Mettl3
-
Official Full Name
methyltransferase-like 3
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- Insect Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- DDK
- Myc
- GST
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- Flag
Background
What is METTL3 protein?
METTL3 (methyltransferase 3, N6-adenosine-methyltransferase complex catalytic subunit) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 14 at locus 14q11. M3 is a protein that plays a key role in the human body and is involved in the methylation process of RNA. Specifically, METTL3 is the only catalytic subunit in the methyltransferase complex that catalyzes N6-methyladenylate (m6A) modification. m6A is one of the most abundant internal modifications on eukaryotic mRNA, and METTL3 plays an important role in regulating biological processes such as gene expression, cell proliferation, differentiation, and tumourgenesis. The function of METTL3 is not limited to its activity as m6A RNA methyltransferase, it also acts as a positive regulator that promotes mRNA translation independently of its methyltransferase activity. In addition, METTL3 is involved in regulating the methylation of pri-miRNAs, labeling them for recognition and processing by DGCR8. The METTL3 protein is consisted of 580 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 64.5 kDa.
What is the function of METTL3 protein?
METTL3 catalyzes the addition of a methyl group to the N6 position of adenosine residues in RNA, leading to the formation of m6A. This process is essential for proper mRNA function. METTL3-mediated m6A methylation can affect the stability of certain mRNAs, with implications for the regulation of gene expression. METTL3 can enhance the translation of certain mRNAs by promoting the circularization of mRNA, which facilitates the interaction between the translation initiation and elongation factors. METTL3's role in mRNA methylation can influence cell cycle progression and differentiation, which are critical for tissue homeostasis and regeneration. METTL3 interacts with other proteins, such as the translation initiation factor eIF4G, to modulate translation and potentially other aspects of RNA metabolism.
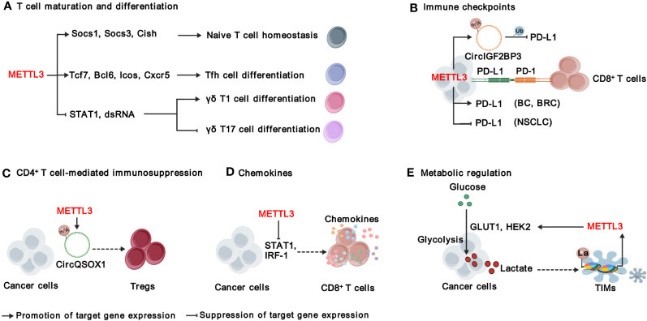
Fig1. Functions and mechanisms of METTL3 in modulating adaptive immunity. (Weiqi Su, 2024)
METTL3 Related Signaling Pathway
METTL3 is a key enzyme in the m6A methylation pathway, which influences RNA splicing, transport, translation and degradation by catalyzing N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification on mRNA. METTL3 affects colorectal cancer progression through the m6A-CRB3-Hippo axis, in which METTL3 knockdown activates the Hippo pathway. METTL3 affects osteoblast differentiation and SMAD-dependent signaling by regulating the mRNA expression and stability of Smad7 and Smurf1, negative regulators of Smad signaling. METTL3 knockdown enhanced the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and increased the phosphorylation of ERK, p38 and JNK in MAPK signaling pathway, regulating the LPS-induced inflammatory response. In the tumor microenvironment, METTL3-mediated m6A modification promotes the activation of JAK1-STAT3 signaling pathway and enhances tumor immune escape.
METTL3 Related Diseases
METTL3 has a novel role in inflammatory diseases, including cardiovascular, metabolic, degenerative, immune, and infectious diseases, as well as tumors. It also regulates the function of immune cells associated with inflammation, such as macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic cells, Th17 cells and NK cells. METTL3 plays a role in several types of cancer, including acute leukemia, liver, stomach, lung, and colorectal cancer. It is involved in the genesis and development of tumors by affecting the splicing, transport, translation and degradation of mRNA. Downregulation of METTL3 expression in osteoblasts is associated with enrichment of ribosome and translation-related genes, and knockdown of METTL3 inhibits biogenesis and oxidative phosphorylation of ribosomes in LPS-stimulated osteoblasts. In addition, it also includes some inflammation such as periodontitis, colitis and so on.
