PHB
-
Official Full Name
prohibitin -
Overview
The prohibitins, called PHB1 and PHB2, are highly conserved proteins that are present in multiple compartments in eukaryotic cells. PHB1 is 30kDa tumor suppressor protein involved in cell cycle control. PHB1 has been found in mitochondria, the nucleus and -
Synonyms
PHB;prohibitin;PHB1
Recombinant Proteins
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Chicken
- Rat
- Burkholderia pickettii
- Mammalian Cells
- E.coli
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Yeast
- Baculovirus
- His
- T7
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
- GST
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is PHB Protein?
Prohibitin 1 (PHB1) is a protein found throughout the body, taking on various biological roles. It's mainly situated in the inner membrane of mitochondria, where it pairs with PHB2 to form complexes that help manage key mitochondrial functions like metabolism, energy production, and cell survival. These proteins can also be located in the nucleus and cytoplasm, where they take on different roles based on their location. PHB1, initially identified for its anti-proliferative qualities in mammals, consists of a transmembrane domain and a coiled-coil domain, crucial for interactions. These proteins can act as virus receptors and influence signaling pathways like Raf-1/ERK, aiding in cancer cell movement. In the nucleus, PHB1 interacts with transcription factors such as p53, affecting cell growth. Abnormalities in PHB proteins link to aging, cancer, and diseases involving mitochondrial damage. Thus, PHB is emerging as a key player in disease progression and a potential target for cancer treatment.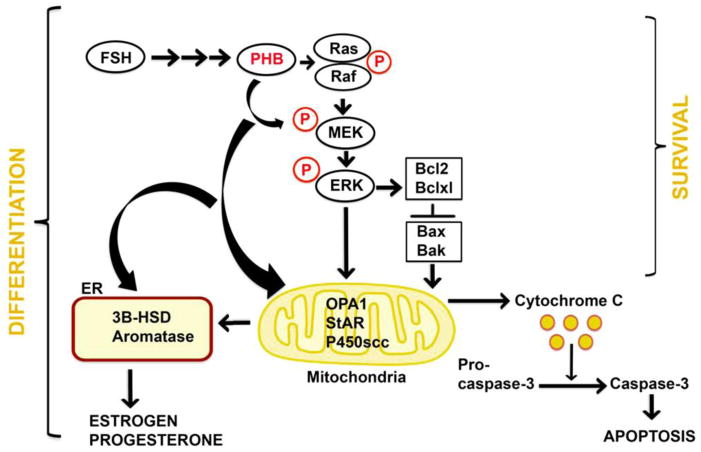
Fig1. Schematic representation of involvement of the prohibitin (PHB/PHB1) in granulosa cell (GCs) survival and differentiation functions. (Indrajit Chowdhury, 2016)
What is the Function of PHB Protein?
PHB proteins, such as Prohibitin 1, play various roles within cells, focusing largely on mitochondrial function. They are primarily located in the mitochondria's inner membrane, where they assist in preserving the organelle's structure and overall operation. This includes overseeing mitochondrial dynamics, energy production, and stress responses. PHB proteins are vital for keeping the mitochondrial membrane stable and ensuring proper function, even during stress. They also partake in the breakdown of subunits in the mitochondrial respiratory chain, building oxidative phosphorylation systems, and aiding mitochondrial growth and activities. In the cell nucleus, PHB proteins link up with transcription factors, influencing the cell cycle and proliferation. In terms of cancer, PHB proteins are significant—irregular expression is linked to various cancers and they might be promising targets for diagnosis and treatment. Overall, PHB proteins play essential roles in energy metabolism, maintaining mitochondrial health, and impacting both cell death and cancer development.PHB Related Signaling Pathway
PHB proteins are involved in several signaling pathways, including those related to mitochondrial autophagy, the mitochondrial unfolded protein response (UPRmt), and pathways tied to cell metabolism and cancer. They interact with m-AAA and OMA1 proteases, influencing the breakdown and stability of proteins in the mitochondrial inner membrane. PHB2 acts as a receptor for mitochondrial autophagy, binding to LC3 through its interaction domain to promote selective autophagy of mitochondria. Additionally, PHB proteins are part of the PINK1-PRKN/Parkin-dependent