Tfpi
-
Official Full Name
Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor) -
Overview
Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (or TFPI) is a single-chain polypeptide which can reversibly inhibit Factor Xa (Xa) and Thrombin (Factor IIa). While Xa is inhibited, the Xa-TFPI complex can subsequently also inhibit the FVIIa-tissue factor complex. TFPI contributes significantly to the inhibition of Xa in vivo, despite being present at concentrations of only 2.5 Nm. This gene encodes a protease inhibitor that regulates the tissue factor (TF)-dependent pathway of blood coagulation. The coagulation process initiates with the formation of a factor VIIa-TF complex, which proteolytically activates additional proteases (factors IX and X) and ultimately leads to the formation of a fibrin clot. The product of this gene inhibits the activated factor X and VIIa-TF proteases in an autoregulatory loop. The encoded protein is glycosylated and predominantly found in the vascular endothelium and plasma in both free forms and complexed with plasma lipoproteins. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene have been described, but the full-length nature of some of these variants has not been confirmed. -
Synonyms
TFPI;EPI;TFI;LACI;TFPI1;tissue factor pathway inhibitor;anti-convertin;extrinsic pathway inhibitor
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Mouse
- Rat
- Rabbit
- HEK293
- E.coli
- Human Cells
- Rabbit
- Insect Cells
- Baculovirus
- Yeast
- His
- GST
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is TFPI protein?
TFPI gene (tissue factor pathway inhibitor) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 2 at locus 2q32. This gene encodes a Kunitz-type serine protease inhibitor that regulates the tissue factor (TF)-dependent pathway of blood coagulation. The coagulation process initiates with the formation of a factor VIIa-TF complex, which proteolytically activates additional proteases (factors IX and X) and ultimately leads to the formation of a fibrin clot. The product of this gene inhibits the activated factor X and VIIa-TF proteases in an autoregulatory loop. The TFPI protein is consisted of 304 amino acids and TFPI molecular weight is approximately 35.0 kDa.
What is the function of TFPI protein?
TFPI is a key natural anticoagulant protein that directly inhibits the activity of factor Xa and factor VIIa/tissue factor complexes through its Kunitz type domain, thereby controlling the initiation phase of blood coagulation. TFPI is expressed on a variety of cell surfaces and works synergistically with protein S to enhance its ability to inhibit Xa. It plays a vital role in maintaining blood flow and preventing thrombosis, and is also involved in the regulation of vascular inflammation, tumor growth and metastasis. The expression level of TFPI changes in some diseases, such as increased expression in atherosclerosis, and reduces mortality by improving symptoms in diseases such as sepsis and DIC. In addition, TFPI has anti-inflammatory effects and may be used to inhibit intimal hyperplasia and postoperative deep vein thrombosis.
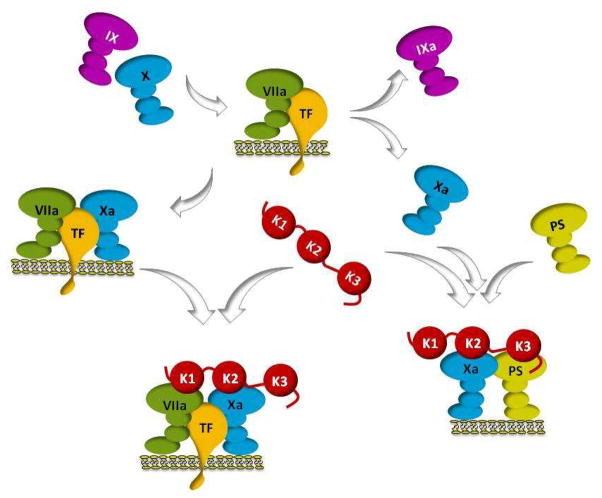
Fig1. Functions of TFPI. (George J Broze Jr, 2012)
TFPI related signaling pathway
TFPI is a key regulatory protein involved in the coagulation cascade, primarily functioning to inhibit the tissue factor-mediated activation of coagulation factors VIIa and Xa. This inhibition helps maintain blood fluidity by preventing excessive clot formation. TFPI achieves this through direct binding to these activated factors, effectively blocking their interaction with other components of the coagulation pathway. Additionally, TFPI plays a role in modulating inflammation and angiogenesis, demonstrating its significance beyond mere anticoagulation. Dysregulation of TFPI signaling can lead to thrombotic disorders, highlighting its importance in maintaining hemostasis.
