SMOC1
-
Official Full Name
SPARC related modular calcium binding 1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Zebrafish
- HEK293
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Human Cells
- His
- GST
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is SMOC1 Protein?
SMOC1, short for SPARC-related modular calcium-binding protein 1, is a secreted protein belonging to a family known for regulating various cellular functions. It features diverse domains like follistatin-like, thyroglobulin-like, unique modular regions, and EF-hand structures for calcium binding. SMOC1 is not just a bystander; it plays pivotal roles in cells, influencing the cell cycle, extracellular matrix attachment, tissue fibrosis, calcification, and even angiogenesis. It’s also a key player in understanding how birth defects and cancer develop. In embryos, this protein is crucial for development, but it’s also a vital part of how cells cycle and form blood vessels, as well as how cancers begin and grow. SMOC1 can even affect how the liver responds to glucose, influencing glucose balance in the body. In the context of bone health, it promotes osteoblast differentiation and mineralization, while its counterpart, SMOC2, has the opposite effect. When it comes to cancer, shifts in the expression of SMOC1 and SMOC2 have been tied to the progression of several types, including gallbladder, breast, and head and neck cancers. As a result, SMOC1 is not only crucial to cellular operations but is also seen as a promising target for treatments aimed at cancer and birth defects.What is the Function of SMOC1 Protein?
SMOC1, short for SPARC-related modular calcium-binding protein 1, is a secreted protein that plays multiple roles in cellular functions. It’s crucial during embryonic development, maintaining cell balance, and understanding how diseases work. SMOC1 helps regulate things like cell cycle progress, how cells stick to the extracellular matrix, tissue scarring, calcification, blood vessel formation, birth defects, and cancer growth. In embryos, SMOC1 is vital for development post-gastrulation and helps shape anatomy by inhibiting bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling. It’s also involved in bone formation by promoting the differentiation and mineralization of osteoblasts, while SMOC2 has the opposite effect. When it comes to cancer, SMOC1 and SMOC2 affect how tumor cells interact with their environment. SMOC1 is often found at higher levels in some cancers, like oligodendrogliomas and astrocytomas. It’s also been identified as a liver factor responding to glucose and helps regulate glucose levels by inhibiting the cAMP-PKA-CREB signaling pathway in the liver, which can improve blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity. Overall, SMOC1 is a key player in many biological processes and might be a potential target for therapies in cancer and birth defects.SMOC1 Related Signaling Pathway
SMOC1 protein is quite the player in a bunch of signaling pathways related to embryonic development, cell balance, and disease processes. It interacts with the Smad signaling pathway to activate MAPK signaling, which is a key factor in joint formation. Acting as a BMP signaling antagonist, SMOC1 uses MAPK-induced Smad phosphorylation to manage the development of embryonic organs. When it comes to bone calcification, SMOC1 pushes for osteoblast differentiation and mineralization, while its counterpart SMOC2 tends to inhibit