MRC2
-
Official Full Name
mannose receptor, C type 2 -
Overview
MRC2 is a recycling endocytic receptor that functions in cell motility and remodeling of the extracellular matrix by promoting cell migration and uptake of collagens for intracellular degradation (Wienke et al., 2007 -
Synonyms
MRC2;mannose receptor, C type 2;C-type mannose receptor 2;CD280;CLEC13E;ENDO180;KIAA0709;C-type lectin domain family 13 member E;CD 280;CD280 antigen;CLEC 13E;ENDO 180;Endocytic receptor (macrophage mannose receptor family);Endocytic receptor 180;FLJ35911;Macrophage mannose receptor 2;Mannose receptor C type 2;MRC 2;MRC2_HUMAN;UPAR-associated protein;UPARAP;Urokinase plasminogen activator receptor associated protein;Urokinase receptor associated protein;Urokinase receptor-associated protein;Urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor-associated protein;urokinase plasmino
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Canine
- Rat
- Mouse
- C-His
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- E.coli
- Insect cells
- HEK293
- Human Cells
- His
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
- Flag
- GST
Background
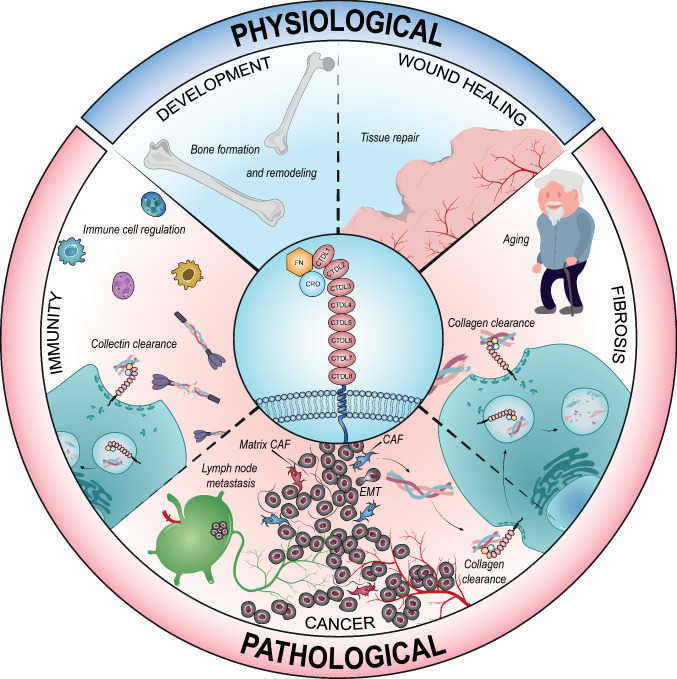
Fig1. The involvement of uPARAP/Endo180 in physiologic and pathological conditions. (Fabrice Gucciardo, 2022)
What is MRC2 protein?
MRC2 gene (mannose receptor C-type 2) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 17 at locus 17q23. This gene encodes a member of the mannose receptor family of proteins that contain a fibronectin type II domain and multiple C-type lectin-like domains. The encoded protein plays a role in extracellular matrix remodeling by mediating the internalization and lysosomal degradation of collagen ligands. Expression of this gene may play a role in the tumorigenesis and metastasis of several malignancies including breast cancer, gliomas and metastatic bone disease. The MRC2 protein is consisted of 1479 amino acids and MRC2 molecular weight is approximately 166.7 kDa.
What is the function of MRC2 protein?
MRC2 plays a role in extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling by mediating the internalization and lysosomal degradation of collagen ligands. It has an impact on cell migration and invasion, which are involved in tissue repair and cancer progression. MRC2 may be involved in the plasminogen activation system, controlling the extracellular level of urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) and thus regulating protease activity at the cell surface. It may contribute to the cellular uptake, remodeling, and degradation of extracellular collagen matrices. MRC2 has been shown to be expressed differently in many cancers and is significantly associated with immune cell infiltration, immune modulators, and immunotherapeutic markers.
