TUBB4A
-
Official Full Name
tubulin, beta 4A class IVa -
Synonyms
TUBB4A;tubulin, beta 4A class IVa;TUBB4, tubulin, beta 4 , tubulin, beta 4 class IVa;tubulin beta-4 chain;beta 5;class IVa beta tubulin;Beta 4;Beta 4 tubulin;MC1R;TBB4_HUMAN;TUB B4;TUBB 4;TUBB4;TUBB5;Tubulin 5 beta;Tubulin beta 3;Tubulin beta 4;Tubulin beta 4 chain;Tubulin beta 5;Tubulin beta IV;tubulin, beta, 5;class IVa beta-tubulin;tubulin, beta 4 class IVa;beta-5
Recombinant Proteins
- Cynomolgus
- Mouse
- Human
- Mammalian Cells
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Yeast
- His
- Non
- Flag
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is TUBB4A Protein?
TUBB4A is part of the β-tubulin group, which helps build microtubules, the structures that give cells shape and support. These structures are crucial for cell movement and division. Normally, TUBB4A isn't found in high amounts in most tissues, but it shows up more in certain cancers, like prostate cancer, where it links to aggressive behavior and worse outcomes. In cancer, TUBB4A helps cells grow, move, and shield their DNA during stress. By digging into TUBB4A's role, researchers aim to find new ways to tackle cancer, focusing on how it affects tumor growth and spread.What is the Function of TUBB4A Protein?
TUBB4A is a protein that helps form microtubules, acting like scaffolding inside cells to maintain their shape and support their movement and division. This protein is key to building and stabilizing these structures, ensuring cells function properly. While TUBB4A is low in most normal tissues, it becomes more significant in certain cancers, where it can affect how aggressively cancer cells grow and spread. By looking into TUBB4A’s function, researchers aim to figure out how cells normally work and what happens when things go wrong, like in cancer. This understanding could lead to new treatments by targeting how TUBB4A contributes to disease.TUBB4A Related Signaling Pathway
The TUBB4A protein is part of some crucial signaling pathways that are essential for cell stability and function. It plays a role in the pathways that oversee the organization of microtubules, which are vital for keeping cells in shape and helping them divide properly. In cancer, these pathways can become more active, with TUBB4A contributing to changes that make cancer cells grow and move more aggressively. One key pathway involving TUBB4A interacts with proteins like MYH9 to protect cells’ DNA under stress. When something disrupts this pathway, it can lead to issues like increased DNA damage or altered cell signaling. By exploring the TUBB4A-related pathways, researchers are trying to understand better how cells maintain balance and what goes awry in diseases like cancer. This could open doors to new treatments that specifically target these pathways to control or prevent cancer progression.TUBB4A Related Diseases
TUBB4A is linked to some important health problems, especially neurological disorders and cancer. For certain brain conditions, changes in the TUBB4A gene can cause issues like dystonia, where muscles tighten and move without control, or other movement challenges. These genetic changes may affect the brain's white matter, which has a role in managing coordination and muscle control. On the cancer front, high levels of TUBB4A are found in certain aggressive types, such as prostate cancer. Here, TUBB4A might encourage faster tumor growth and spread, complicating treatment efforts. Researchers are digging into how TUBB4A functions in these diseases to better understand its roles and to potentially uncover new ways to treat or manage these conditions by targeting the protein or its pathways.Bioapplications of TUBB4A
TUBB4A is grabbing attention in medical research, especially for neurological issues and cancer. Scientists are exploring how it plays a role in these conditions to develop better treatments. In neurology, understanding TUBB4A might lead to new therapies for movement disorders caused by gene changes. In cancer, especially prostate cancer, TUBB4A could help identify aggressive tumors and guide treatment strategies. Since it helps form cell structures, TUBB4A is also a potential target for drugs designed to stop cancer cells from growing and spreading. Overall, its study opens up new possibilities for treating brain disorders and cancer.Case Study
Case Study 1: Liang X. et al. Cell Discov. 2024
Researchers found that a long noncoding RNA, TubAR, plays a role in microtubule assembly, especially in the cerebellum. It interacts with tubulins TUBB4A and TUBA1A, which are important for brain function. When TubAR is reduced in mice, it leads to brain cell loss, demyelination, and movement issues. TubAR helps TUBB4A and TUBA1A pair up for microtubule formation. Interestingly, the TUBB4A-R2G mutation allows these tubulins to interact without TubAR. Restoring this pairing with specific mutations can counteract the negative effects of TubAR loss.-
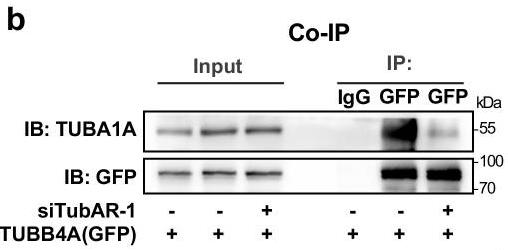 Fig1. Co-IP showing decreased interaction of TUBB4A–TUBA1A in Neuro-2a cell.
