TRAF6
-
Official Full Name
TNF receptor-associated factor 6, E3 ubiquitin protein ligase -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the TNF receptor associated factor (TRAF) protein family. TRAF proteins are associated with, and mediate signal transduction from, members of the TNF receptor superfamily. This protein mediates signaling from members of the TNF receptor superfamily as well as the Toll/IL-1 family. Signals from receptors such as CD40, TNFSF11/RANCE and IL-1 have been shown to be mediated by this protein. This protein also interacts with various protein kinases including IRAK1/IRAK, SRC and PKCzeta, which provides a link between distinct signaling pathways. This protein functions as a signal transducer in the NF-kappaB pathway that activates IkappaB kinase (IKK) in response to proinflammatory cytokines. The interaction of this protein with UBE2N/UBC13, and UBE2V1/UEV1A, which are ubiquitin conjugating enzymes catalyzing the formation of polyubiquitin chains, has been found to be required for IKK activation by this protein. This protein also interacts with the transforming growth factor (TGF) beta receptor complex and is required for Smad-independent activation of the JNK and p38 kinases. This protein has an amino terminal RING domain which is followed by four zinc-finger motifs, a central coiled-coil region and a highly conserved carboxyl terminal domain, known as the TRAF-C domain. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants, encoding an identical protein, have been reported. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2012] -
Synonyms
TRAF6;TNF receptor-associated factor 6, E3 ubiquitin protein ligase;RNF85;MGC:3310;TNF receptor-associated factor 6;RING finger protein 85;interleukin-1 signal transducer;E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRAF6
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Zebrafish
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Chicken
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- GST
- Non
- Flag
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
- SUMO
Background

Fig1. AngII-induced MAPK/TGF-β1/TRAF6/TAK1 signaling pathway in postoperative atrial fibrillation. (Daoliang Zhang, 2017)
What is TRAF6 Protein?
TRAF6 gene (TNF receptor associated factor 6) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 11 at locus 11p12. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the TNF receptor associated factor (TRAF) protein family. TRAF proteins are associated with, and mediate signal transduction from, members of the TNF receptor superfamily. This protein has an amino terminal RING domain which is followed by four zinc-finger motifs, a central coiled-coil region and a highly conserved carboxyl terminal domain, known as the TRAF-C domain and mediates signaling from members of the TNF receptor superfamily as well as the Toll/IL-1 family. This protein functions as a signal transducer in the NF-kappaB pathway that activates IkappaB kinase (IKK) in response to proinflammatory cytokines. The TRAF6 protein is consisted of 522 amino acids and TRAF6 molecular weight is approximately 59.6 kDa.
What is the Function of TRAF6 Protein?
TRAF6 protein (TNF receptor associated factor 6) is a key signal transduction molecule belonging to the tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor family. It acts as an E3 ubiquitin ligase and acts as a signal converter in the cell. TRAF6 activates signaling pathways including NF-κB and MAPKs through its TRAF domain interaction with a variety of cell surface receptors to regulate immune response, inflammatory processes, and cell survival and apoptosis. In addition, TRAF6 promotes polyubiquitination of multiple proteins, including itself, by binding to the E2 ubiquitin binding enzyme Ubc13/Uev1A, activating downstream signaling pathways. This involves ubiquitination and phosphorylation of AKT, phosphorylation of TAK1, and cross-action through the JAK-STAT pathway.
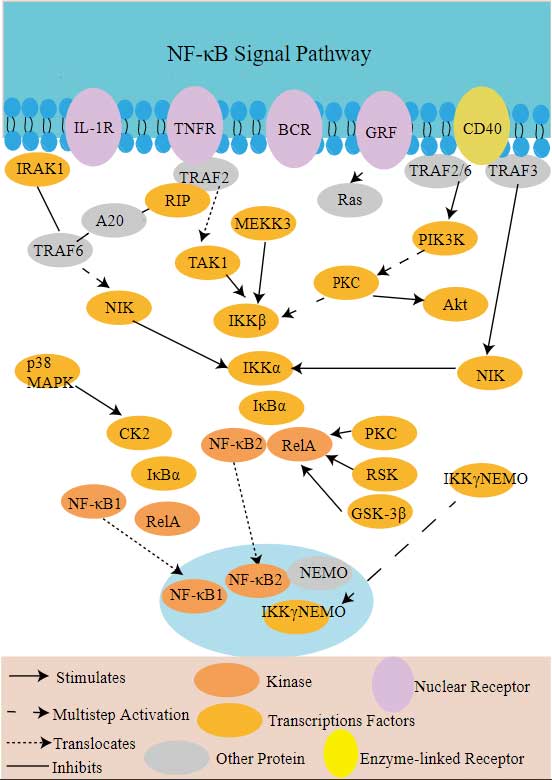
TRAF6 Related Signaling Pathway
The autoubiquitination of TRAF6 is independent of its ability to activate the NF-κB and MAPK pathways. After RANKL binds to RANK, TRAF6 triggers the NF-κB signaling pathway, leading to nuclear transfer of NF-κB and transcription of target genes through activation of IKKs. After TLRs activation, MyD88 attracts IRAK-4 to TLRs, which is subsequently activated by IRAK-1 phosphorylation and interacts with TRAF6 to activate the IKK complex, leading to the activation of MAP kinase (JNK, p38 MAPK) and NF-κB. The JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway is closely related to RANKL expression. After IL-6 binds to IL-6R, JAK kinase is activated, STAT3 is phosphorylated, and RANKL gene transcription is activated, thus a large amount of RANKL is expressed.