TFPI related diseases
TFPI is a key natural anticoagulant protein that controls the initiation phase of blood clotting by inhibiting the activity of factor Xa and factor VIIa/tissue factor complexes. TFPI plays a role in a variety of diseases, including atherosclerosis, infectious diseases, malignancies, cardiovascular diseases, and pregnancy-related conditions such as preeclampsia and HELLP syndrome. Expression levels of TFPI may vary in these diseases, making it a potential biomarker and therapeutic target.
Bioapplications of TFPI
As a natural anticoagulant protein, TFPI controls the initiation phase of blood clotting by inhibiting the activity of factor Xa and factor VIIa/tissue factor complexes. It plays a role in the treatment of atherosclerosis, infectious diseases, malignancies, cardiovascular diseases, and pregnancy-related diseases, and is a potential biomarker and therapeutic target in the research and treatment of these diseases
In addition, the application of TFPI in the treatment of hemophilia also shows potential. By inhibiting TFPI, thrombin production during clotting can be restored, thereby improving clotting function in hemophiliacs. At present, monoclonal antibody and oligonucleotide drugs targeting TFPI have been shown to improve the clotting ability of hemophilia patients in clinical trials. The advantage of these therapies is that they can be administered by subcutaneous injection, which is expected to reduce the treatment burden of patients.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Julie A Peterson, 2021
ELISA and immunofluorescence tests showed that TFPIα is found in the extracellular matrix of endothelial cells, with a distinct intracellular and matrix pattern. Flow cytometry revealed TFPIβ on the cell surface, but not TFPIα. Further confirmation of TFPIα in the matrix came from ELISA and immunohistochemistry on umbilical cord veins. The C terminus of TFPIα binds to glycosaminoglycans in the matrix, and this binding can be competed by a VEGF peptide, indicating a role in modulating VEGF responses. TFPIα also interacts with specific extracellular matrix proteoglycans, as shown by immunofluorescence in the human kidney. The findings suggest that TFPIα is associated with unique proteoglycan structures rather than being present on the cell surface.
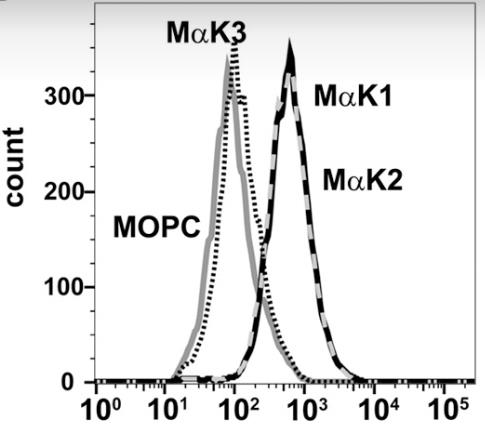
Fig1. Flow cytometry was used to identify TFPIα and TFPIβ on the surface of suspended Ea.hy926 cells.
