SOX4
-
Official Full Name
SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 4 -
Overview
SOX genes comprise a family of genes that are related to the mammalian sex determining gene SRY. These genes similarly contain sequences that encode for the HMG-box domain, which is responsible for the sequence-specific DNA-binding activity. SOX genes encode putative transcriptional regulators implicated in the decision of cell fates during development and the control of diverse developmental processes. The highly complex group of SOX genes cluster at a minimum of 40 different loci that rapidly diverged in various animal lineages. At present 30 SOX genes have been identified, and members of this family have been shown to be conserved during evolution and to play key roles during animal development. Some are involved in human diseases, including sex reversal. -
Synonyms
SOX4;SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 4;transcription factor SOX-4;SRY-related HMG-box gene 4;ecotropic viral integration site 16;EVI16
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Human
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- His
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- Flag
- DDK
- Myc
Background
What is SOX4 Protein?
SOX4 is a key player in the SRY-related HMG box family of transcription factors. It's vital in embryonic development, where it influences stem cell characteristics, differentiation, and progenitor cell development. It also engages in important pathways like PI3K, Wnt, and TGFβ. In many types of cancer, SOX4 is found to be frequently amplified and overexpressed, acting like an oncogene. This contributes to processes such as cell survival, maintaining stem cell traits, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), as well as cell migration and spread. Besides cancer, SOX4 is crucial for normal processes like heart development and the formation of B lymphocytes.What is the Function of SOX4 Protein?
SOX4 is an important transcription factor from the SRY-related HMG box family. It's crucial during embryonic development, influencing stem cell traits, differentiation, and progenitor cell growth, and is part of key pathways like PI3K, Wnt, and TGFβ. In various cancers, SOX4 is often found in higher amounts, acting like an oncogene and promoting cell survival, stem cell characteristics, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), cell movement, and metastasis. But it's not just about cancer; SOX4 also plays a critical role in normal development processes, such as forming the heart and developing B lymphocytes.SOX4 Related Signaling Pathway
SOX4 influences cell functions and disease progression through its role in various signaling pathways. It activates the NF-κB pathway, which is important in the formation of inflammation-related cancers. SOX4 also affects epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by working with TGF-β and Wnt pathways, promoting tumor cell growth and spread. In liver cancer, norepinephrine can raise SOX4 levels via the PI3K/Akt pathway, boosting the cancer cells' ability to self-renew. These roles highlight SOX4's significance in how cancer starts and develops.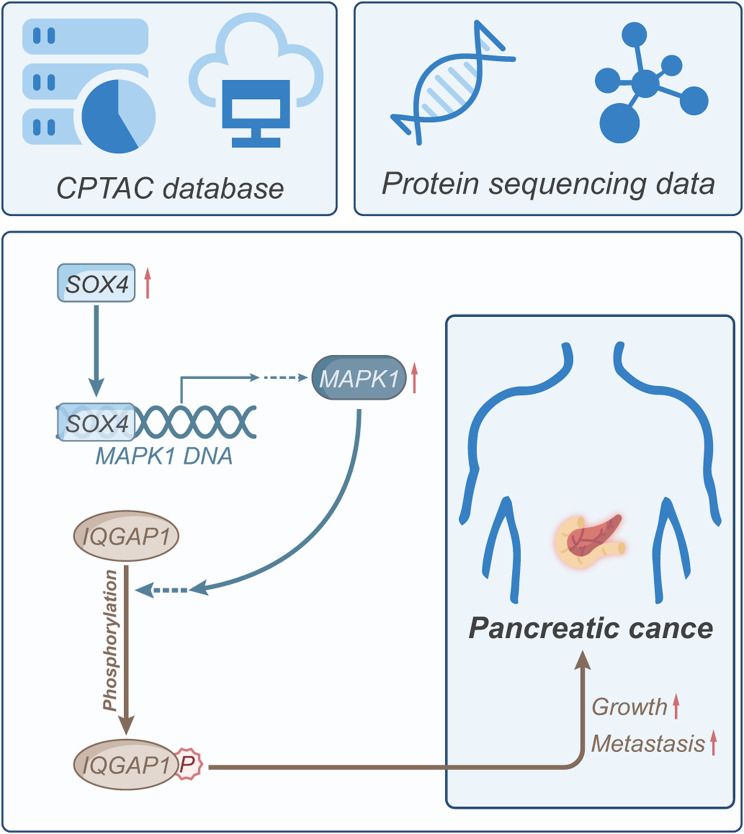
Fig1. Schematic diagram illustrating the molecular mechanisms by which SOX4 regulates MAPK1-IQGAP1 phosphorylation to influence pancreatic cancer growth and metastasis. (Chao Song, 2024)
SOX4 Related Diseases