TRAF6 Related Diseases
Abnormal activity of TRAF6 protein has been associated with a variety of diseases, especially in autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus, where TRAF6 is involved in inflammatory responses and immune cell regulation through activation of NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways; In tumor development, TRAF6 is closely related to the occurrence and development of some cancers by promoting the proliferation, survival and metastasis of tumor cells. In addition, TRAF6 also plays a role in bone metabolism, and its dysfunction may lead to bone diseases such as osteoporosis. Therefore, TRAF6 is a target with potential therapeutic value in a variety of pathological processes.
Bioapplications of TRAF6
TRAF6 has become a hot target for drug development due to its central role in a variety of inflammatory and immune-related diseases. Currently, off-the-shelf applications for TRAF6 are focused on developing small molecule inhibitors or biologics to regulate its activity to treat autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and certain types of cancer. For example, several studies have identified compounds that block TRAF6 and its interacting partners, which inhibit the activation of NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways, reducing inflammation and tumor cell proliferation. Although no drugs specifically targeting TRAF6 are currently widely available in the clinic, advances in research in this area offer hope for new strategies to treat these diseases in the future.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Han Xu, 2023
Ample evidence reveals that glycolysis is crucial to tumor progression; however, the underlying mechanism of its drug resistance is still worth being further explored. TRAF6, an E3 ubiquitin ligase, is well recognized to overexpress in various types of cancer, which predicts a poor prognosis. In this study, TRAF6 was expressed more significantly in the case of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) than in other of breast cancers, promoting chemoresistance to paclitaxel; that inhibited TRAF6 expression in the chemoresistant TNBC (TNBC-CR) cells enhanced the sensitivity by decreasing glucose uptake and lactate production; that TRAF6 regulated glycolysis and facilitated chemoresistance via binding directly to PKM2; and that overexpressing PKM2 in the TNBC-CR cells with TRAF6 knocked down regained significantly TRAF6-dependent drug resistance and glycolysis. Additionally, TRAF6 could facilitate PKM2-mediated glycolysis and chemoresistance in animal models and clinical tumor tissues.
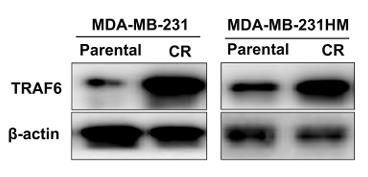
Fig1. Western blotting conducted to detect the expression of TRAF6 in TNBC parental and chemoresistant cells.
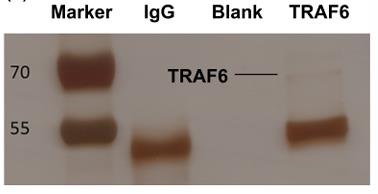
Fig2. Binding proteins of TRAF6 identified by immunoprecipitation and silver nitrate staining.
Case Study 2: Anubrita Das, 2023
For many inflammatory cytokines, the response elicited is dependent on the recruitment of the tumour necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) family of adaptor proteins. All TRAF proteins have a trimeric C-terminal TRAF domain, while at the N-terminus most TRAFs have a RING domain that forms dimers. The symmetry mismatch of the N- and C-terminal halves of TRAF proteins means that when receptors cluster, it is presumed that RING dimers connect TRAF trimers to form a network. Here, using purified TRAF6 proteins, researchers provide direct evidence in support of this model, and show that TRAF6 trimers bind Lys63-linked ubiquitin chains to promote their processive assembly.
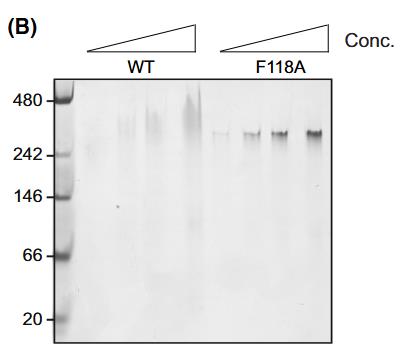
Fig3. Native PAGE gel showing oligomerisation of TRAF6 wild-type and dimer interface mutant (F118A) RZCC proteins.
