SQSTM1
-
Official Full Name
sequestosome 1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- GST
- His
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
- Flag
Background
What is SQSTM1 Protein?
The SQSTM1 protein, commonly called sequestosome 1 or p62, is key in maintaining cellular function. It is encoded by the SQSTM1 gene and has a vital role in autophagy, a process where cells clean out damaged components. This function is crucial as it helps in tagging damaged proteins for breakdown, ensuring the cell remains healthy. p62 has the ability to bind with numerous proteins, directing them towards degradation, which is important in regulating aging and other cellular functions. Notably, interactions with proteins like GATA4 can inhibit aging processes in cells. Changes in the SQSTM1 gene are often found to cause Paget's disease of bone, which can affect bone structure and strength. The presence of p62 in numerous cellular locations, from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, highlights its multiple functions, including controlling programmed cell death, immune response, and stress. Furthermore, its involvement in mitophagy, the specific breakdown of mitochondria, underscores its essential role in managing cellular health and energy regulation.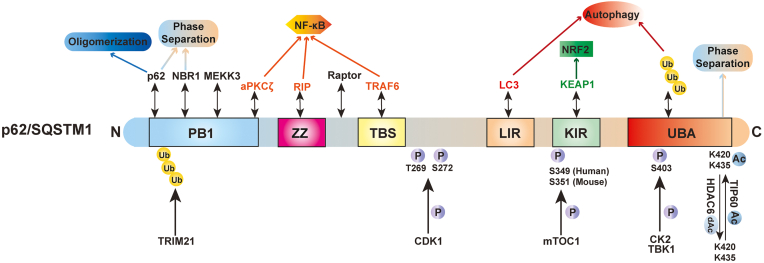
Fig1. Schematic domain structure of sequestosome 1 (SQSTM1/p62). (Hui Qian, 2023)
What is the Function of SQSTM1 Protein?
The protein SQSTM1, often referred to as p62, is quite a multitasker when it comes to the inner workings of cells. It's heavily involved in autophagy, which is the process that breaks down and recycles parts of the cell that are no longer needed or are damaged. This is vital for keeping cells tidy and functional. p62 acts like a bridge to the NF-kB signaling pathway too, which is key in managing how the body responds to stress and fights off infections. You'll find p62 everywhere in the cell, from the cytoplasm to lysosomes, emphasizing its role in various essential functions. Interestingly, changes in the SQSTM1 gene can be linked to Paget's disease of bone, a condition affecting bone structure. Beyond cleaning up cells, p62 helps with signaling and getting rid of unnecessary proteins, showing just how crucial it is for healthy cell operations.SQSTM1 Related Signaling Pathway
The protein SQSTM1, often called p62, has a strong connection to the NF-kB signaling pathway, which is vital for the way our body manages stress and fights infections. Functioning as a kind of adaptor or scaffold, p62 assists in passing on signals inside cells, especially within the NF-kB pathway. This pathway plays an essential role in controlling how the immune system reacts and how inflammation is handled. It essentially facilitates the movement and activation of various proteins involved in this pathway, enabling cells to react appropriately to different signals. This function is vital, especially in conditions related to immune system function and inflammation. Moreover, any mutations in the SQSTM1 gene can influence these signaling pathways and are linked to diseases like Paget's disease of bone, emphasizing its essential role in maintaining bone health and overall cellular communication pathways.SQSTM1 Related Diseases
