negative regulatory signals to modulate immune responses. However, it is important to note that the LAIR family does not have well-established co-stimulatory pathways like other receptor families such as the TNF superfamily or the B7-CD28 family. Nevertheless, the LAIR family can interact with other receptors and molecules to influence immune cell functions. Here are some interactions and potential modulatory roles of the LAIR family:
| Type | Interactions and potential modulatory roles |
|---|---|
| Interaction with ITIM-Containing Receptors |
|
| Cross-Talk with Other Inhibitory Receptors |
|
| Influence on Immune Cell-Matrix Interactions |
|
It is important to note that the LAIR family's primary function is inhibitory, and its role as a co-stimulator in immune responses is not extensively characterized. While LAIR receptors can interact with other receptors and modulate immune cell functions, these interactions typically result in inhibitory signals that dampen immune activation. Further research is needed to fully understand the co-stimulatory or synergistic roles of the LAIR family in immune responses and to explore potential therapeutic applications.
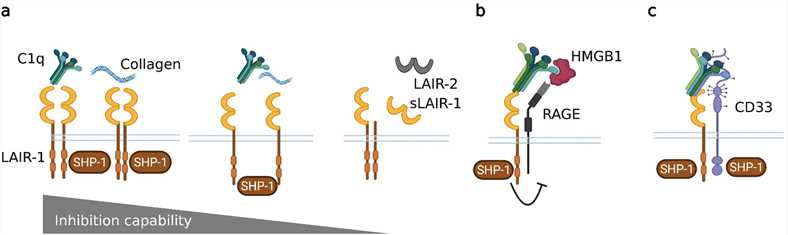 Fig.2 Regulation of LAIR-1-mediated inhibition. (Van Laethem F, et al., 2022)
Fig.2 Regulation of LAIR-1-mediated inhibition. (Van Laethem F, et al., 2022)(a) The expression levels of the receptor and soluble forms of LAIR-1 and LAIR-2 alter the strength of LAIR-1 inhibition. In addition, partnering of existing ligands with other receptors, such as (b) RAGE or (c) CD33, may also alter the function of LAIR-1.
LAIR Family Molecules
The LAIR family consists of several molecules that share structural similarities and belong to the immunoglobulin superfamily. The known members of the LAIR family include:
| Key molecules | Functions |
|---|---|
| LAIR-1 (CD305) | LAIR-1 is the most studied member of the LAIR family. It is expressed on various immune cells, including subsets of T cells, B cells, NK cells, monocytes, and dendritic cells. LAIR-1 possesses an extracellular immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domain that can interact with collagens and collagens-related peptides. Its cytoplasmic tail contains an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM), which enables the transduction of inhibitory signals upon ligand binding. |
| LAIR-2 (CD306) | LAIR-2 is a soluble homolog of LAIR-1. It is primarily expressed in skin and mucosal tissues. LAIR-2 acts as a decoy receptor by binding to collagens and preventing their interaction with LAIR-1, thus potentially modulating LAIR-1-mediated signaling. |
| LAIR-3 (CD307) | LAIR-3 is a less characterized member of the LAIR family. It shares structural similarities with LAIR-1 and LAIR-2 and is expressed on immune cells, including B cells and monocytes. Its specific functions and ligand interactions are not well understood. |
| LAIR-4 (CD307d) | LAIR-4 is another member of the LAIR family. It is expressed on B cells and monocytes. Similar to LAIR-1, LAIR-4 contains an ITIM motif in its cytoplasmic tail, suggesting a potential role in immune regulation. However, its ligand interactions and functions are not extensively studied. |
These LAIR family molecules are involved in immune regulation and modulation of cellular functions. Their interactions with collagens and potential cross-talk with other receptors allow them to influence immune cell activation, adhesion, and migration. Further research is needed to fully elucidate the functions and molecular mechanisms of the LAIR family members in immune responses and disease contexts.
Role of LAIR Family Molecules in Different Diseases
The LAIR family molecules have been implicated in various diseases, primarily due to their roles in immune regulation and modulation of immune cell functions. Here are some examples of diseases where LAIR family molecules have been studied:
Autoimmune Diseases
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): LAIR-1 has been investigated in RA, and its expression on synovial fibroblasts has been associated with disease severity and joint destruction. LAIR-1 engagement can inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokine production and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) expression, potentially influencing the pathogenesis of RA.
Cancer
- Solid Tumors: LAIR-1 expression has been observed in various solid tumors, including breast cancer, lung cancer, and colorectal cancer. LAIR-1 can contribute to tumor immune evasion by suppressing immune cell activation and antitumor responses.
- Hematological Malignancies: LAIR-1 and LAIR-2 have been investigated in hematological malignancies, such as acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Their expression patterns and interactions with collagens or other receptors may affect immune cell functions and disease progression.
Infectious Diseases
- Viral Infections: LAIR-1 has been implicated in viral infections, such as human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) and HIV. In HCMV infection, LAIR-1 can modulate NK cell responses and influence viral control. In HIV infection, LAIR-1 expression on T cells has been associated with disease progression and immune dysfunction.