this process. SMOC1 also keeps a check on aortic valve calcification through the TGF-β signaling pathway. In terms of blood vessel formation, SMOC1 shows pro-angiogenic activity and targets anti-angiogenic microRNA-223, influencing endothelial cell sprouting and retinal vascular development. Both SMOC1 and SMOC2 contribute to angiogenesis, fibrosis, cell movement, and adhesion but differ in tissue distribution and cellular functions. Understanding SMOC1’s regulatory role in these pathways is crucial for grasping its importance in embryonic development, cell cycle regulation, vascular formation, and cancer progression.SMOC1 Related Diseases
SMOC1 is noted as a biomarker for early Alzheimer’s disease (AD), showing increased levels in brain tissue, cerebrospinal fluid, and plasma from the preclinical stages onward. It is found in amyloid plaques across AD subtypes and linked to cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA), suggesting a role beyond plaques. In colorectal cancer, SMOC1 gene methylation increases with disease progression but is rare in serrated adenomas/hyperplastic polyps, where its expression decreases only in serrated adenomas. This highlights its diagnostic potential for serrated lesions. SMOC2 aids lung cancer metastasis, with suppression reducing spread. SMOC1 is pivotal in neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, and metabolic regulation, making it crucial for research and diagnosis.Bioapplications of SMOC1
Recombinant SMOC1 protein is quite useful in science, industry, and medical research. In science, it’s vital for studying eye and limb development and acts as a regulator for bone cell differentiation. It’s also key to understanding how it affects cell-matrix interactions by interfering with growth factor signaling. In industry, it’s used to develop antibodies for experiments like Western Blot and ELISA, showing reactivity to human samples. In medical research, studying SMOC1 helps us understand its role in aortic valve calcification, Alzheimer’s, and heart muscle fibrosis. These insights point to SMOC1 as a potential therapeutic target, especially in cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases, making it crucial for advancing scientific research and medical progress.Case Study
Case Study 1: Vannahme C. et al. J Biol Chem. 2002
Our team discovered a gene called SMOC-1, which makes a modular protein that gets secreted. This protein has a special calcium-binding feature similar to one in BM-40 and also contains two thyroglobulin-like domains, a follistatin-like domain, and something entirely new. When we expressed it in human cells, we found out that SMOC-1 acts as a glycoprotein that changes its shape with calcium. Through various tests like Northern blots, RT-PCR, and immunoblots, we noticed that SMOC-1 is expressed in many different tissues. Using immunofluorescence with specific antiserum against human SMOC-1, we located the protein mainly in basement membranes and other places outside cells. Techniques like immunogold electron microscopy further confirmed its presence in the basement membranes of the kidney and skeletal muscle, and even in the zona pellucida that surrounds oocytes.-
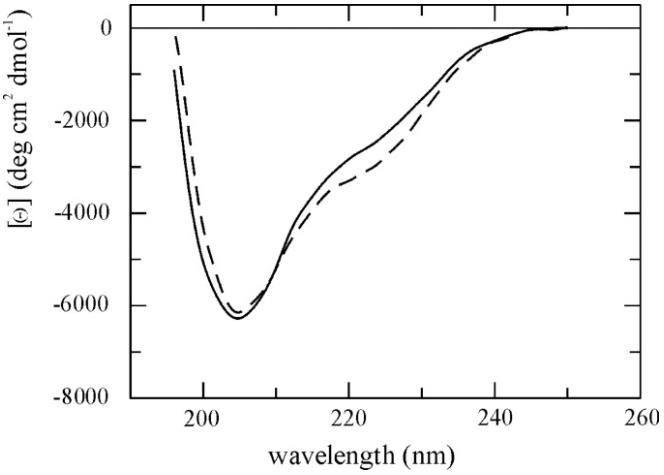 Fig1. Circular dichroism spectra of SMOC-1.
Fig1. Circular dichroism spectra of SMOC-1. -
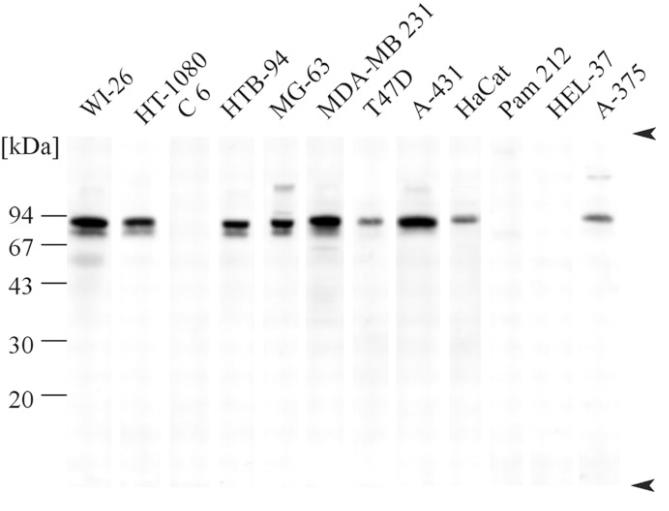 Fig2. Immunoblots of media from cultured cells.
Fig2. Immunoblots of media from cultured cells.