autophagy pathway, with PHB2 playing a role via the PHB2-PARL-PGAM5-PINK1 axis, which is a newly identified route for PHB2-mediated mitochondrial autophagy. In relation to UPRmt, a stress response to abnormal protein buildup in mitochondria, PHB proteins help manage this through increasing chaperone proteins, activating protein degradation enzymes, and putting defective proteins through mitochondrial autophagy. PHB proteins also interact with Rict-1, affecting lifespan and UPRmt signaling. In cancer development, they modulate the Ras-driven c-Raf-MEK-ERK pathway, impacting cell growth, resistance, and metastasis. These roles highlight PHB proteins' crucial involvement in cellular metabolism and disease.PHB Related Diseases
PHB proteins are linked to various diseases like neurodegenerative conditions, cancer, metabolic, and inflammatory disorders. In neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and ALS, they help maintain cell balance and health. Changes in PHB relate to aging and metabolic issues; loss of PHB in mice can cause embryo death and neuron problems in adulthood. In cancer, high PHB levels are connected to cells resisting death, while lower levels make cancer cells more susceptible to it. PHB affects cancer cell growth and survival, with reduced PHB significantly slowing cell division. They're involved in cancers like stomach, esophageal, colorectal, prostate, breast, bladder, thyroid, and blood cancers. During viral infections, PHB2 helps DENV-2 enter cells, but silencing it can improve survival in EV-A71 cases. PHB proteins also relate to a stress response for dealing with abnormal protein buildup in the mitochondria. Thus, their abnormal expression in various conditions points to PHB proteins as potential treatment targets.Bioapplications of PHB
PHB proteins (Prohibitin 1) have significant potential in both biomedical research and industrial uses. They form oligomers through a coiled-coil area at their carboxy end, which helps regulate the fusion of mitochondrial membranes and maintain mtDNA stability. This makes PHB1 crucial for managing cell metabolism and how mitochondria work. It holds potential for treating conditions like cancer, inflammatory bowel disease, insulin resistance/type 2 diabetes, and obesity, which are tied to oxidative stress and mitochondrial problems. PHB1 also works with the transcription factor STAT3 to influence cell growth and inflammation, providing new approaches to address mitochondrial dysfunction in inflammatory bowel disease. Researching PHB1 enhances our understanding of mitochondrial biology and supports developing new treatments for related conditions.Case Study
Case Study 1: Li XH. et al. Asian J Androl. 2020
Prohibitin (PHB) is a mitochondrial protein found in cells with strong energy needs. This research showed that removing Phb in spermatocytes harms mitochondrial performance. In human sperm, more PHB in mitochondria links to less reactive oxygen, better membrane potential, and enhanced motility. This hints at PHB's role in sperm movement, but the details were unclear. They discovered for the first time that PHB interacts with AKT in murine sperm, forming a complex with phosphorylated PHB and AKT. When AKT was blocked using wortmannin, mouse sperm motility dropped, alongside a decrease in phosphorylated PHB and AKT. In infertile men with poor sperm motility, the PI3K/AKT pathway was less active, leading to low phosphorylated PHB levels. This suggests the pathway's role in sperm function and fertility.-
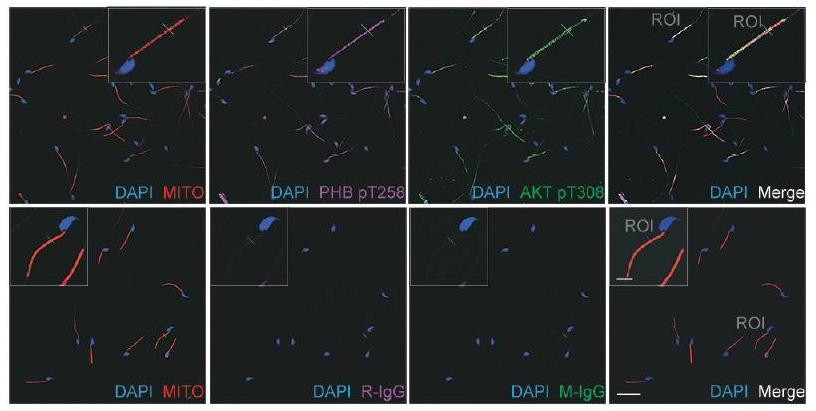 Fig1. Colocalization of phospho-PHB with AKT.
