NCAPG
-
Official Full Name
non-SMC condensin I complex, subunit G -
Overview
This gene encodes a subunit of the condensin complex, which is responsible for the condensation and stabilization of;chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis. Phosphorylation of the encoded protein activates the condensin complex. There;are pseudogenes for this gene on chromosomes 8 and 15. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. -
Synonyms
NCAPG;non-SMC condensin I complex, subunit G;condensin complex subunit 3;CAP G;chromosome condensation protein G;FLJ12450;hCAP G;XCAP-G homolog;condensin subunit CAP-G;melanoma antigen NY-MEL-3;chromosome-associated protein G;CAPG;CHCG;HCAP-G
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCAPG-4613H | Recombinant Human NCAPG Protein, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST | 336-435 a.a. |
|
| NCAPG-8127Z | Recombinant Zebrafish NCAPG | Mammalian Cells | Zebrafish | His |
|
Background
What is NCAPG Protein?
NCAPG gene (non-SMC condensin I complex subunit G) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 4 at locus 4p15. The NCAPG protein, full name Non-SMC Condensin I Complex Subunit G, is a chromosome aggregation protein associated with mitosis. It plays a key role in the cohesion and stability of chromosomes, especially during meiosis and mitosis, ensuring the correct separation of sister chromatids. The expression of NCAPG is closely related to the proliferation, invasion, metastasis and apoptosis of tumor cells, and its expression level is significantly related to clinical stage, lymph node metastasis and prognosis. The NCAPG protein is consisted of 1015 amino acids and NCAPG molecular weight is approximately 114.3 kDa.
What is the Function of NCAPG Protein?
The NCAPG protein, also known as Non-SMC Condensin I Complex Subunit G, is a protein that regulates chromosome cohesion and stability. It belongs to the condensin complex associated with the cell cycle and is involved in the dynamic changes of chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis. NCAPG expression has been upregulated in a variety of tumors, including hepatocellular carcinoma, colorectal cancer, breast cancer, stomach cancer, glioma, lung adenocarcinoma, ovarian cancer, and endometrial cancer. In colorectal cancer, NCAPG promotes cancer cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial-stromal transformation (EMT) by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
NCAPG Related Signaling Pathway
Studies have shown that overexpression of NCAPG can increase the expression of p-Smad2 and p-Smad3 in TGF-β signaling pathway, and inhibitors of TGF-β signaling pathway can restore the effect of NCAPG overexpression in lung adenocarcinoma cells, suggesting that NCAPG may promote the progression of lung adenocarcinoma through TGF-β signaling pathway. For colorectal cancer, NCAPG promotes cancer cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial-stromal transformation (EMT) by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. In esophagogastric junction adenocarcinoma, the mechanism of action of NCAPG involves the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
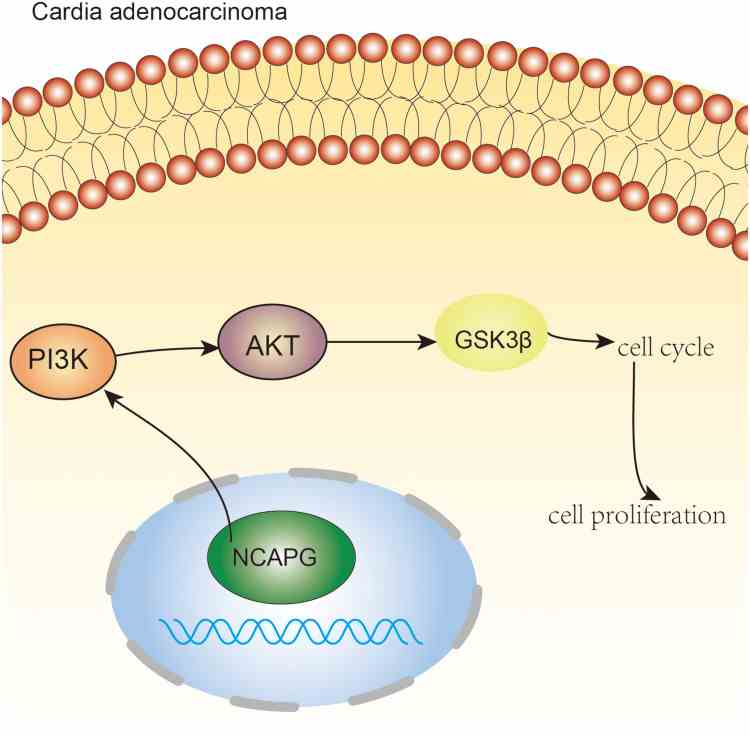
Fig1. NCAPG regulates the cell cycle and promotes cell proliferation through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in cardio adenocarcinoma. (Xinxin Zhang, 2020)
NCAPG Related Diseases
Abnormal expression of NCAPG protein is closely related to the occurrence, development and prognosis of many cancers, including lung adenocarcinoma, colorectal cancer, esophagogastric junction adenocarcinoma, etc. Its high expression in tumor cells is related to tumor proliferation, migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transformation (EMT) process, as well as poor prognostic factors such as clinical stage, lymph node metastasis and vascular invasion. Therefore, NCAPG is considered as a potential cancer therapeutic target and prognostic biomarker.