Allergic Diseases
- Asthma: LAIR-1 expression has been investigated in asthma. It has been suggested that LAIR-1 on airway smooth muscle cells can modulate cell proliferation and migration, potentially contributing to airway remodeling in asthma.
Fibrotic Diseases
- Pulmonary Fibrosis: LAIR-1 has been implicated in pulmonary fibrosis, where excessive collagen deposition and tissue remodeling occur. LAIR-1 expression on fibroblasts can influence collagen synthesis and fibrotic processes.
These examples highlight the involvement of LAIR family molecules in various diseases, although the specific mechanisms and their roles may vary depending on the disease context. Further research is needed to fully understand the contributions of LAIR family molecules in disease pathogenesis and to explore their potential as therapeutic targets.
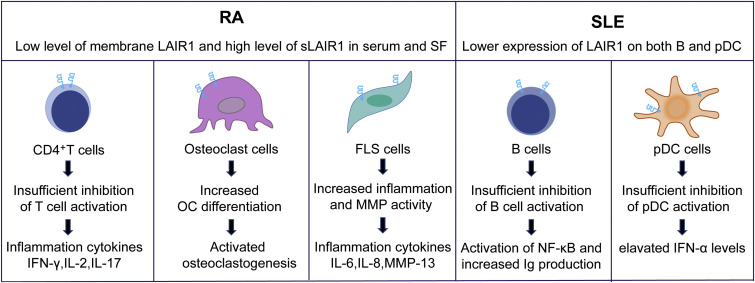 Fig.3 Mechanism involved in the regulation of RA and SLE by LAIR-1. (Van Laethem F, et al., 2022)
Fig.3 Mechanism involved in the regulation of RA and SLE by LAIR-1. (Van Laethem F, et al., 2022)Case Study
Case 1: Helou DG, Quach C, Hurrell BP, et al. LAIR-1 limits macrophage activation in acute inflammatory lung injury. Mucosal Immunol. 2023;16(6):788-800.
Airflow resistance is one among other features of ALI/ARDS in animal models. More importantly, neutrophil infiltration and capillary-alveolar permeability are the major hallmarks of ARDS. Therefore, the author investigated the effect of LAIR-1 deficiency on these key features in Poly(I:C)-induced acute lung inflammation. (A) As expected, Poly(I:C) stimulation induced airway hyperreactivity in response to increasing concentrations of methacholine as compared to PBS control mice. Moreover, LAIR-1 KO mice displayed higher lung resistance in response to methacholine doses as compared to WT, suggesting an exacerbated alteration of lung respiratory functions (B). Additionally, immune CD45+ cells showed higher recruitment to the airway lumen as revealed by flow cytometry analysis in the bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) (C and D). This is mainly due to the increased recruitment of neutrophils, which constitute the most frequent population in Poly(I:C)-treated mice (E). LAIR-1 KO mice displayed significantly higher levels of FITC in the plasma as compared to WT mice, revealing increased lung permeability (H). Despite the increased protein leakage, LAIR-1 KO mice still display a higher total protein concentration in the BAL, suggesting a more potent lung inflammation as compared to WT mice (I). Altogether, these results suggest that LAIR-1 contributes to the downregulation of lung resistance, permeability, and inflammation in ALI/ARDS.
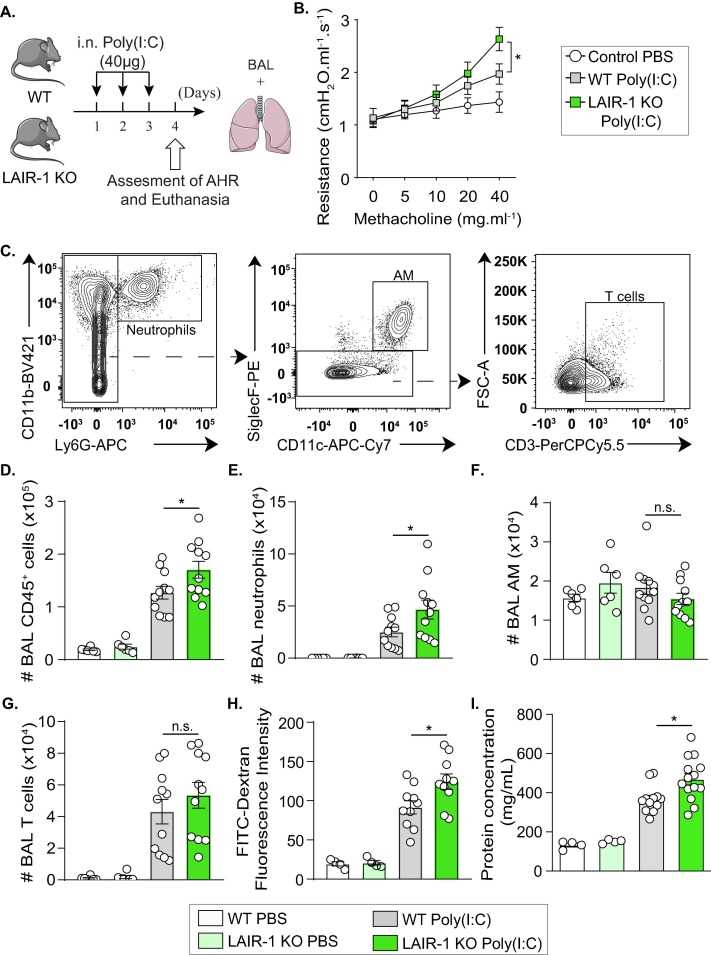 Fig.1 LAIR-1 deficiency increases lung resistance, inflammation, and permeability.
