RAB43
-
Official Full Name
RAB43, member RAS oncogene family -
Synonyms
RAB43;RAB43, member RAS oncogene family;ras-related protein Rab-43;ISY1;RAB11B;RAB41;ras-related protein Rab-41;MGC90481
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Chicken
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- His
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAB43-2128H | Recombinant Human RAB43, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 1-212aa | |
| RAB43-2804H | Recombinant Human RAB43 protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 91-212 aa | |
| RAB43-4895R | Recombinant Rat RAB43 Protein | Mammalian Cells | Rat | His |
|
|
| RAB43-5238C | Recombinant Chicken RAB43 | Mammalian Cells | Chicken | His |
|
|
| RAB43-5417Z | Recombinant Zebrafish RAB43 | Mammalian Cells | Zebrafish | His |
|
|
| RAB43-2590HCL | Recombinant Human RAB43 293 Cell Lysate | HEK293 | Human | Non |
|
|
| RAB43-2541H | Recombinant Human RAB43 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | HEK293 | Human | DDK&Myc |
|
|
| RAB43-4554R | Recombinant Rat RAB43 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Rat | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| RAB43-4554R-B | Recombinant Rat RAB43 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Rat |
|
||
| Rab43-5323M | Recombinant Mouse Rab43 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | DDK&Myc |
|
Background
What is RAB43 Protein?
Rab43 is a protein that's part of a big family known as Rab GTPases, which are like cellular traffic controllers. Found in many different organisms, Rab43 is particularly involved in the movement of proteins from one part of a cell to another, specifically from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus. Think of it as a key player in sorting and directing the proteins to their proper destinations within the cell. By managing this transport, Rab43 helps maintain the smooth operation of cellular processes. Scientists are still uncovering exactly how Rab43 does all this, but it's clear that it plays a crucial role in ensuring that cells function correctly.What is the Function of RAB43 Protein?
Rab43 is like a cellular logistics expert, part of the Rab GTPase family, making sure proteins get from point A to point B within the cell. Imagine it's in charge of directing traffic from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to the Golgi apparatus, a key pathway in cellular shipping. This protein doesn't just shuffle things around aimlessly; it ensures proteins are sorted and delivered correctly, a bit like a postal worker making sure the mail gets to the right address. Its function is vital for the smooth operation of cellular activities, helping maintain everything from protein processing to overall cell health. Scientists are still diving into all the details, but Rab43 is definitely a big deal in keeping cells running smoothly.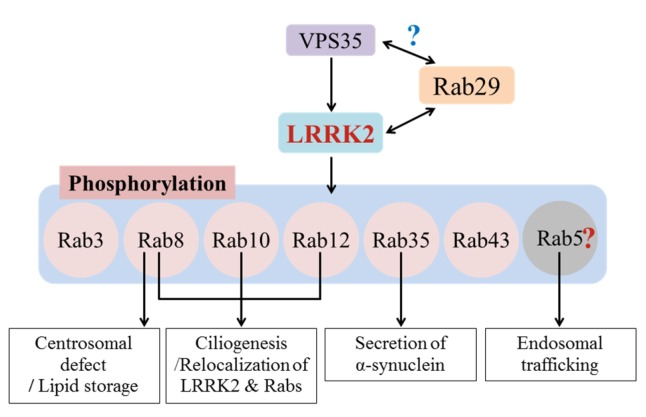
Fig1. A summary of consequences of LRRK2-mediated Rab phosphorylations. (Wongi Seol, 2019)
RAB43 Related Signaling Pathway
Rab43 is involved in some pretty interesting signaling pathways within the cell. Picture it as a key player in the communication network that keeps cellular functions ticking along smoothly. In particular, Rab43 is linked to the pathway managing the transport between the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the Golgi apparatus, crucial hubs in the cell's logistics. This pathway ensures proteins are processed and sent to where they're needed, playing a part in everything from building new cell components to sending out cellular messages. Rab43 helps coordinate these activities, ensuring that the proteins and molecules are properly sorted and directed as they should be. While scientists are still piecing together the full story, it's clear that Rab43 is indispensable for this intracellular communication and transport system, making it an exciting area of study for understanding cell biology better.RAB43 Related Diseases