Fig1. Colocalization of phospho-PHB with AKT. -
 Fig2. PHB interacts with AKT and exists in a complex with phospho-PHB (pT258) and phospho-AKT (pT308) in mouse mature sperm.
Fig2. PHB interacts with AKT and exists in a complex with phospho-PHB (pT258) and phospho-AKT (pT308) in mouse mature sperm.
Case Study 2: Sharma A. et al. J Biomed Sci. 2020
Few studies have pinpointed receptors for dengue virus (DENV) in neural cells. This research zeroed in on potential receptors that let DENV-3 into different human neural cells: neuronal-SH-SY5Y, astroglial-U-87 MG, and microglial-CHME-3. Using methods like protein binding assays and mass spectrometry, they found prohibitin1/2 (PHB1/2) on these cells as interacting proteins. Tests with infection blockers and siRNA showed that PHB1/2 helps DENV-3 enter SH-SY5Y and CHME-3 cells, but not U-87 MG cells. Techniques like immunofluorescence, flow cytometry, and other assays confirmed PHB1/2's presence on cell surfaces and its interaction with DENV-3's EDIII protein.-
 Fig3. The efficiency of siRNA knockdown in reverse transfected SH-SY5Y cells with siPHB1_ (A/B/C).
Fig3. The efficiency of siRNA knockdown in reverse transfected SH-SY5Y cells with siPHB1_ (A/B/C). -
 Fig4. Co-localization of PHB1/2 and DENV-3 infected SH-SY5Y cells.
Fig4. Co-localization of PHB1/2 and DENV-3 infected SH-SY5Y cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PHB-4887H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PHB-4887H) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (PHB-1257H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (PHB-1257H)
Involved Pathway
PHB involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PHB participated on our site, such as ARMS-mediated activation,Axon guidance,Cytokine Signaling in Immune system, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PHB were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Developmental Biology | MED15,ACTR3,CARM1,DNM1,EPHB4A,MARK3,DUSP9,BOC,JAK1,COL4A4 |
| DAP12 interactions | CSF2RA,NRG3,NEFLB,KLB,PRKAR1AA,KBTBD7,SIGLEC15,FRS3,LAMTOR2,NRG4 |
| Downstream signal transduction | FGF18B,DUSP7,SPTA1,FRS3,KBTBD7,PAQR3B,DUSP2,SPRED3,SPRED2,SPNA1 |
| Downstream signaling of activated FGFR1 | SPTB,PTPRA,PEA15A,SPNA1,RASGRP4,CNKSR1,IL17RD,SPRED1,KBTBD7,AGO2 |
| Cytokine Signaling in Immune system | GBP6,TRIM29,ARIH1L,DUSP5,EIF4A2,DPF1,NRG4,IFITM2,DUSP6,IFI6 |
| Axon guidance | CAP1,DUSP1,CHL1,UNC5D,ABL1,SHB,CLASP1,NRP2,COL9A1A,EFNB3B |
| ARMS-mediated activation | CSF2RA,JAK1,RASGEF1A,DUSP2,CSK,NTF7,MARK3,PSME3,LAMTOR2,NEFLB |