Case Study 2: DeGroot MS. et al. PLoS Biol. 2023
Secreted modular calcium-binding proteins (SMOCs) are essential matricellular proteins found across various species, from Caenorhabditis elegans to humans. They typically feature extracellular calcium-binding (EC) domains and thyroglobulin type-1 (TY) domains. In studies involving Drosophila and Xenopus, SMOC proteins have been observed interacting with cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs), affecting the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling pathway. Through a mix of biochemical, structural modeling, and genetic approaches, we examined the single SMOC protein in C. elegans, CeSMOC-1. We discovered that CeSMOC-1 binds to both the GPC3 homolog LON-2/glypican and the BMP2/4 homolog DBL-1. It can attach to LON-2/glypican via its EC domain and needs its entire structure to bind effectively with DBL-1/BMP. This protein functions by differently influencing BMP signaling depending on its interaction with LON-2/glypican or DBL-1/BMP. This research also showed that SMOC proteins in Drosophila and vertebrates could potentially bind mature BMP dimers, highlighting their role in modulating BMP signaling across species.-
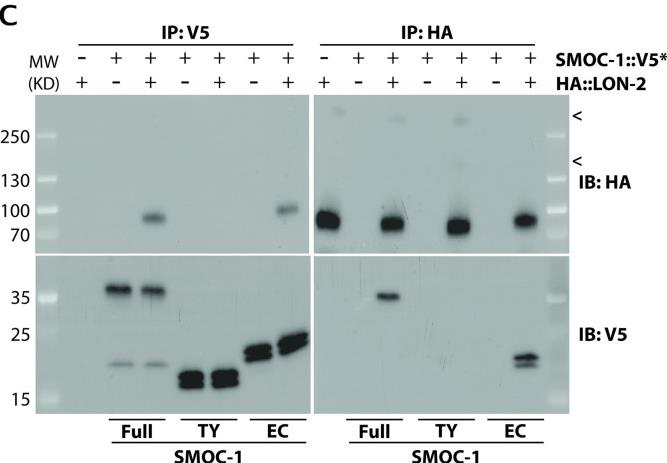 Fig3. Results of co-IP experiments testing the interaction of HA::LON-2 with different versions of SMOC-1::V5.
Fig3. Results of co-IP experiments testing the interaction of HA::LON-2 with different versions of SMOC-1::V5. -
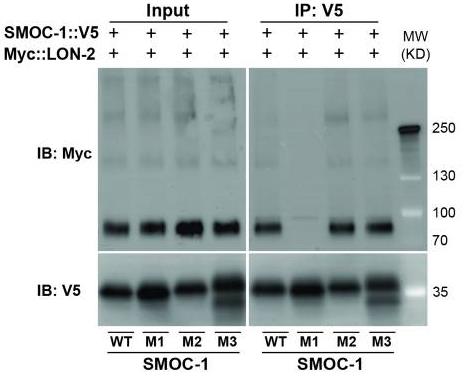 Fig4. Results of co-IP experiments testing the interaction between LON-2::Myc and V5-tagged WT and mutant SMOC-1 proteins.
Fig4. Results of co-IP experiments testing the interaction between LON-2::Myc and V5-tagged WT and mutant SMOC-1 proteins.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (SMOC1-2085H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (SMOC1-2085H)
-
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (SMOC1-024H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (SMOC1-024H)
Involved Pathway
SMOC1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways SMOC1 participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with SMOC1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
Protein Function
SMOC1 has several biochemical functions, for example, calcium ion binding,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by SMOC1 itself. We selected most functions SMOC1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with SMOC1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| calcium ion binding | CETN4,TLL2,EHD3,KCNIP3B,ANXA4,SNED1,ACTN2B,CRTAC1,DLL4,PCDH2G16 |
| protein binding | PALB2,FAM120B,GTF2I,AQP1,MGAT5B,DARS,PUM1,PSTPIP1,MAP3K4,TEN1 |
Interacting Protein
SMOC1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with SMOC1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of SMOC1.
TCF4;KRTAP10-8;NOTCH2NL;Hoxa1;bipA
Resources
Research Area
Osteoclast MarkersCalcium-binding Proteins and Related Molecules
Osteoblast and Osteoclast Markers
Extracellular Matrix Molecules
Related Services
Related Products
References


