PPARA
-
Official Full Name
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha -
Overview
Peroxisome proliferators include hypolipidemic drugs, herbicides, leukotriene antagonists, and plasticizers; this term arises because they induce an increase in the size and number of peroxisomes. Peroxisomes are subcellular organelles found in plants and animals that contain enzymes for respiration and for cholesterol and lipid metabolism. The action of peroxisome proliferators is thought to be mediated via specific receptors, called PPARs, which belong to the steroid hormone receptor superfamily. PPARs affect the expression of target genes involved in cell proliferation, cell differentiation and in immune and inflammation responses. Three closely related subtypes (alpha, beta/delta, and gamma) have been identified. This gene encodes the subtype PPAR-alpha, which is a nuclear transcription factor. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described for this gene, although the full-length nature of only two has been determined. -
Synonyms
PPARA;peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha;peroxisome proliferative activated receptor, alpha , PPAR;hPPAR;NR1C1;MGC2237;MGC2452;Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group C member 1;OTTHUMP00000197740;OTTHUMP00000197741;Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha;PPAR;PPAR-alpha;PPARA_HUMAN;PPARalpha;peroxisome proliferative activated receptor, alpha;peroxisome proliferator-activated nuclear receptor alpha var
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Sf9 Cells
- HEK293
- Insect Cells
- His
- GST
- Non
- MBP
- Flag
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is PPARA Protein?
PPARA, or Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Alpha, is a type of protein that acts as a nuclear receptor. It primarily regulates genes responsible for metabolism and inflammation, mainly found in tissues like the liver, heart, and muscles. PPARA plays a key role in lipid metabolism, helping control cholesterol levels and fat usage. By binding to specific molecules, it activates and influences the expression of genes involved in energy balance, making it significant in studies on metabolic disorders and cardiovascular health.What is the Function of PPARA Protein?
PPARA, or Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Alpha, plays a key role in managing energy balance by controlling fat metabolism. It's mainly found in the liver and muscles, where it activates genes that break down fats for energy and reduce fat storage. PPARA also helps regulate cholesterol and lessen inflammation. Its function is important for understanding metabolic conditions and how the body reacts to medications that target fats and insulin response.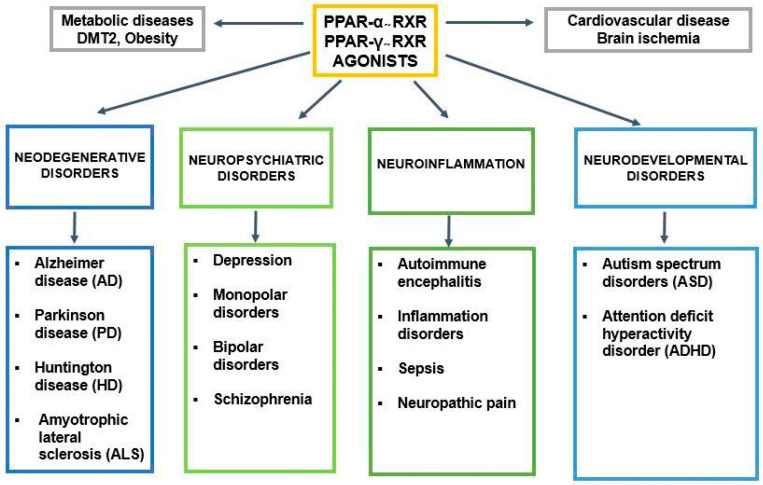
Fig1. PPAR-α and its engagement in metabolic, cardiovascular, and neurological/neuropsychiatric disorders. (Sylwia Żulińska, 2024)
PPARA Related Signaling Pathway
PPARA, or Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Alpha, plays a crucial role in how the body handles fats, particularly in breaking down fatty acids for energy. It’s mostly found in the liver, heart, and muscles, where it helps switch on genes that burn fat, thus providing necessary fuel for the body. PPARA’s actions are vital for maintaining energy balance and are central to managing conditions like high cholesterol and diabetes.PPARA Related Diseases