Rab43 is a protein that plays a crucial role in moving proteins around within cells, but when it doesn't work right, things can go a bit haywire. Although direct links to specific diseases are still being researched, disruptions in the function of Rab43 could potentially contribute to various disorders. If Rab43 can't do its job properly in moving proteins between the ER and Golgi, it could mess up important cellular processes vital for cell health and function. This disruption might play a role in neurodegenerative diseases or other disorders where normal cell activity is off track. Scientists are actively investigating these connections to better understand how Rab43 might be implicated in such conditions, so it's an emerging field with lots of potentials.Bioapplications of RAB43
Rab43 isn't just any protein; it's got exciting potential in biotech and medical research. Scientists are exploring how its knack for managing protein movement inside cells could be used in treatments. By getting a grip on Rab43's part in protein trafficking, researchers could devise ways to fix cellular transport problems that may cause diseases. Additionally, its pathways could be targeted to improve drug delivery systems, ensuring medications reach the right part of a cell more effectively. There’s also interest in exploring Rab43's functions to create bioengineered tissues or organs, as maintaining correct protein transport is crucial for cell viability. As researchers delve deeper, Rab43 could become a key player in developing innovative treatments and technologies.Case Study
Case Study 1: Li C. et al. Cell Rep. 2017
GPCRs are big players in cell signaling, but how they get to the cell surface is still a bit of a mystery. Researchers took a look at the Rab family of proteins and found that tweaking Rab43 changes how GPCRs are presented and work on the cell surface, but it leaves other proteins alone. Rab43 is all about moving new GPCRs from the ER to the Golgi. What's cool is that Rab43 hooks up with GPCRs when they're active, and a specific part of GPCRs can even make other proteins follow Rab43's lead.-
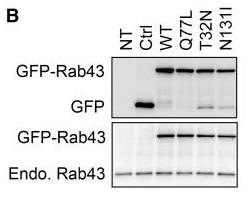 Fig1. Western blot analysis of expression of Rab43 and its mutants by using GFP (top) and Rab43 antibodies (bottom).
Fig1. Western blot analysis of expression of Rab43 and its mutants by using GFP (top) and Rab43 antibodies (bottom). -
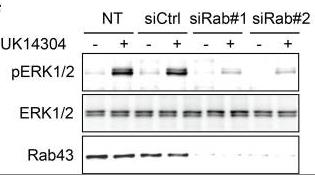 Fig2. Effect of Rab43 siRNA on α2B-AR-mediated ERK1/2 activation.
Fig2. Effect of Rab43 siRNA on α2B-AR-mediated ERK1/2 activation.
Case Study 2: Cox JV. et al. Mol Biol Cell. 2016
Researchers tagged VSV G tsO45 with different tails and found they moved through the Golgi at different rates. Rab43 played a key role, as GFP-Rab43 blocked G(AE) in the Golgi, stopping its sugar modifications and delivery to the surface. Knocking down Rab43 made more G(AE) reach the surface, while G remained mostly unchanged.-
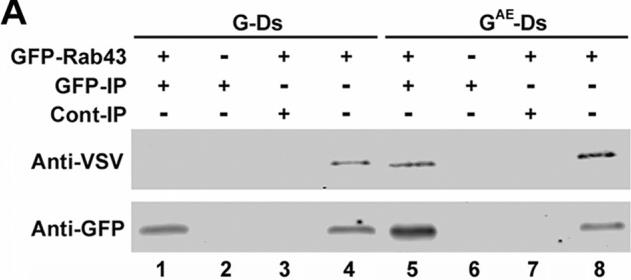 Fig3. COS7 cells expressing GFP-Rab43 were infected with adenovirus encoding GAE-Ds or G-Ds and grown at restrictive temperature for 24 h.