MRC2 Related Signaling Pathway
MRC2 is involved in the remodeling of the extracellular matrix (ECM), especially through interaction with collagen, promoting its internalization and degradation in lysosomes. MRC2, as an endocytogenic lectin receptor, mediates the endocytosis of glycosylated ligands from the extracellular space through calcium-dependent lectin activity and is released into the endosomal compartment through clathrin-dependent endocytosis. MRC2 may be involved in regulating the level of extracellular uPA, which may regulate the protease activity on the cell surface and affect the processes of cell migration and invasion. MRC2 is expressed in immune cells such as macrophages and is involved in the regulation of immune response. MRC2 plays a role in atrial fibrillation (AF) through the PPAR signaling pathway, regulating the growth and apoptosis of cardiac fibroblasts.
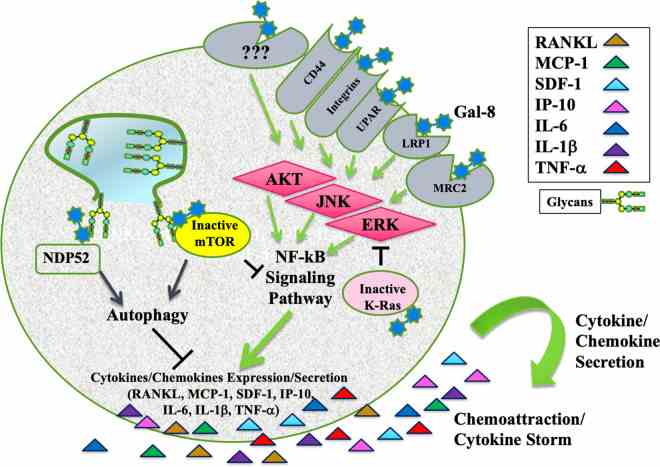
Fig2. Extracellular Gal-8 binds to a complex and the ligation triggers many signaling cascades including AKT, ERK, and JNK that stimulate the NFkB signaling pathways. (Yehiel Zick, 2022)
MRC2 Related Diseases
In the field of oncology, the expression of MRC2 is associated with tumor aggressiveness and metastasis, especially in breast cancer, glioma, and bone metastatic disease. In addition, the role of MRC2 in diabetic nephropathy (DN) has also attracted attention. Studies have found that the expression of MRC2 is up-regulated in the mouse model of DN, and the knockdown of MRC2 can inhibit the proliferation of mesangial cells and induce apoptosis, suggesting that MRC2 may be used as a molecular marker and therapeutic target of DN. In leukemia, the expression of MRC2 may be related to the dry characteristics of leukemia stem cells (LSCs), influencing their interaction with the microenvironment.
Bioapplications of MRC2
The expression level of MRC2 in multiple tumors is closely related to tumor aggressiveness and prognosis, making it a potential target for cancer therapy. By targeting MRC2 therapeutic strategies, it is possible to help inhibit the proliferation and metastasis of tumor cells. The function and regulatory mechanisms of MRC2 provide new perspectives for drug development, and by modulating the activity of MRC2 or the signaling pathways in which it is involved, new drugs can be developed to treat related diseases. The variation of the expression level of MRC2 in different diseases can be used as a biomarker for disease diagnosis and prognosis assessment, which helps in early identification and risk stratification. In the field of cell therapy, the expression of MRC2 may affect cell proliferation and survival, which has potential application value to improve the safety and effectiveness of cell therapy.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Lanlan Li, 2021
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is an important microvascular complication of diabetes and is the main cause of end-stage renal disease. Type 2 mannose receptor C (MRC2) is a member of the mannose receptor protein family, which has been confirmed to have the ability to promote the cell migration signaling pathway and invasion. By complementary DNA chip screening and analysis, researchers found that the expression of MRC2 was upregulated in the kidneys of mice with diabetic nephropathy. However, the role of MRC2 in diabetic nephropathy is still unclear. This work studied the effect of MRC2 on diabetic nephropathy. After verifying the results of the chip by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and western blotting, they used small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) to knock down the expression of MRC2 in mouse mesangial cells (MMCs) and analyzed the level of cell proliferation and apoptosis using western blotting, Cell Counting Kit-8, and flow cytometry.
