RALA
-
Official Full Name
v-ral simian leukemia viral oncogene homolog A (ras related) -
Overview
RalA and RalB are members of the Ras family of small GTPases and are highly homologous in protein sequence. The functions of RalA and RalB are distinct yet overlapping. By binding to various effector proteins, RalA and RalB serve as important GTP sensors -
Synonyms
RALA;v-ral simian leukemia viral oncogene homolog A (ras related);RAL;ras-related protein Ral-A;Ras family small GTP binding protein RALA;RAS like protein A;Ras related protein Ral A;RAS-like protein A;MGC48949
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Human
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- His
- Non
- GST
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
Background
What is RALA Protein?
The RALA protein is like a switch inside our cells that belongs to the Ras protein family, playing a key role in various cellular processes. Imagine it as part of the cellular control room, regulating things like cell growth, movement, and survival. It switches between "on" (active) and "off" (inactive) states depending on what the cell needs. When active, RALA can help cells communicate better and respond to changes, almost like a manager directing different operations within the cell. Its role becomes particularly interesting when looking at its involvement in cancer, as it can drive certain cancerous behaviors if overactivated. Researchers are diving into understanding how exactly RALA works to find potential ways to target it for cancer therapies, making it a hot topic in cell biology and oncology.What is the Function of RALA Protein?
The RALA protein works like a cellular traffic cop, helping guide and control various processes such as cell growth, movement, and signal routing. It's part of the Ras protein family, shifting between active and inactive forms to manage how cells respond to signals. When RALA is active, it plays a crucial role in making sure cells communicate efficiently and react appropriately to their environment. It's also involved in processes like endocytosis, where the cell takes in substances, and exocytosis, where it secretes materials. In the realm of cancer research, RALA gets attention because its overactivity can push cells towards becoming cancerous, driving uncontrolled growth and movement. Scientists are keen to figure out how RALA functions in detail, aiming to tap into its regulatory roles to potentially influence cancer treatment strategies.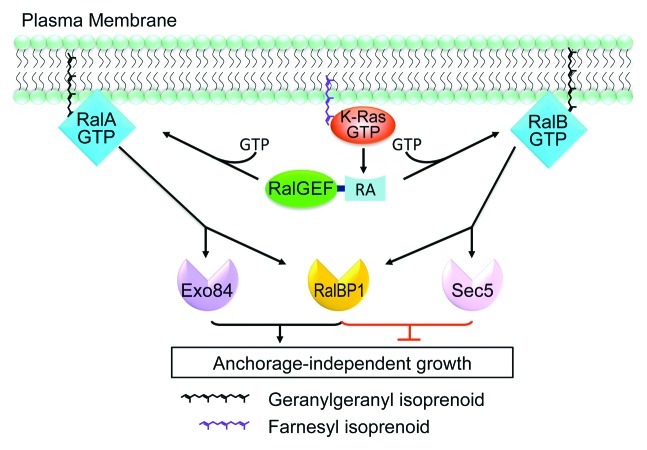
Fig1. Divergent roles for RalA and RalB in the regulation of CRC anchorage-independent growth. (Timothy D Martin, 2012)
RALA Related Signaling Pathway
The RALA signaling pathway is a bit like a communication highway inside our cells. It's part of the larger Ras family pathways that handle important messages about growth, movement, and survival. When RALA is activated, it passes down signals that tell the cell to do specific tasks, such as dividing or moving to a new location, and it plays a key role in processes like endocytosis and exocytosis. This pathway isn't working alone; it interacts with other proteins like RALBP1 and RALGDS, which help fine-tune the messages being sent. What makes the RALA pathway particularly interesting is its link to cancer. If something goes haywire, leading to overactive signaling, it can push cells to grow uncontrollably, contributing to tumor development and spread. Researchers are really interested in this pathway as they believe that targeting it could offer new ways to tackle cancer.RALA Related Diseases