Fig.1 LAIR-1 deficiency increases lung resistance, inflammation, and permeability.Case 2: Zhou T, Liu L, Lan H, Fang D. Effects of LAIR-1 on hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and invasion via PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway regulation. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023;11(8):e982.
The authors have shown that the knockdown of LAIR-1 promoted MHCC97-H cell viability, colony formation, and invasive ability. The author confirmed the effect of LAIR-1 on the malignant phenotypes of other HCC cells by further stably overexpressing LAIR-1 in Huh-7, an HCC cell line with lower level LAIR-1 expression as shown in Figure 1. The overexpression of LAIR-1 was confirmed by WB (A). Cell viability assay using a CCK-8 kit revealed that overexpression of LAIR-1 significantly inhibited Huh-7 cell viability (B). The author also performed a CFA to verify the antiproliferative activity of LAIR-1. LAIR-1 overexpression significantly reduced the clonogenic ability of Huh-7 cells (C). Next, the author examined whether LAIR-1 could affect the invasion properties of Huh-7 cells in vitro. The trans-well assay showed that LAIR-1 suppressed Huh-7 cell invasion (D). These data indicated that LAIR-1 has an anti-tumorigenic role in HCC cells.
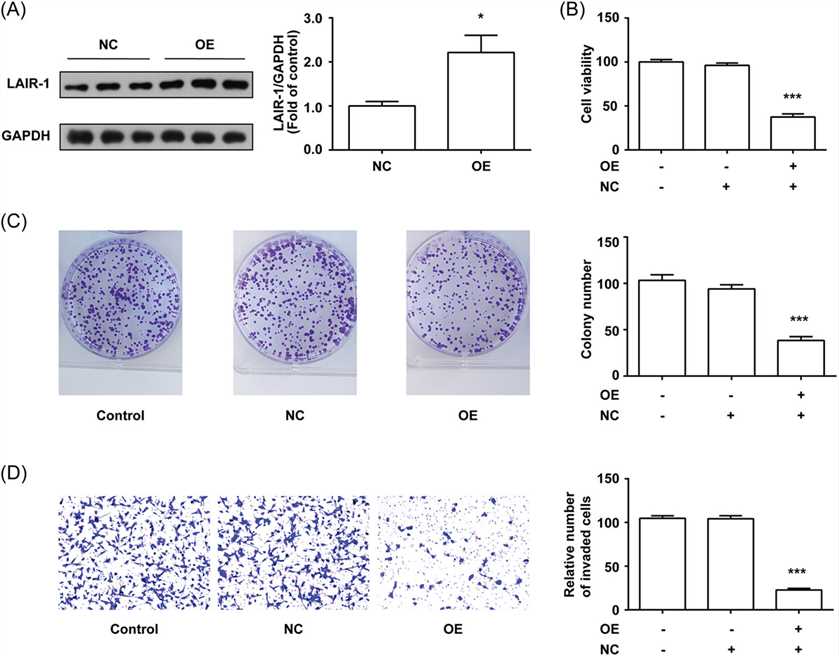 Fig.2 LAIR-1 inhibited Huh-7 cells viability, colony formation, and invasion.
Fig.2 LAIR-1 inhibited Huh-7 cells viability, colony formation, and invasion.References
- Van Laethem F, Donaty L, Tchernonog E, et al. LAIR1, an ITIM-Containing Receptor Involved in Immune Disorders and in Hematological Neoplasms. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(24):16136.
- Guo N, Zhang K, Gao X, et al. Role and mechanism of LAIR-1 in the development of autoimmune diseases, tumors, and malaria: A review. Curr Res Transl Med. 2020;68(3):119-124.
- Joseph C, Alsaleem MA, Toss MS, Kariri YA, Althobiti M, Alsaeed S, Aljohani AI, Narasimha PL, Mongan NP, Green AR, et al. The ITIM-Containing Receptor: Leukocyte-Associated Immunoglobulin-Like Receptor-1 (LAIR-1) Modulates Immune Response and Confers Poor Prognosis in Invasive Breast Carcinoma. Cancers. 2021; 13(1):80.
- Xie J, Gui X, Deng M, et al. Blocking LAIR1 signaling in immune cells inhibits tumor development. Front Immunol. 2022;13:996026.