Bioapplications of NCAPG
Due to the abnormal expression of NCAPG protein in a variety of cancers and its important role in tumor development, its relevant off-the-shelf applications mainly focus on the role of biomarkers for cancer diagnosis, prognosis assessment and treatment response monitoring. Although there are currently no approved drugs that directly target NCAPG, the mechanism of action of NCAPG in the proliferation, migration and invasion of tumor cells is being deeply studied as a molecular target in research, and may help develop new cancer treatment strategies in the future. In particular, interventions targeting signaling pathways such as Wnt/β-catenin, TGF-β, and PI3K/AKT.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Haiting Yu, 2022
This study aims to explore the roles of NCAPG in ovarian cancer. The mRNA expression, overall survival, and disease-free survival of NCAPG in ovarian cancer were analyzed by GEPIA and KM plotter database, and the expression levels of NCAPG in OC tissues and cell lines were determined by qPCR and immunohistochemistry analysis. shRNA targeting NCAPG gene (sh-NCAPG) was utilized to knock down NCAPG expression in OVCAR3 and SKOV3 cells. The results showed that the silencing of NCAPG inhibited OC cell proliferation and invasion, and induced cell apoptosis. Additionally, flow cytometric analysis revealed that NCAPG knockdown arrested the cell cycle at G2 and S phases. Furthermore, we also found that downregulation of NCAPG could suppress OC cell proliferation and invasion via activating the p38 MAPK signaling pathway.
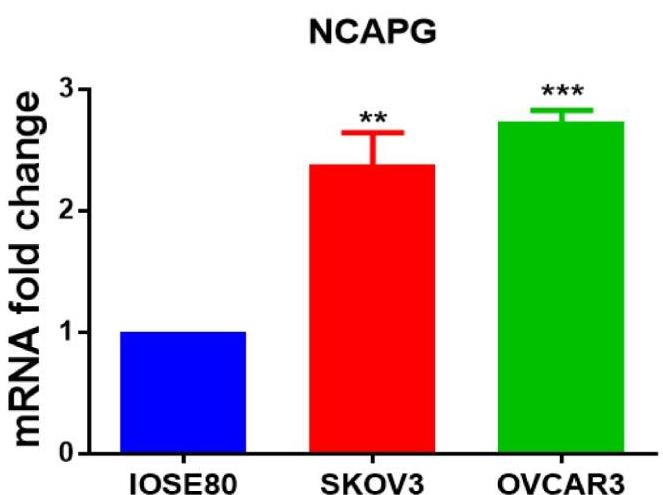
Fig1. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction of NCAPG mRNA level.
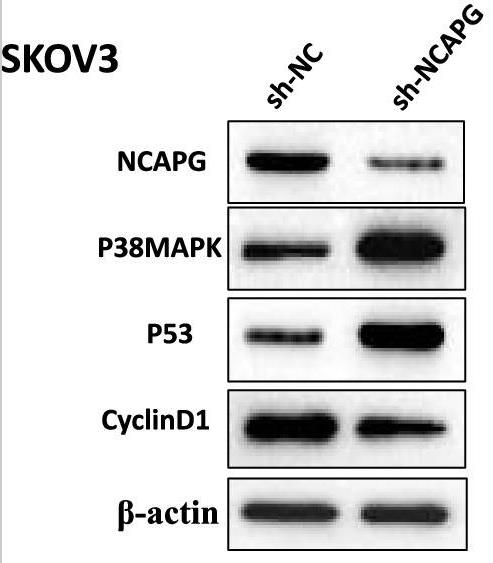
Fig2. NCAPG knockdown activates the p38 MAPK signaling pathway in OC cells.