Fig1. Co-IP showing decreased interaction of TUBB4A–TUBA1A in Neuro-2a cell. -
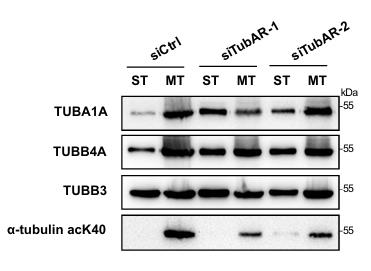 Fig2. Distribution of TUBA1A, TUBB4A, and TUBB3 in soluble tubulin fraction or microtubule fraction.
Fig2. Distribution of TUBA1A, TUBB4A, and TUBB3 in soluble tubulin fraction or microtubule fraction.
Case Study 2: Gao S. et al. Nat Commun. 2022
TUBB4A is low in most tissues but high in aggressive prostate cancer, especially in African-American men, linking to worse survival. Knocking out TUBB4A in cancer cells slows their growth and increases DNA damage. It partners with MYH9 to protect cells under stress. Losing TUBB4A disrupts this protection, leading to severe DNA damage and less NF-κB activity. TUBB4A affects pathways like β-catenin by influencing MYH9 and GSK3β. Deleting TUBB4A reduces tumor growth and spread by affecting key signaling pathways, including NF-κB and c-MYC.-
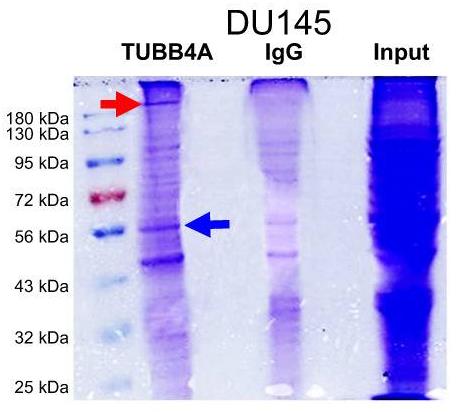 Fig3. Bands on an SDS-PAGE gel after TUBB4A protein pull-down in DU145 cells.
Fig3. Bands on an SDS-PAGE gel after TUBB4A protein pull-down in DU145 cells. -
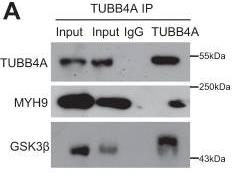 Fig4. Co-IP assay of TUBB4A in DU145 cells.