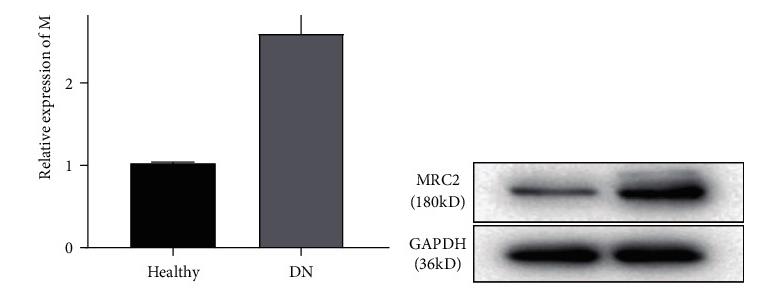
Fig1. MRC2 expression in cell and animal models of DN and MRC2 silencing.
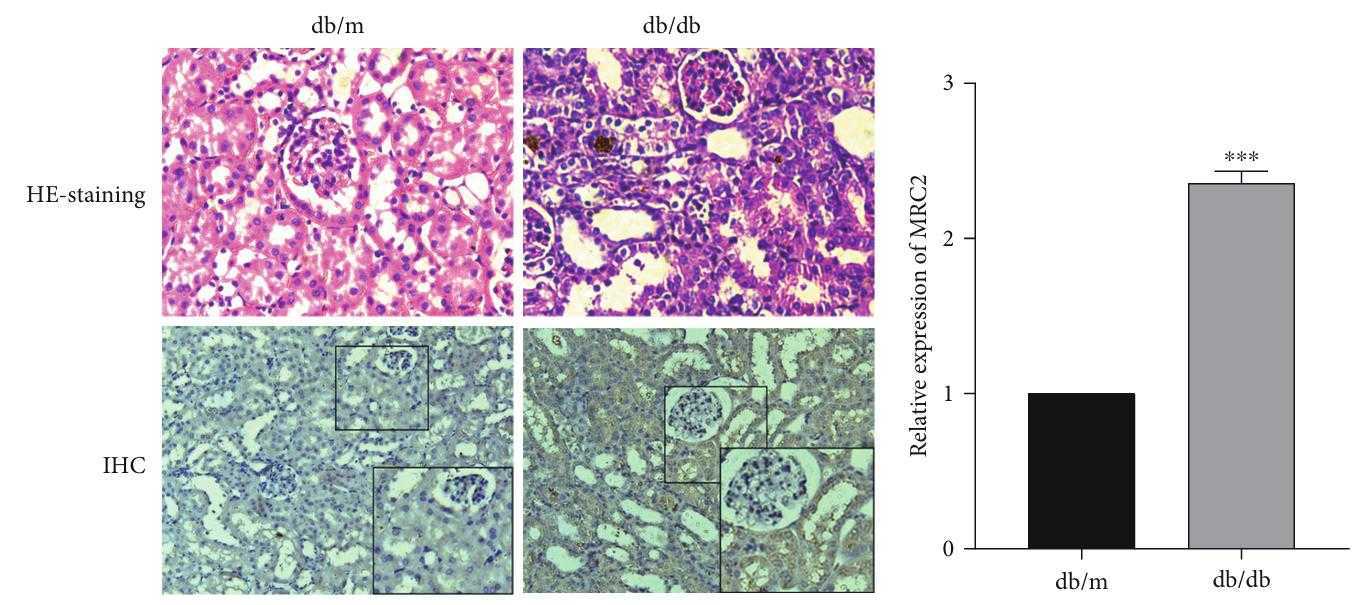
Fig2. The renal tissues of normal and DN mice were collected for H&E staining and immunohistochemistry analysis.