SOX4 is connected to many diseases, particularly in cancer. It acts as an oncogene located on chromosome 6 and is often increased in cancers like lung, ovarian, bladder, triple-negative breast, liver, prostate, and stomach cancer. In these cancers, SOX4 is tied to how tumors grow, move, and spread. Apart from cancer, SOX4 is important in heart development, and changes in its levels are linked to heart issues like cardiomyopathy and heart failure. This shows that SOX4 plays a key role in how diseases develop and could be a target for treatment.Bioapplications of SOX4
SOX4 protein plays a significant role across research, industrial, and clinical domains. It's a crucial transcription factor in cancer research, especially in understanding its overexpression in various cancers and its links to EMT and stem cell traits. In industry, recombinant SOX4 is essential for creating experimental reagents and research tools. Clinically, it's eyed as a potential biomarker for several cancers, with high expression often indicating poor prognosis, highlighting its promise in diagnosis and treatment strategies.Case Study
Case Study 1: Nagaoka Y. et al. Mol Biol Rep. 2024
SOX4, part of the SOX family of transcription factors, is key to several biological processes throughout life. In adults, it's found in the skin and is linked to wound healing, tumor growth, and metastasis. This study focused on how SOX4 affects keratinocyte changes. Researchers created a keratinocyte cell line that overexpresses SOX4 when treated with doxycycline (DOX). Under this treatment, cells changed from a pavement-like shape to a spindle shape. RNA sequencing showed SOX4 increased genes tied to morphogenesis and cell differentiation while reducing those for epithelial formation, pointing to an EMT-like switch in keratinocytes. RNA-seq findings, verified by qRT-PCR, indicated a drop in epithelial markers (KRT15, KRT13, KRT5, CLDN1) and a rise in the mesenchymal marker FN1. Western blotting confirmed these shifts, showing reduced epithelial proteins and increased mesenchymal proteins like fibronectin. Removing DOX reversed these effects, restoring original marker levels.-
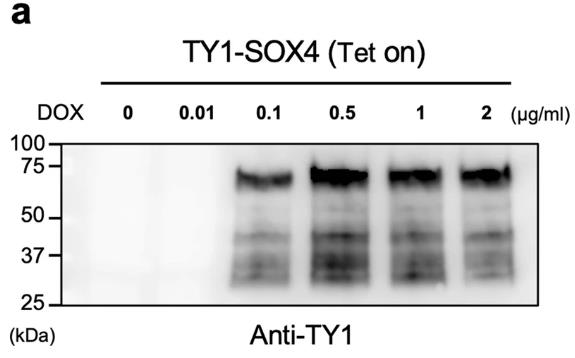 Fig1. Western blot image of DOX-dependent TY1-SOX4 protein expression.
Fig1. Western blot image of DOX-dependent TY1-SOX4 protein expression. -
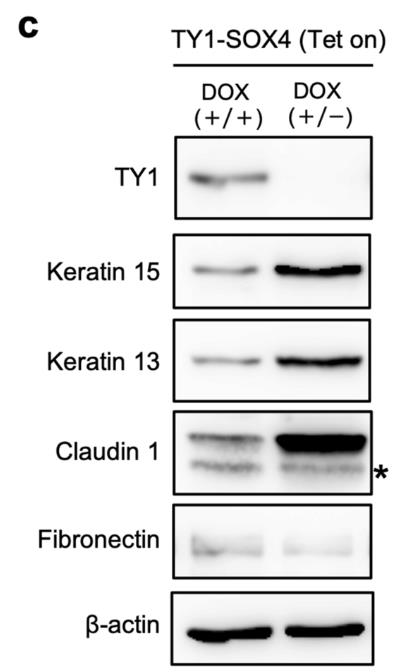 Fig2. Western blot image of the epithelial markers (keratin15, keratin13, and claudin1) and the mesenchymal marker fibronectin in DOX(+/+) and DOX(+/−) cells.
Fig2. Western blot image of the epithelial markers (keratin15, keratin13, and claudin1) and the mesenchymal marker fibronectin in DOX(+/+) and DOX(+/−) cells.
Case Study 2: Yang J. et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020
Transfer RNAs (tRNAs), made by RNA polymerase III, are vital for translating mRNA, leading to cell growth and division. The specific regulation of individual tRNA genes is still unclear. This study reveals that SOX4, known for its role as a Pol II transcription factor in neurogenesis and reprogramming, also surprisingly regulates some tRNA genes, affecting protein synthesis and growth in human glioblastoma cells. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing, we found SOX4 specifically targets certain tRNA genes, like tRNAiMet. SOX4 binds in a sequence-specific manner, hampering TATA box binding protein and Pol III from accessing these genes, thereby repressing them. When tRNAiMet is down-regulated using CRISPR/Cas9, glioblastoma cell growth slows down significantly. On the other hand, adding extra tRNAiMet can partially counteract SOX4's suppression of cell proliferation.-
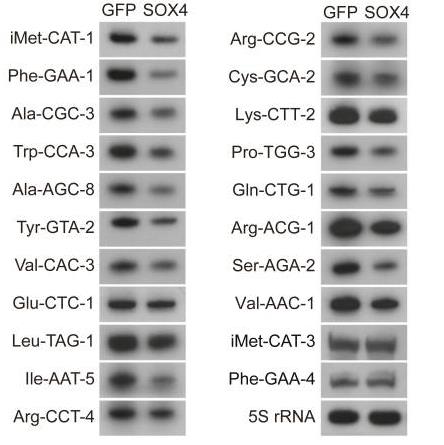 Fig3. Representative images of Northern blots for the indicated tRNAs at 3 dpi.