RALA is a protein that's caught the eye of researchers, especially when it comes to its link with certain diseases. One of the big areas where RALA makes an impact is cancer. It plays a part in signaling pathways that can drive the growth and spread of tumors if it gets too active. This is why scientists are looking at RALA in the context of different cancers, such as pancreatic, lung, and prostate cancers. They suspect that this protein's overactivity could be encouraging cancer cells to multiply and invade other areas. Beyond cancer, RALA might also be involved in metabolic disorders. Since it has roles in cellular processes like trafficking and signaling, any imbalance could potentially contribute to other diseases. The ongoing study of RALA in these diseases might lead to new therapeutic targets, giving hope for treatments that could specifically curb its disease-promoting activities.Bioapplications of RALA
The RALA protein is turning heads in research circles, thanks to its intriguing bioapplications. In cancer treatment, it's a hot topic because of its role in helping tumors grow and spread. Scientists are keen to find ways to target RALA, with the hope of slowing down or halting cancers like lung and pancreatic cancer. Beyond its cancer connections, RALA might also be a game-changer in gene therapy. Its knack for assisting with internal cell transport opens the door to using it in delivering therapeutic genes exactly where they're needed inside cells. In regenerative medicine, RALA's involvement in processes like endocytosis might mean it could play a role in tissue repair and regeneration. These efforts underscore RALA’s potential not just in understanding diseases but also in shaping new treatments for health issues.Case Study
Case Study 1: Tian L. et al. Hepatology. 2022
RalA and RalB, part of the Ras pathway, switch between active and inactive forms. They're kept in check by RalGAP. Researchers explored their role in liver cancer (HCC) and found that RalA levels were higher in patients, linked to aggressive tumors and poor outcomes. Lowering RalA in lab tests reduced tumor growth and spread. This increase in RalA was due to extra gene copies driven by SP1 and ETS2 factors. Also, downregulating RalGAPA2 raised RalA activity, aiding cancer spread. Blocking Ral with RBC8 reduced tumor aggression and improved responses to the drug sorafenib.-
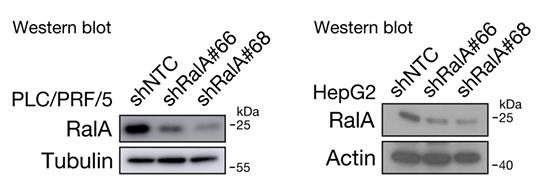 Fig1. Successful RalA KD in PLC/PRF/5 and HepG2 cells checked by western blotting.
Fig1. Successful RalA KD in PLC/PRF/5 and HepG2 cells checked by western blotting. -
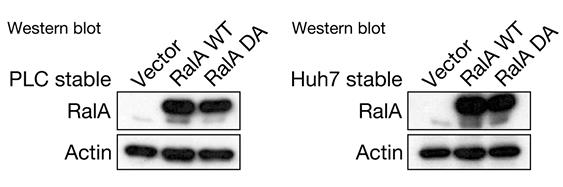 Fig2. Overexpression of RalA wild‐type (WT) or dominant active (DA) form in PLC/PRF/5 and Huh7 cells.
Fig2. Overexpression of RalA wild‐type (WT) or dominant active (DA) form in PLC/PRF/5 and Huh7 cells.
Case Study 2: Ezzeldin M. et al. Mol Oncol. 2014
RalA, a key player in the Ras pathway, gets overactive in liver cancer (HCC) compared to non-cancerous samples. Other parts like RalBP1 and RalGDS are also more expressed in cancerous tissues. Shutting down RalA with specific gene silencing greatly cut down the growth and invasiveness of HCC cells. Using inhibitors like GGTI and Aurora kinase inhibitor II also slashed HCC cell proliferation. RalA activity was especially high in CD133+ HCC stem cells. In mouse models, higher RalA-GTP levels were noted in liver tumors, and blocking the aurora kinase/RalA pathway reduced tumor growth.-
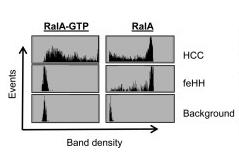 Fig3. Evaluation of band density (left) and comparing the averages (right) for RalA‐GTP in HCC cell lines.
Fig3. Evaluation of band density (left) and comparing the averages (right) for RalA‐GTP in HCC cell lines. -
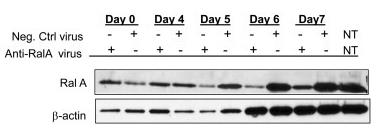 Fig4. Expression of RalA was investigated by Western blotting for this protein.