Case Study 2: Xiaodong Wang, 2022
There are few studies on NCAPG in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD). Our research is to explore the role of NCAPG in LUAD and try to reveal the possible molecular mechanism. Public databases and tissue samples from LUAD patients were used to verify that NCAPG is significantly up-regulated in LUAD, and the high expression of NCAPG is related to the poor prognosis of patients. Subsequently, silencing NCAPG can inhibit the proliferation and invasion of LUAD cells in vitro and the growth of subcutaneous tumors in nude mice in vivo. In order to explore the possible molecular mechanism of NCAPG's function, researchers found out the genes co-expressed with NCAPG through the cBioportal database, and discovered that these genes were significantly enriched in the cell cycle and other pathways through DAVID analysis, which implies the importance of NCAPG in the cell cycle. Finally, we confirmed by flow cytometry that NCAPG affects the conversion of cell cycle mitosis from G1 to S.
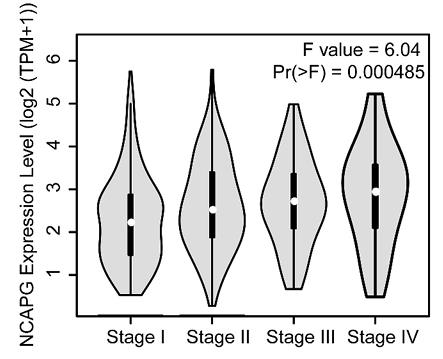
Fig3. NCAPG mRNA levels at different stages of LUAD.
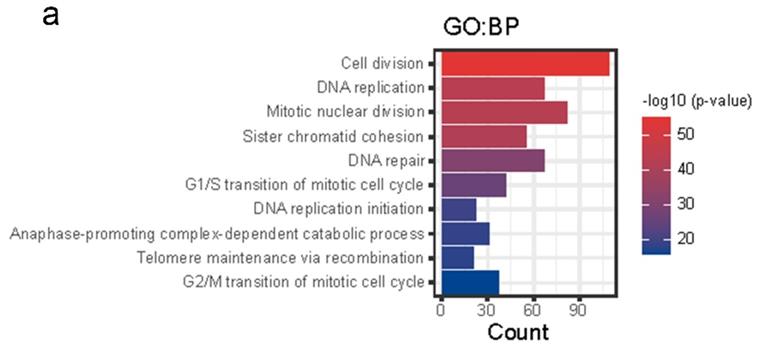
Fig4. Enrichment analysis of NCAPG co-expressed genes.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (NCAPG-4613H)
Involved Pathway
NCAPG involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways NCAPG participated on our site, such as Cell Cycle,Cell Cycle, Mitotic,Condensation of Prometaphase Chromosomes, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with NCAPG were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Condensation of Prometaphase Chromosomes | CSNK2A2,SMC4,CSNK2B,NCAPH,CSNK2A1,SMC2,NCAPD2 |
| Cell cycle | CCND3,CLASP1A,CDKN1C,KIF2B,FOXM1,HIST3H2BB,CDC16,GADD45G,STAG2,DHFR |
| Mitotic Prometaphase | DSN1,AHCTF1,RANGAP1B,RCC2,NDEL1B,NCAPH,CENPI,SKA1,NSL1,CENPN |
| Cell Cycle, Mitotic | CDK7,APITD1,GORASP2,NCAPD2,CSNK2A1,CEP70,CNEP1R1,CENPE,DHFR,GINS1 |
| M Phase | CENPE,NCAPD3,SGOL1,PANE1,PMF1,NIPBLA,CDCA5,KNTC1,CENPI,BLZF1 |
Protein Function
NCAPG has several biochemical functions, for example, . Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by NCAPG itself. We selected most functions NCAPG had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with NCAPG. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|
Interacting Protein
NCAPG has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with NCAPG here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of NCAPG.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References