PPARA, known as Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Alpha, plays a significant role in lipid metabolism and energy homeostasis. It's involved in the regulation of genes encoding enzymes related to fatty acid oxidation, which is essential for maintaining energy balance, especially during fasting. PPARA’s function has implications in several metabolic disorders and conditions. For instance, mutations or alterations in PPARA activity are associated with metabolic syndrome components, like increased cholesterol and triglyceride levels, hypertension, and insulin resistance. Moreover, PPARA impacts liver health, influencing hepatic fat accumulation and liver enlargement in response to certain chemicals. It's also linked to body weight regulation through its interaction with natural ligands that affect feeding behavior and fat storage. In rodents, lack of PPARA led to severe metabolic imbalances, including hypoglycemia and hypothermia during fasting. Despite being an intriguing target for therapies, like fibrates for lowering lipid levels, PPARA’s role in complex diseases like cancer or cardiovascular conditions remains an area of active research, with studies continuing to unravel its multifaceted roles in health and disease.Bioapplications of PPARA
PPARA, or Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Alpha, is a key player in the regulation of lipid metabolism and energy homeostasis. It’s mainly found in tissues that oxidize fatty acids, like the liver, heart, and muscles. Its importance is underscored by its role in controlling the expression of genes involved in fatty acid transport and oxidation. Now, one of the really cool bioapplications of PPARA is in the medical field, particularly for developing treatments for metabolic diseases. For example, certain drugs known as fibrates activate PPARA and are used to lower triglycerides and cholesterol levels. Research even suggests PPARA could be applied in therapies for reducing inflammation and potentially in cancer treatment by influencing cell growth and metabolism. There's also interest in its role in energy balance, making it a target for combating obesity and related conditions. All in all, PPARA is not just a crucial metabolic regulator—it’s a promising target for therapeutic innovations.Case Study
Case Study 1: Kamata S. et al. STAR Protoc. 2021
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors, or PPARs, are transcription factors that play a role in how cells differentiate and manage their metabolism. There are three subtypes: PPARα, δ, and γ. It's been tough to get clear X-ray crystallography images of the PPARα’s ligand-binding domain complexed with its ligand because they aren’t easy to crystallize. Part of the challenge is that the proteins, when made in bacteria, have fatty acids stuck to them which can make them unstable without other molecules around. To tackle this,researchers used a mix of strategies like co-crystallization, cross-seeding, and adding specific peptides to get stable crystals for analysis, as detailed by Kamata and colleagues in 2020.-
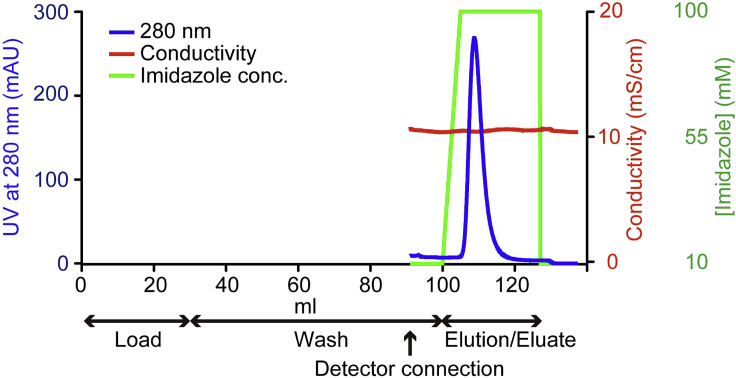 Fig1. The representative affinity column chromatography profile for hPPARα-LBD purification.