Case Study 2: Xiaohong Gai, 2014
This study attempted to determine MRC2 expression on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and its significance on postsurgical prognosis of HCCs. The expression of both MRC2 and transforming growth factor (TGFβ1) was detected in tumor tissues and adjacent liver tissues from 96 HCCs by immunohistochemistry staining, and it was found that MRC2 expression in HCC tissues was significantly higher than in adjacent liver tissues. HCCs with higher MRC2 expression had worse prognosis after liver resection. Univariate analysis showed that advanced TNM staging of HCC, higher Edmonson-Steiner classification, intrahepatic metastases, portal vein invasion, higher MRC2 and higher TGFβ1 were the poor prognostic factors. Furthermore, multivariate analysis revealed that intrahepatic metastases, higher MRC2 and higher TGFβ1 were the independent prognostic factors. TGFβ1 treatment up-regulated MRC2 expression, cell migration and invasion of Huh7 cells notably.
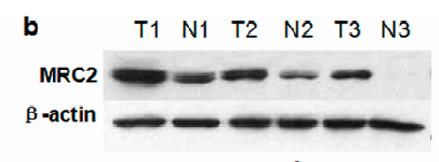
Fig3. The western immunoblotting results of MRC2 in 3 pairs of representative HCC tissues (T) and adjacent liver tissues (N).
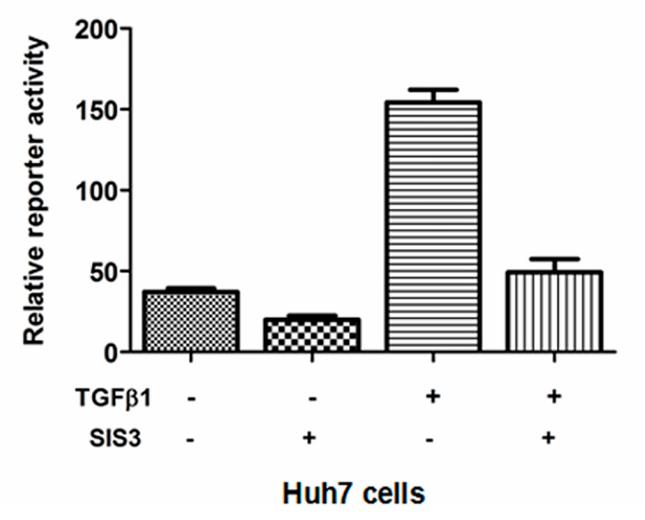
Fig4. The luciferase reporter assay showed that TGFβ1 treatment leaded to more MRC2 luciferase activity in Huh7 cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (MRC2-825H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (MRC2-5535H)
Involved Pathway
MRC2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways MRC2 participated on our site, such as Phagosome,Tuberculosis, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with MRC2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Phagosome | Itgam&Itgb2,ATP6V1F,HLA-DOB,HGS,ATP6V1E1B,TUBA3B,TUBA8,FCGR2B,HLA-DRB4,cgr2b |
| Tuberculosis | Itgam&Itgb2,CARD9,CAMP,HLA-DRB1,HLA-DQA1,BAD,ATP6V0B,TLR1,RAB5C,FCGR1A |
Protein Function
MRC2 has several biochemical functions, for example, carbohydrate binding,collagen binding,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by MRC2 itself. We selected most functions MRC2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with MRC2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| carbohydrate binding | MAN2A1,CHIA,CD209B,PYGB,LGALS9L1,GALNT1,NOMO1,EMC7,KRT1,CD72 |
| protein binding | LEMD3,DLC1,ELANE,RLN3,ADORA1,PKD1L3,OPRK1,TMEM140,SYTL4,COQ7 |
| collagen binding | ASPN,USH2A,CTSB,LACRT,SERPINH2,GP6,CD44,PDGFA,CTSS,VWF |
Interacting Protein
MRC2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with MRC2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of MRC2.
PPM1D;XRCC3;BAG4;RAF1;PTPN1;AKT1;PAX2;PALB2;RB1CC1;ESR2;NDEL1;BRMS1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