The SQSTM1 gene, better known for encoding the p62 protein, is linked to a few notable health issues. One of the primary conditions associated with mutations in this gene is Paget's disease of bone, where bones become enlarged and brittle over time. Both inherited and random forms of this disease can stem from changes in SQSTM1. In addition, changes in the SQSTM1 gene have been linked to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), a condition that impacts nerve cells and results in muscle weakness. SQSTM1 also takes part in important cellular activities, such as managing the body's inflammation and stress reactions, further influencing how the immune system functions. Understanding these connections is key for developing therapies and interventions for these related disorders.Bioapplications of SQSTM1
SQSTM1, or sequestosome 1, plays a significant role in various biotechnological applications, primarily centered on its involvement in autophagy—a natural process to clean up damaged cells. This feature makes it useful in studying the mechanisms of diseases where protein aggregation is an issue, such as certain neurodegenerative disorders. Researchers utilize p62 in applications aiming to understand how cells handle stress and accumulate damaged proteins, potentially leading to therapeutic strategies that can activate or mimic autophagy processes. Moreover, its role in regulating immune responses gives SQSTM1 a spotlight in developing treatments for inflammatory conditions. In cancer research, understanding SQSTM1’s actions can lead to novel approaches in tackling tumor growth and resistance, offering insights into how cells survive under duress by either suppressing or promoting autophagy pathways.Case Study
Case Study 1: Li Z. et al. Sci Rep. 2024
Researchers identified that macrophages defend against Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), with increased circRNA_SLC8A1 in infected cells. They explored its role in fighting TB and found elevated circRNA_SLC8A1 in TB patients. Using StarBase and experiments, they confirmed that miR-20b-5p targets circRNA_SLC8A1 and SQSTM1/p62 mRNA, noting that miR-20b-5p decreases while SQSTM1 increases in Mtb-exposed macrophages. Adjusting circRNA_SLC8A1, miR-20b-5p, and SQSTM1 levels showed that high circRNA_SLC8A1 or miR-20b-5p inhibitors enhanced inflammatory factors, NO, and iNOS, reduced ROS, and cell death, aiding Mtb survival. SQSTM1 silencing reduced inflammation and blocked NF-κB, while miR-20b-5p elevation stopped circ-SLC8A1 from boosting SQSTM1.-
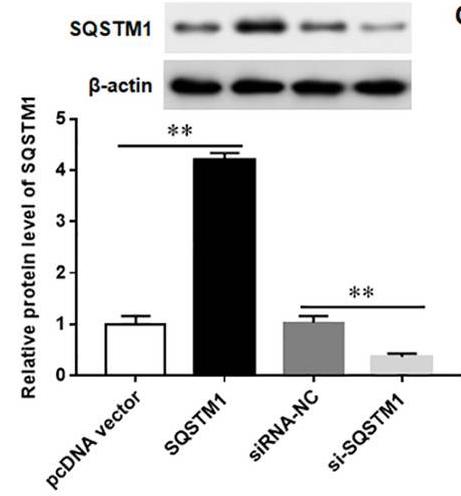 Fig1. The protein expression of SQSTM1/p62 was detected with Western blotting.
Fig1. The protein expression of SQSTM1/p62 was detected with Western blotting. -
 Fig2. The protein expression levels of SQSTM1/p62 were detected.
Fig2. The protein expression levels of SQSTM1/p62 were detected.
Case Study 2: He Q. et al. J Mol Cell Biol. 2023
Researchers noted that pterygium, an eye condition, involves fibrovascular overgrowth and reduced autophagy in affected tissues. Using fibroblasts treated with TGF-β1, they modeled fibrosis, noting increased growth and invasion. They found that enhancing autophagy slowed fibrosis, while blocking it made it worse. The key player, SQSTM1, activates the PKCι-NF-κB pathway to speed up fibrosis. Lowering SQSTM1, PKCι, or p65 delayed the fibrosis, while boosting SQSTM1 negated treatment effects. Their findings suggest poor autophagy in fibroblasts drives fibrosis through the SQSTM1-PKCι-NF-κB pathway.-
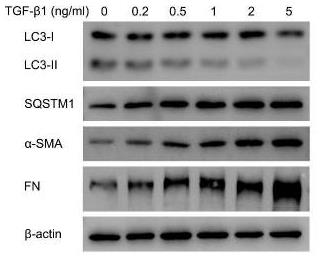 Fig3. Immunoblots showing protein levels of LC3, SQSTM1, α-SMA, and FN.
Fig3. Immunoblots showing protein levels of LC3, SQSTM1, α-SMA, and FN. -
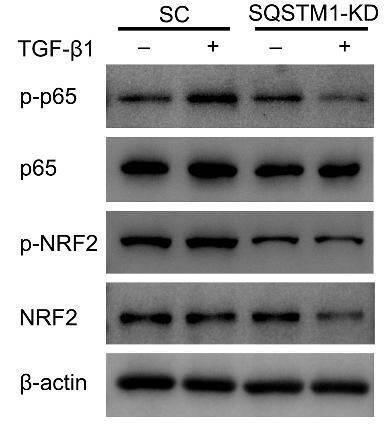 Fig4. Immunoblots showing total and phosphorylated levels of p65 and NRF2.