Fig1. The representative affinity column chromatography profile for hPPARα-LBD purification. -
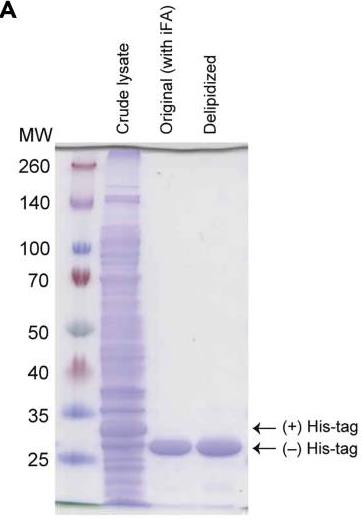 Fig2. SDS-PAGE gel of original and delipidized hPPARα-LBD.
Fig2. SDS-PAGE gel of original and delipidized hPPARα-LBD.
Case Study 2: Kuramoto K. et al. Genes (Basel). 2021
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) have unique energy systems, relying on lipid droplets for energy storage. These droplets, which hold neutral lipids, are linked to signaling pathways like the PPAR pathway. It's still vague how lipid-derived signals affect CSC traits. Our study focused on the role of these droplets in CSCs, especially in pancreatic and colorectal cancers. We found that PPARα is active in CSCs with these lipid droplets, unlike non-CSCs. Blocking PPARα reduced the CSC traits. Moreover, halting lipid processes such as re-esterification and breakdown also diminished CSC characteristics. This points to targeting lipid metabolism and PPARα as potential CSC therapies.-
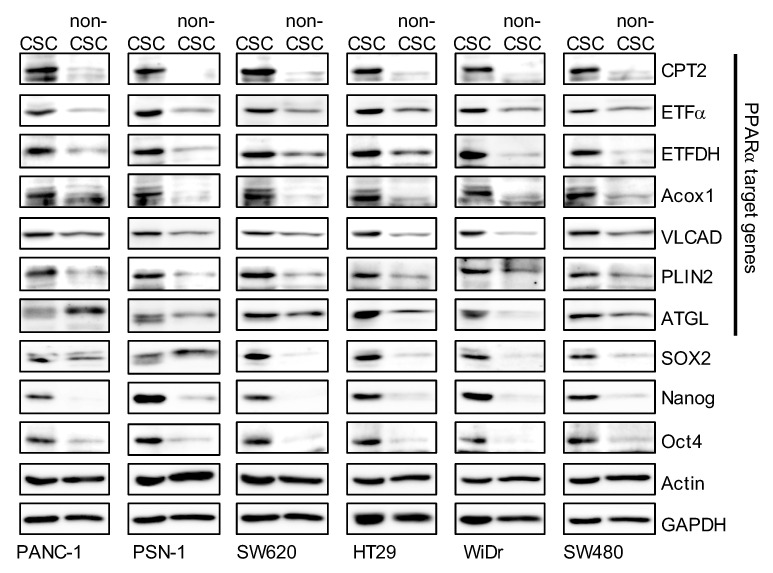 Fig3. The expression levels of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) target genes in cancer stem cells (CSCs) were higher than in non-cancer stem cells (non-CSCs).
Fig3. The expression levels of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) target genes in cancer stem cells (CSCs) were higher than in non-cancer stem cells (non-CSCs). -
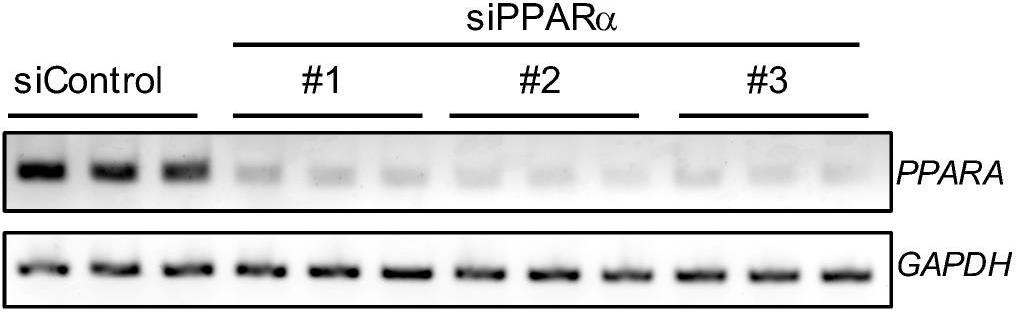 Fig4. Genetic silencing of PPARα causes the loss of stemness in PANC-1 CSCs.