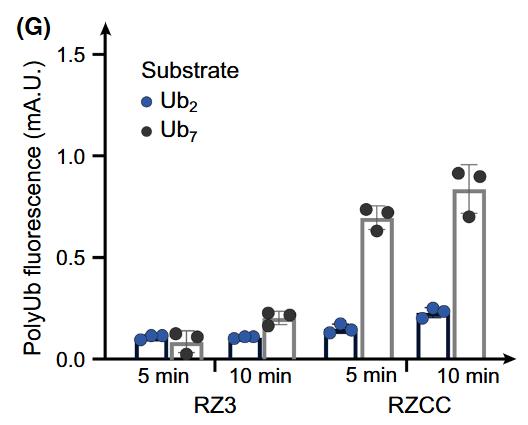
Fig4. The addition of ubiquitin to di- and hepta-ubiquitin substrates at each time point is shown for both TRAF6 RZ3 and RZCC.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TRAF6-105HFL)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (TRAF6-555H)
Involved Pathway
TRAF6 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways TRAF6 participated on our site, such as MAPK signaling pathway,NF-kappa B signaling pathway,Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with TRAF6 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Hepatitis C | IFNA16,AKT2,IFN-a,TRAF2,TRAF3,PIK3CG,PPP2CB,PIK3CA,IKBKE,RNASEL |
| Tuberculosis | H2-AA,HSPD1,IFNB1,CLEC4E,IFNA12,IFNA17,BAX,SYK,IFNA6,Il23a |
| Endocytosis | FGFR4,CHMP2BA,GRK1A,AP2M1B,HRASA,ZFYVE16,PRKCZ,CAV1,CHMP6B,CCR5 |
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | CDC42,MAP3K3,YWHAE,PSEN1,TP73,CAMK2D,NGF,CALML3,RPS6KA2,RPS6KA6 |
| MAPK signaling pathway | RASA2,PDGFAB,FGF13A,MAP2K3,NFKB2,PRKCB,FGF18,FGF9,RPS6KA6,GADD45AA |
| Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | UBE2E1,CUL1A,CBLB,TCEB2,UBE2D3,UBE2IB,UBE2N,UBE2W,FBXO4,CDC26 |
| Measles | FYN,FASLG,PRKCQ,Cd209g,IFNAR2,IFNA21,TYK2,Fasl,PIK3CB,RELA |
| Herpes simplex infection | TNF,Casp3,TLR2-1,H2-Q10,HLA-DQA1,TNFRSF1A,CYCSB,TLR2,OAS3,MAPK8A |
| Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis) | AKT2,Il2,PLCB1,MAPK13,NFKB1,IFNGR1,PPP2R1B,TLR2,PIK3CG,PPP2R2C |
Protein Function
TRAF6 has several biochemical functions, for example, histone deacetylase binding,identical protein binding,ligase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by TRAF6 itself. We selected most functions TRAF6 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with TRAF6. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| ubiquitin protein ligase activity | MED31,CDC42,RNF222,MED24,RNF19A,MSL2A,TOPORS,UBR3,UBR5,MSL2B |
| ubiquitin-protein transferase activity | G2E3,LMO7,PRKCQ,RNF152,FLJ11011L,WWP1,MUL1B,TRAF7,MARCH1,TRIM24 |
| ubiquitin conjugating enzyme binding | RNF40,ARIH1,RNF144A,ZMYM2,FOXL2,MARCH6,RNF180,DCUN1D3,DCUN1D2B,DCUN1D4 |
| thioesterase binding | CALM,CALM2,HAUS7,CALM1,ARF6,TRAF4,TRAF2,RAC1,TRAF3,CALM3 |
| protein binding | TLX2,TGFB2,BCL10,TFF3,MLST8,ADAMTS4,MED26,THBS2,SULT1E1,ATG16L1 |
| identical protein binding | ERN1,PCM1,TYROBP,WAS,POLG2,MMP9,PUF60,PARK2,DES,LUC7L |
| protein N-terminus binding | EXOC4,MYO7A,TSC1,CSNK2A2,ZWINT,TARBP2,THAP7,RASSF1,KCNQ2,PDCD10 |
| ubiquitin protein ligase binding | LYN,GPR19,SMAD3,PRKACB,UCHL1,PER1,UBE2O,BCL2,TRIB3,VCP |
| ligase activity | BIRC7,PJA1,RANBP2,PET112L,HLTF,MGRN1,BIRC3,TRIM63,RNF138,RNF14 |
Interacting Protein
TRAF6 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with TRAF6 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of TRAF6.
TRAF2;TAX1BP1;TRAF5
TRAF6 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Research Area
E3 Ubiquitin LigasesIL-1 Family Signaling Molecules
IL-17 Signaling Related Molecules
Related Services
Related Products
References