Fig4. Immunoblots showing total and phosphorylated levels of p65 and NRF2.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (SQSTM1-3257H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (SQSTM1-3257H) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (SQSTM1-6676H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (SQSTM1-6676H)
Involved Pathway
SQSTM1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways SQSTM1 participated on our site, such as Osteoclast differentiation, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with SQSTM1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Osteoclast differentiation | LCK,TGFBR2,LILRB4,PPP3CB,TNF,ITGB3,IFNGR2,MAPK3,IKBKB,IFNG |
-
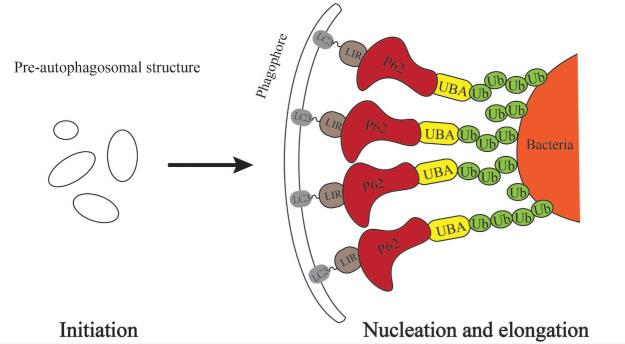 Fig1. Mechanisms in linking the bacteria to a growing phagophore. (Yuhao Zhou, 2023)
Fig1. Mechanisms in linking the bacteria to a growing phagophore. (Yuhao Zhou, 2023) -
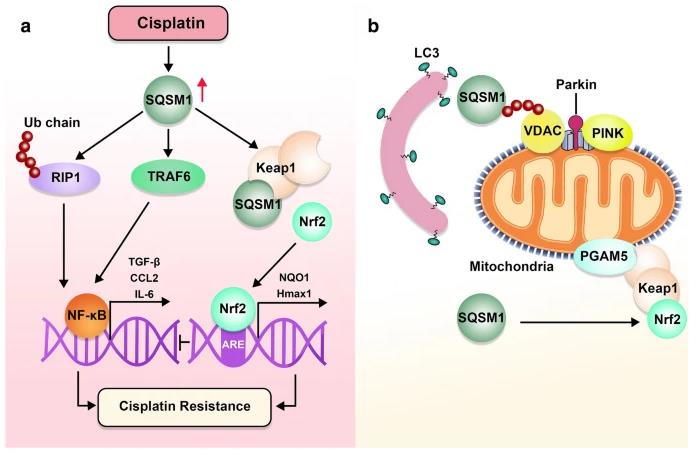 Fig2. Regulation of pro-survival signaling in ovarian cancer cells by SQSTM1. (Maryam Nurzadeh, 2023)
Fig2. Regulation of pro-survival signaling in ovarian cancer cells by SQSTM1. (Maryam Nurzadeh, 2023)
Protein Function
SQSTM1 has several biochemical functions, for example, K63-linked polyubiquitin binding,SH2 domain binding,identical protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by SQSTM1 itself. We selected most functions SQSTM1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with SQSTM1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | MYLK4,DYRK1B,MAP4K4,SRPK1A,PASK,PKZ,HIPK3,MAP3K13,VRK2,GSK3B |
| protein homodimerization activity | RIPK2,GSTM2,GSTM3,SUMF1,IKZF4,VPS4B,PAFAH1B1,GRIK1,CADM2A,STK25 |
| zinc ion binding | LNX2A,PGLYRP6,TRIM40,RNF146,ZDHHC5,PHC2A,SEC23B,ZDHHC18,RNF152,DNAJC21 |
| receptor tyrosine kinase binding | PTPN2,DNAJA3,ANGPT4,ANGPT2A,TP53,ZFP259,HYAL2,ARHGEF16,GAS6,ANGPT2 |
| protein kinase C binding | PKN1,YWHAG,NELL2,ADAM9,FEZ1,C1QBP,TWF2,PLEK,SDPR,HDAC7 |
| K63-linked polyubiquitin binding | ZRANB3,OTUD7B,PRPF8,SPRTN,IKBKG,RNF169,ATRIP,RNF168,ZRANB1,TAB2 |
| ubiquitin binding | DNAJC2,HSPB1,FAF2,SMAD3,OTUB1,RBCK1,TOP2A,CRY2,DYRK2,UBXN1 |
| identical protein binding | VWA2,VPS4B,HOOK1,ADIPOQ,SNRNP200,GUCY2E,PARK2,STXBP1,RB1,SF1 |
| ubiquitin protein ligase binding | UBE2O,VCL,PRKAR1A,ANAPC2,PACRG,FZD5,TUBA1B,BRCA1,UBE2G2,MYOD1 |
Interacting Protein
SQSTM1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with SQSTM1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of SQSTM1.
MAP1LC3B;GABARAPL2
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Whyte, MP; Madson, KL; et al. Rapid Skeletal Turnover in a Radiographic Mimic of Osteopetrosis. JOURNAL OF BONE AND MINERAL RESEARCH 29:2601-2609(2014).
- Kang, M; Jeong, CW; et al. Inhibition of Autophagy Potentiates Atorvastatin-Induced Apoptotic Cell Death in Human Bladder Cancer Cells in Vitro. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR SCIENCES 15:8106-8121(2014).