| DAP12 signaling | SPTB,GRAP2A,THEM4,DAB2IPB,LAMTOR2,WDR83,GRAP2B,CSF2RA,MARK3,JAK3 |
-
 Fig1. Simplified model of the opposing roles of PHB1 in tumorigenesis. (Arianne L Theiss, 2011)
Fig1. Simplified model of the opposing roles of PHB1 in tumorigenesis. (Arianne L Theiss, 2011) -
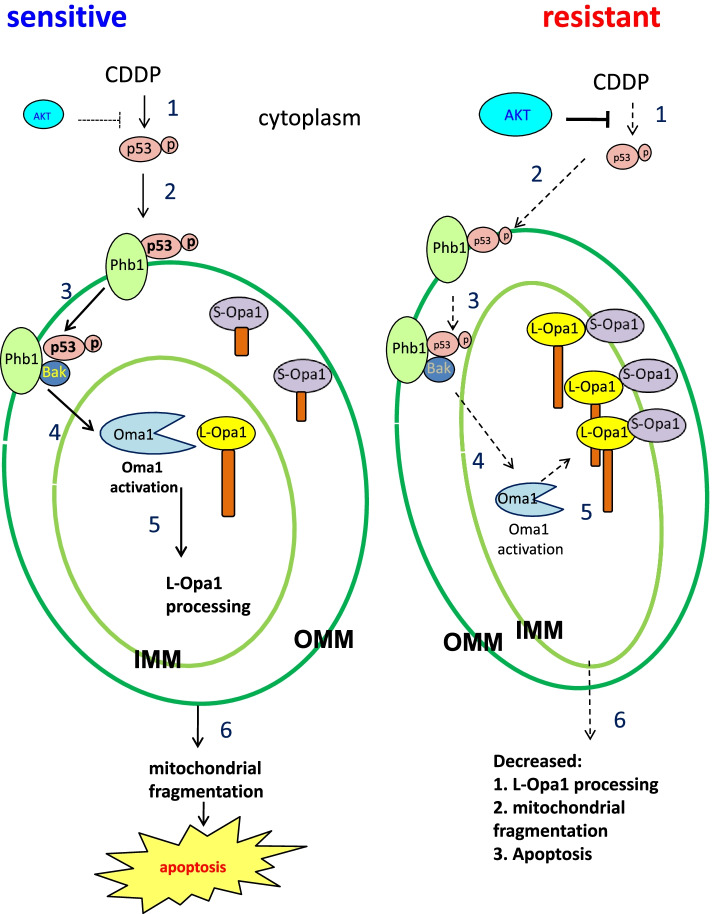 Fig2. Hypothetical model illustrating in the regulation of mitochondrial fragmentation, apoptosis, and chemosensitivity in gynecologic cancer cells. (Bao Kong, 2022)
Fig2. Hypothetical model illustrating in the regulation of mitochondrial fragmentation, apoptosis, and chemosensitivity in gynecologic cancer cells. (Bao Kong, 2022)
Protein Function
PHB has several biochemical functions, for example, RNA polymerase II transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding,complement component C3a binding,complement component C3b binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PHB itself. We selected most functions PHB had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PHB. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| enzyme binding | UGT1A2,JUN,CYP2E1,GBP1,EGLN1,GSTM1,TAL1,NOXA1,PARK7,MAPK14 |
| protein binding | TTR,ZNF572,SOX7,BBOX1,COX5A,AVPR1A,TJP2,POU4F1,ZNF276,FAM158A |
| protein C-terminus binding | PDZD11,HRAS,TNNI3K,ATP2A2,YAP1,VGLL1,YWHAB,CDC20,TOP2A,PXK |
| complement component C3a binding | C3AR1 |
| transcription regulatory region DNA binding | SMAD3,TP63,ZFP746,ARRB1,FOXC1,FOXH1,HNF1A,STAT3,FOXA2,SMAD6 |
| proteinase activated receptor binding | BICD1,PDCD6IP |
| RNA polymerase II transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | FOXM1,PEG3,FOXI3B,FOXP1,ZNF215,TFAP2A,GCM1,FOXO1B,ZSCAN5A,SOX30 |
| histone deacetylase binding | HOXA10,SRF,NCOR2,SP1,HDAC4,NUDT21,TCF21,NR2C1,NR2E1,FOXP3 |
| complement component C3b binding | CR1 |
Interacting Protein
PHB has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PHB here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PHB.
TP53;VCAM1;LONRF3;env;CHD2;ADAM10;XPO1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Bavelloni, A; Piazzi, M; et al. Prohibitin 2 represents a novel nuclear AKT substrate during all-trans retinoic acid-induced differentiation of acute promyelocytic leukemia. FASEB JOURNAL 28:2009-2019(2014).
- Chen, SX; Parlane, NA; et al. New Skin Test for Detection of Bovine Tuberculosis on the Basis of Antigen-Displaying Polyester Inclusions Produced by Recombinant Escherichia coli. APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY 80:2526-2535(2014).