Fig4. Co-IP assay of TUBB4A in DU145 cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TUBB4A-1213HFL)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TUBB4A-1213HFL) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (TUBB4A-1942H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (TUBB4A-1942H)
Involved Pathway
TUBB4A involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways TUBB4A participated on our site, such as Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane,Assembly of the primary cilium,Cell Cycle, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with TUBB4A were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Chaperonin-mediated protein folding | TUBB4B,CCT8,CCT2,PFDN5,FBXW4,PFDN4,PFDN2,FBXW2,CCT3,CCT7 |
| Cell cycle | FGFR1OP,RUVBL2,WEE1,SMAD3A,DHFR,RAD9,CENPJ,ACD,MAD1L1,POT1 |
| Assembly of the primary cilium | EXOC6,CEP290,DYNC1I2,KIF3B,SCLT1,NPHP4,CCT2,IFT81,CCT4,MKKS |
| Cooperation of Prefoldin and TriC/CCT in actin and tubulin folding | TUBB4B,TUBA1B,CCT8,CCT2,PFDN6,PFDN1,CCT5,VBP1,PFDN4,PFDN2 |
| Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane | NPHP1,ODF2,TMEM216,AKAP9,CDK5RAP2,MAPRE1B,SDCCAG8,DCTN3,CC2D2A,CSNK1E |
| Formation of tubulin folding intermediates by CCT/TriC | CCT4,TUBA3D,CCT7,TUBA1B,TCP1,CCT2,CCT6A,CCT5,CCT3,TUBB4B |
| Cell Cycle, Mitotic | LIN37,CDKN1B,HAUS2,CSNK2A1,NINL,ZWINT,CENPI,USO1,DYNC1I2,TUBB4B |
| Centrosome maturation | OFD1,TSGA14,MAPRE1B,TUBGCP5,CSNK1E,CP110,CEP63,CLASP1,CEP290,PCM1 |
-
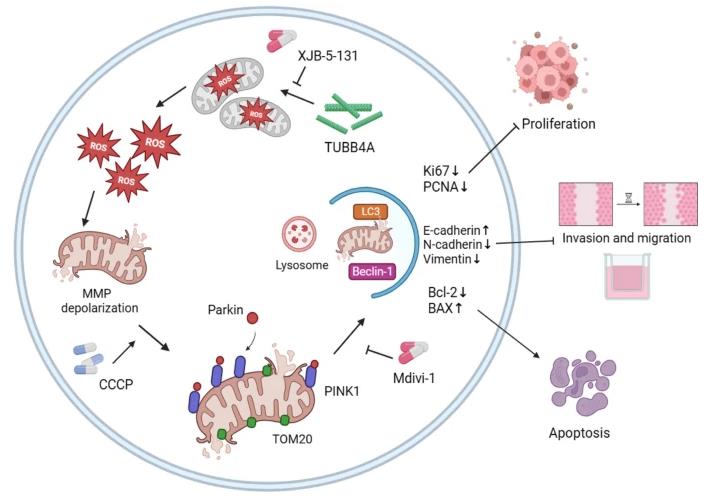 Fig1. Schematic of the mechanism by which TUBB4A inhibits glioma development. (Xueru Xi, 2025)
Fig1. Schematic of the mechanism by which TUBB4A inhibits glioma development. (Xueru Xi, 2025)
Protein Function
TUBB4A has several biochemical functions, for example, GTP binding,GTPase activity,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by TUBB4A itself. We selected most functions TUBB4A had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with TUBB4A. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| GTPase activity | TUBG2,RAB30,RHOJ,RAB27B,ARF3,EIF2S3,TRIM23,TUBA2,RHOT1,RAC3 |
| protein binding | LSM10,MRPL28,PRCC,INSR,PRAM1,PLIN1,SRPK2,GMPPB,SREBF1,CTCF |
| structural constituent of cytoskeleton | LOR,TUBA8L2,TNNT2A,COX4I2,SORBS3,NEFL,KRT16,DSP,KRT15,TUBGCP3 |
| GTP binding | RAB39B,SEPT5A,RABL2A,ARL11,RAB18B,DNM1,SPAG1,GIMAP5,ERAS,ARFRP1 |
Interacting Protein
TUBB4A has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with TUBB4A here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of TUBB4A.
LRRK2;P;NR4A1;a8k1f4_human;NFKB2;NFKBIE;IKBKB;CHUK;MAP3K7;RIPK2;TNFRSF1A;TNFRSF1B;NFKBIA;MAP3K8
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