Fig3. COS7 cells expressing GFP-Rab43 were infected with adenovirus encoding GAE-Ds or G-Ds and grown at restrictive temperature for 24 h. -
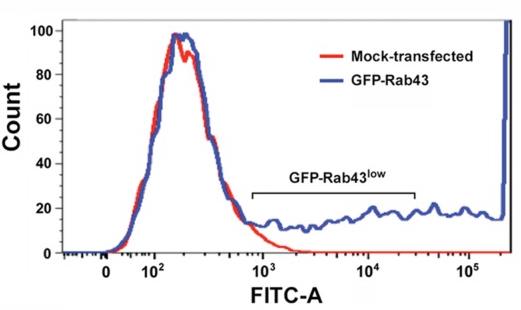 Fig4. COS7 cells were transfected with GFP-Rab43, and 24 h posttransfection, cells expressing low levels of GFP-Rab43 were isolated using a fluorescence-activated cell sorter.
Fig4. COS7 cells were transfected with GFP-Rab43, and 24 h posttransfection, cells expressing low levels of GFP-Rab43 were isolated using a fluorescence-activated cell sorter.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (RAB43-2541H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (RAB43-2541H)
Involved Pathway
RAB43 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways RAB43 participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with RAB43 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
-
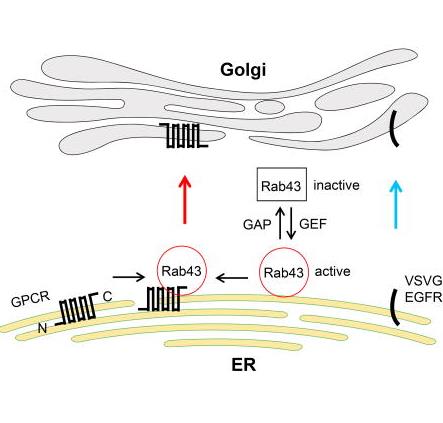 Fig1. Rab43 is key for moving new GPCRs from the ER to the Golgi and sorting them in the ER by direct interaction. (Chunman Li, 2017)
Fig1. Rab43 is key for moving new GPCRs from the ER to the Golgi and sorting them in the ER by direct interaction. (Chunman Li, 2017) -
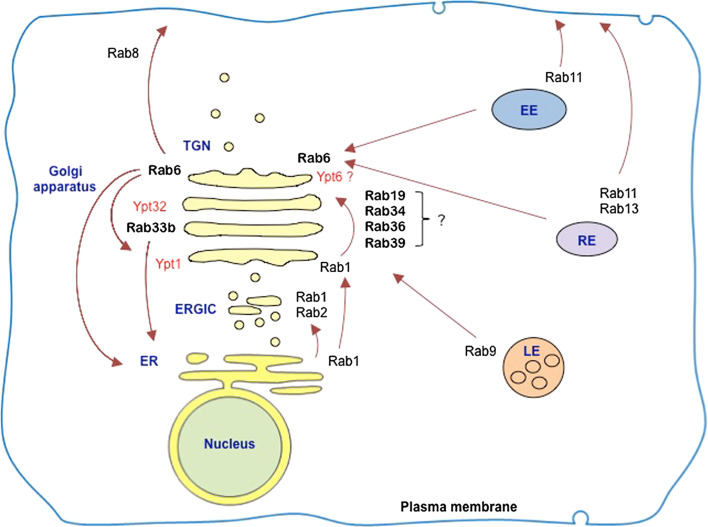 Fig2. Localizations and transport pathways of major Golgi-associated Rab proteins in mammalian cells. (Shijie Liu, 2012)
Fig2. Localizations and transport pathways of major Golgi-associated Rab proteins in mammalian cells. (Shijie Liu, 2012)
Protein Function
RAB43 has several biochemical functions, for example, GTP binding,GTPase activity,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by RAB43 itself. We selected most functions RAB43 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with RAB43. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| GTPase activity | RAB3AB,RHEB,RABL5,EEF1A1B,RRAS2,RAB39B,RAB25A,RAB6C,RAB7L1,RAN |
| GTP binding | RERGLA,RHOT1,RASD1,TRIM66,RHEBL1,SEPHS1,GBP3,RHOAE,RAB1,GTPBP3 |
| protein binding | AP2M1,MMP20,RAF1,KCTD17,CALM3,SNAP29,DNAJB6,CALM1,SEMA4D,TUBA3E |
Interacting Protein
RAB43 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with RAB43 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of RAB43.
HSPB1;pi3p;Rab5c;RAB5C;Crnkl1;Snw1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