Fig4. Expression of RalA was investigated by Western blotting for this protein.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (RALA-6138H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (RALA-6138H)
Involved Pathway
RALA involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways RALA participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with RALA were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
-
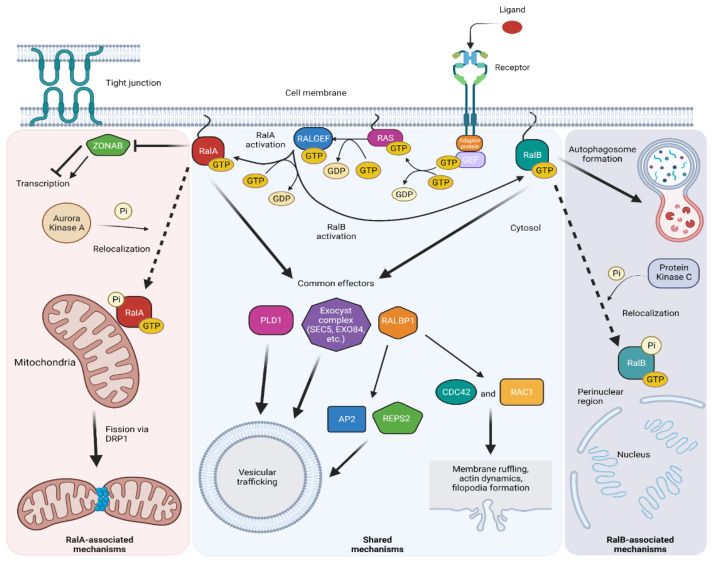 Fig1. Mechanisms of RAL signaling. (Dillon S Richardson, 2022)
Fig1. Mechanisms of RAL signaling. (Dillon S Richardson, 2022) -
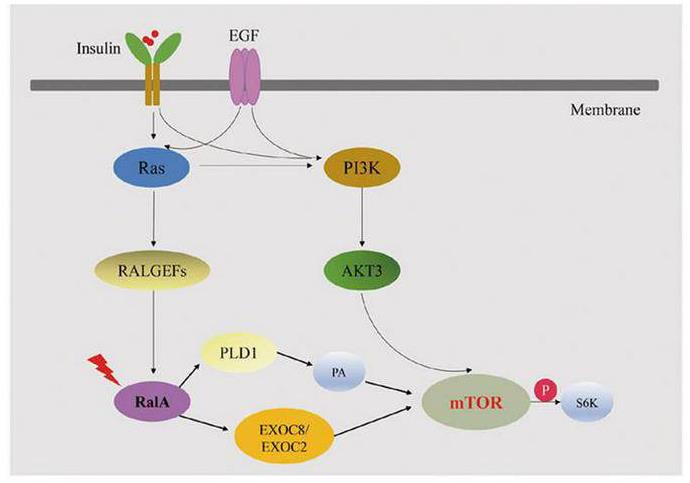 Fig2. RALA somatic variant might activate mTOR pathway through downstream effectors PLD1 or EXOC8/EXOC2. (Han Xu, 2022)
Fig2. RALA somatic variant might activate mTOR pathway through downstream effectors PLD1 or EXOC8/EXOC2. (Han Xu, 2022)
Protein Function
RALA has several biochemical functions, for example, . Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by RALA itself. We selected most functions RALA had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with RALA. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|
Interacting Protein
RALA has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with RALA here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of RALA.
Exoc2;CALM1;PPP2R1B;HRAS;C3;RALBP1;HSPB1;CTCF;SMAD4;pi3p
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Neel, NF; Stratford, JK; et al. Response to MLN8237 in Pancreatic Cancer Is Not Dependent on RalA Phosphorylation. MOLECULAR CANCER THERAPEUTICS 13:122-133(2014).
- Qin, JJ; Wang, XR; et al. Mini-Array of Multiple Tumor-associated Antigens (TAAs) in the Immunodiagnosis of Esophageal Cancer. ASIAN PACIFIC JOURNAL OF CANCER PREVENTION 15:2635-2640(2014).