Fig4. Genetic silencing of PPARα causes the loss of stemness in PANC-1 CSCs.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PPARA-1066H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PPARA-1066H) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (PPARA-2610H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (PPARA-2610H)
Involved Pathway
PPARA involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PPARA participated on our site, such as PPAR signaling pathway,cAMP signaling pathway,Adipocytokine signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PPARA were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Hepatitis C | TYK2,CLDN20,CLDN6,PPP2CB,IKBKE,IFNA8,IRF1,IFNA16,PPP2R1B,CLDN1 |
| Adipocytokine signaling pathway | TRADD,RXRB,SLC2A1,RXRG,IKBKG,ACSL1A,SLC2A1A,ACSL1,PRKAB1A,PRKAB1B |
| Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) | NDUFB5,MLXIPL,BID,NDUFC1,AKT1,PIK3R1,Casp3,PRKAA2,NDUFA4,NDUFA13 |
| cAMP signaling pathway | PPP1R12A,GRIA1,CNGA2,ATP1A2,CALML5,PLD2,FXYD1,CALM4,VAV1,CAMK2A |
| PPAR signaling pathway | APOA1,CYP8B1,SCDB,ACSL4B,MMP1,RXRG,FABP2,CD36,UBC,ACSBG1 |
| Insulin resistance | OGT,PRKCD,GSK3B,GFPT1,PCK2,RELA,NFKBIAA,PRKCDA,CREB3L2,PYGMA |
-
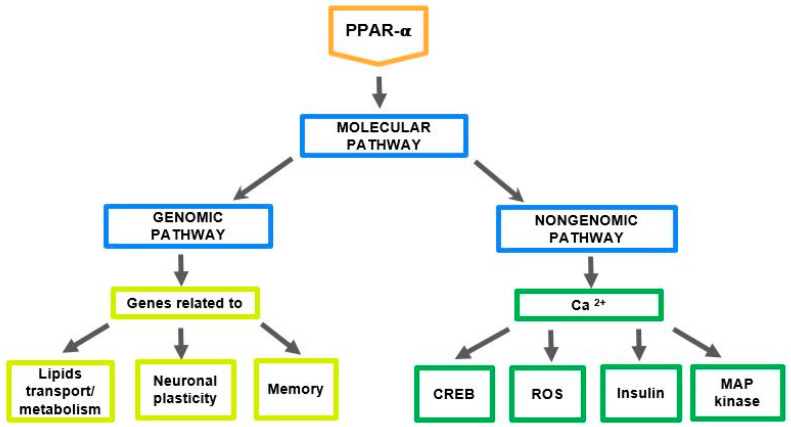 Fig1. PPAR-α and the molecular mechanism of its action through genomic and nongenomic pathways. (Sylwia Żulińska, 2024)
Fig1. PPAR-α and the molecular mechanism of its action through genomic and nongenomic pathways. (Sylwia Żulińska, 2024) -
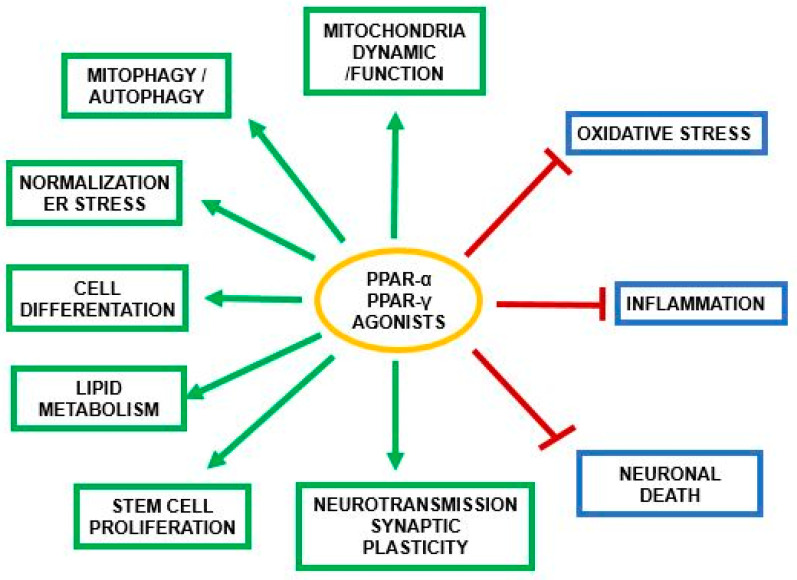 Fig2. PPAR-α and its role in the activation or inhibition of crucial processes engaged in the survival and death of brain cells. (Sylwia Żulińska, 2024)
Fig2. PPAR-α and its role in the activation or inhibition of crucial processes engaged in the survival and death of brain cells. (Sylwia Żulińska, 2024)
Protein Function