Fig3. Representative images of Northern blots for the indicated tRNAs at 3 dpi. -
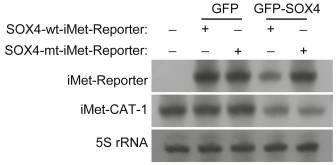 Fig4. Requirement of SOX4-binding to repress tRNA expression.
Fig4. Requirement of SOX4-binding to repress tRNA expression.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (SOX4-931H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (SOX4-931H)
Involved Pathway
SOX4 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways SOX4 participated on our site, such as MicroRNAs in cancer, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with SOX4 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| MicroRNAs in cancer | ZEB1,BCL2L2,RECK,MDM4,ZEB2,NFKB1,PLAU,ABCB1,VEGFA,CCNE1 |
-
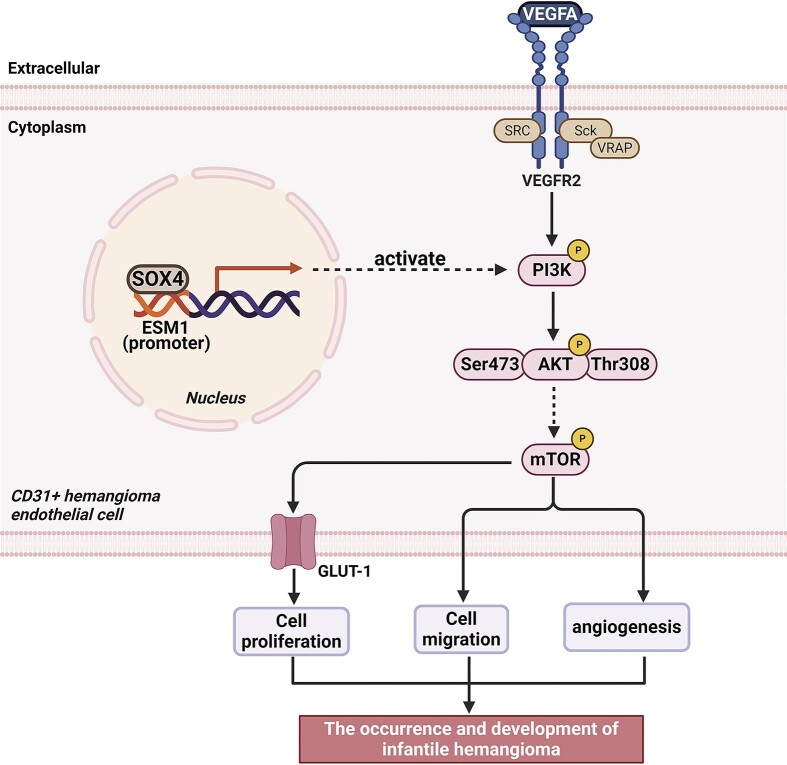 Fig1. The SOX4 protein in the nucleus of CD31+ HemECs binds to the downstream target gene ESM1, further activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. (Yanan Li, 2024)
Fig1. The SOX4 protein in the nucleus of CD31+ HemECs binds to the downstream target gene ESM1, further activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. (Yanan Li, 2024) -
 Fig2. Potential role of KIS in the development of LUAD. (Jing-Xia Chang, 2024)
Fig2. Potential role of KIS in the development of LUAD. (Jing-Xia Chang, 2024)
Protein Function
SOX4 has several biochemical functions, for example, RNA polymerase II transcription coactivator activity,core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding,nucleic acid binding transcription factor activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by SOX4 itself. We selected most functions SOX4 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with SOX4. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| transcriptional activator activity, RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific binding | MITFB,ZFP639,DLX5,IRF4,NUCKS1,MAFB,HOXC13,NR3C1,ELK3,FUBP3 |
| core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding | NR4A3,TP53,MLL1,KLF10,NR1D1,MTA1,MEOX1,SP1,NRIP1,ATF4 |
| protein binding | MSH4,ASNA1,CTBP2,HSPBAP1,CYBRD1,GATA2,CDKL3,CAP2,DOCK2,TNS3 |
| transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding | SIN3A,PSPC1,SUV39H1,BTBD8,PITX2,SOX11,NFE2L2,NFE2L2A,HDAC1,CRY2 |
| RNA polymerase II transcription coactivator activity | POU3F1,PHF17,PITX2,SMARCA4,SOX11,CREBBP,POU1F1,RERE,CITED2,CITED4 |
| nucleic acid binding transcription factor activity | GATA3 |
| protein heterodimerization activity | BNIP3,BNIP3L,HIST2H2BE,NFE2L2A,EPAS1,PKNOX1,Fzd4,HNF1A,ADRA2C,BAXB |
| transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | NR2F6A,CARF,ZFP746,HOXB4,EGR2A,TBR1,TEAD4,FOXJ1A,ELF2B,ZFP42 |
Interacting Protein
SOX4 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with SOX4 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of SOX4.
GATA3
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References