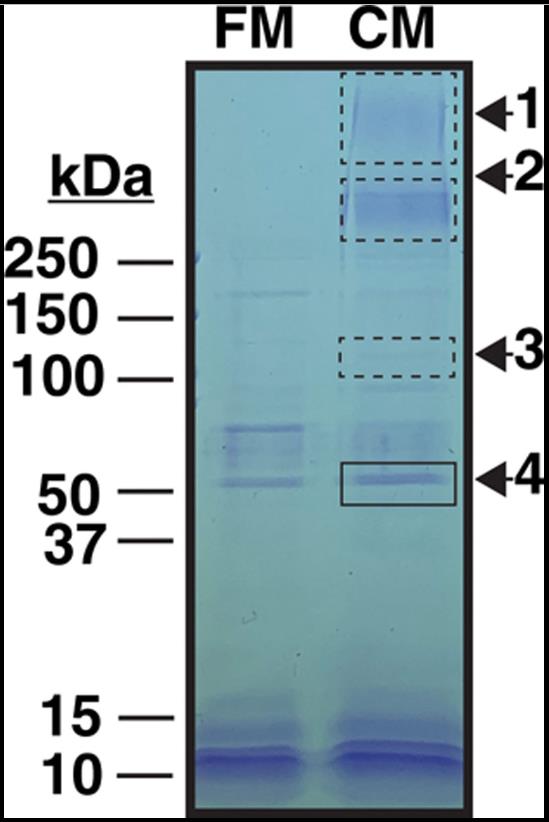
Fig2. Proteins removed from Ea.hy926 conditioned media by the TFPI (tissue factor pathway inhibitor) α C terminus.
Case Study 2: Ann Jeffers, 2015
Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) is a key regulator of the extrinsic coagulation pathway, and its activity can be influenced by pathophysiological factors. Researchers investigated the regulation of TFPI by thrombin in human pleural mesothelial cells (HPMCs) and found that thrombin significantly reduces TFPI expression by over 70%. This reduction enhances factor X activation. The effect of thrombin on TFPI is mediated by protease-activated receptor (PAR)-1 and involves the PI3K/Akt and NF-κB signaling pathways. This study reveals a new mechanism by which thrombin controls TFPI expression in HPMCs, potentially promoting a procoagulant response.
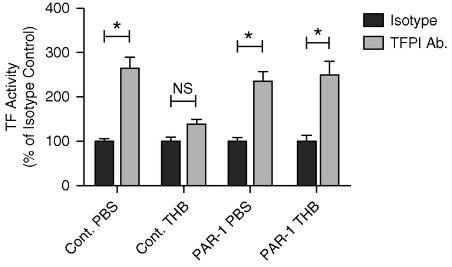
Fig3. Cell surface TF activity was determined in the presence of TFPI neutralizing antibody or isotype control.
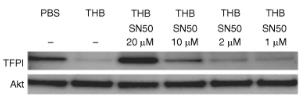
Fig4. CM were resolved by SDS-PAGE and probed for changes in TFPI protein expression.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TFPI-106H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (TFPI-646HB)
Involved Pathway
Tfpi involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Tfpi participated on our site, such as Complement and coagulation cascades, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Tfpi were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Complement and coagulation cascades | SERPINA1D,C3AR1,SERPIND1,GM5077,C7,F2,SERPINA1,KLKB1,PLAT,SERPING1 |
Protein Function
Tfpi has several biochemical functions, for example, endopeptidase inhibitor activity,serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Tfpi itself. We selected most functions Tfpi had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Tfpi. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity | TFPI2,A1i3,CCNH,RECK,PI3,SERPINB9,Serpina1b,SERPINB6,SERPINB1L2,WFIKKN2 |
| endopeptidase inhibitor activity | C3A.3,USP14,SERPINA1A,Cstb,CAST,SERPIND1,CST14B.1,SLPI,PSMF1,A1i3 |
Interacting Protein
Tfpi has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Tfpi here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Tfpi.
ssrna_ug
Resources
Research Area
Serine Proteases and RegulatorsCoagulation Cascade Protease Inhibitors
Endothelial Cell Coagulation Molecules
Inflammatory Mediators
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Luna, E; Agrawal, P; et al. Evaluation of Immunostimulatory Potential of Branded and US-Generic Enoxaparins in an In Vitro Human Immune System Model. CLINICAL AND APPLIED THROMBOSIS-HEMOSTASIS 21:211-222(2015).
- Franchini, M; et al. Next-generation treatment of acquired hemophilia A. EXPERT OPINION ON ORPHAN DRUGS 3:245-251(2015).