PPARA has several biochemical functions, for example, DNA binding,MDM2/MDM4 family protein binding,NFAT protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PPARA itself. We selected most functions PPARA had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PPARA. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| sequence-specific DNA binding | ZNF232,HOXC6B,HOXC4,DLX6A,ZSCAN16,MKX,ATF7,ELF2B,SOX30,HOXA11B |
| transcriptional activator activity, RNA polymerase II transcription factor binding | WWP2,NKX2,MED12,KLF14,CREB1,GBX2,NFE2L1,KLF4,NOTCH1,JUN |
| steroid hormone receptor activity | THRA,PAQR7B,NR4A2A,PPARG,ESRRA,RARA,RXRBB,NR5A5,RXRA,NR4A2 |
| NFAT protein binding | SPI1,GATA4,SFPI1,MAPK14,FOXP3 |
| ubiquitin conjugating enzyme binding | FOXL2,RNF144B,DCUN1D4,UBE2V1,DCUN1D2B,SIAH2,RNF14,RASD2,RNF144A,RNF19A |
| zinc ion binding | ZNF259,DPF2,CA4,RNF34B,TRIM9,NR1D2,BAZ2A,NSMCE1,OTUD7A,AGTPBP1 |
| RNA polymerase II transcription factor activity, ligand-activated sequence-specific DNA binding | RORA,NR4A2B,STAT3,PPARAB,ESRRB,NR1H4,RORB,RORCB,PGR,Ar |
| protein domain specific binding | MLF1,YWHAQA,YWHAE,YWHAE2,DDX20,STRN4,HIST2H4,IPCEF1,ARFIP2A,ATN1 |
| transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | ZC3H8,FEV,TBX2A,ATF4,CEBP1,TAL1,HOMEZB,ZFP27,FOXQ2,IRF5 |
Interacting Protein
PPARA has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PPARA here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PPARA.
NCOR2;GRB2;CHD9;NCOR1;PIK3R3;UBE2I;PRMT2;MED1;LAMTOR5;RXRG;FOXA3;CDK3;PRMT1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Lu, Y; Liu, X; et al. Periostin promotes liver steatosis and hypertriglyceridernia through dovvnregulation of PPAR alpha. JOURNAL OF CLINICAL INVESTIGATION 124:3501-3513(2014).
- Kienesberger, K; Pordes, AG; et al. L-carnitine and PPAR alpha-agonist fenofibrate are involved in the regulation of Carnitine Acetyltransferase (CrAT) mRNA levels in murine liver cells. BMC GENOMICS 15:-(2014).