Bioapplications of METTL3
METTL3 is a key enzyme in m6A methylation, and its abnormal function has been associated with a variety of diseases, so the recombinant protein of METTL3 or its inhibitors may have applications in the treatment of related diseases, such as colitis, tumors, etc. METTL3 is a potential target for drug development, and researchers are searching for and developing small molecule inhibitors of METTL3 that could be used to treat METTL3-related diseases. The role of METTL3 in regulating immune cell function makes it potentially useful in the treatment of immune regulation and related diseases, such as autoimmune diseases and allergic diseases.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Peng Ouyang, 2024
The regulatory role of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification in the onset and progression of cancer has garnered increasing attention in recent years. However, the specific role of m6A modification in pulmonary metastasis of colorectal cancer remains unclear. This study identified differential m6A gene expression between primary colorectal cancer and its pulmonary metastases using transcriptome sequencing and immunohistochemistry. The researchers investigated the biological function of METTL3 gene both in vitro and in vivo using assays such as CCK-8, colony formation, wound healing, EDU, transwell, and apoptosis, along with a BALB/c nude mouse model. The regulatory mechanisms of METTL3 in colorectal cancer pulmonary metastasis were studied using methods like methylated RNA immunoprecipitation quantitative reverse transcription PCR, RNA stability analysis, luciferase reporter gene assay, Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay, and quantitative reverse transcription PCR. The results showed high expression of METTL3 and YTHDF1 in the tumors of patients with pulmonary metastasis of colorectal cancer. METTL3 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer by m6A modification of SNAIL mRNA, where SNAIL enhances the secretion of CXCL2 through the NF-κB pathway. Additionally, colorectal cancer cells expressing METTL3 recruit M2-type macrophages by secreting CXCL2.
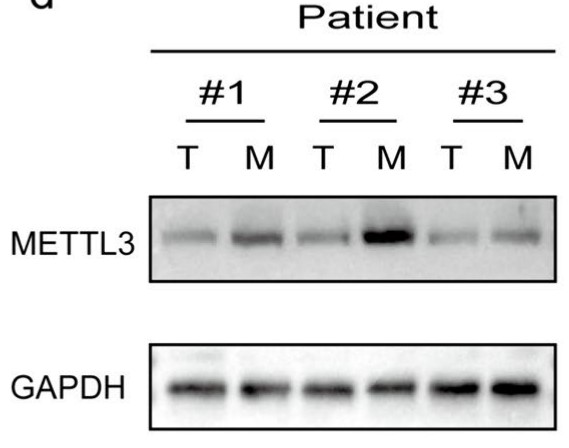
Fig1. Western blotting analysis of METTL3 protein expression in colorectal in situ carcinoma and pulmonary metastatic carcinoma.
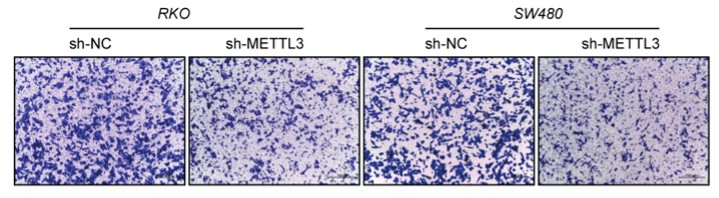
Fig2. Decreased expression of METTL3 restrained CRC cell invasion ability based on transwell assay.
Case Study 2: Guifang Li, 2024
Chemoresistance is a critical factor contributing to poor prognosis in clinical patients with cancer undergoing postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy. The role of gut microbiota in mediating resistance to tumour chemotherapy remains to be investigated. Differential bacterial analysis using 16S rRNA sequencing revealed Desulfovibrio as a distinct microbe between the two groups. Employing a syngeneic transplantation model, the researchers assessed the effect of Desulfovibrio on chemotherapy by measuring tumour burden, weight, and Ki-67 expression. We further explored the mechanisms underlying the compromised chemotherapeutic efficacy of Desulfovibrio using metabolomics, western blotting, colony formation, and cell apoptosis assays. In vivo experiments revealed that Desulfovibrio colonisation in the gut weakened the efficacy of FOLFOX. Treatment with Desulfovibrio desulfuricans elevates serum S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) levels. Interestingly, SAM reduced the sensitivity of CRC cells to FOLFOX, thereby promoting the growth of CRC tumours. These experiments suggest that SAM promotes the growth and metastasis of CRC by driving the expression of methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3).
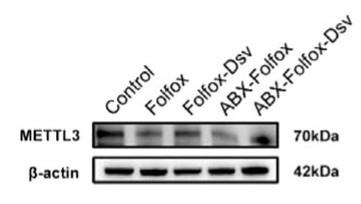
Fig3. The protein expression of METTL3 in mouse tumour tissues.
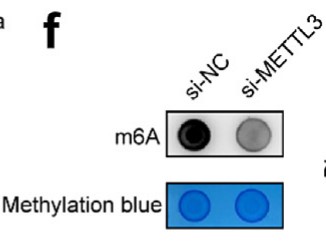
Fig4. Knocking down METTL3 resulted in a decrease in m6A methylation levels in DLD1 cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (METTL3-838H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (METTL3-610H)
Involved Pathway
Mettl3 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Mettl3 participated on our site, such as Gene Expression,Processing of Capped Intron-Containing Pre-mRNA,mRNA processing, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Mettl3 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Gene Expression | ZNF200,CLNS1A,TRMT44,ZBTB8OS,ZNF606,ZNF684,FAM36A,ZNF70,PPARAA,WHSC2 |
| mRNA processing | PTBP1,HNRNPD,RBM12B2,EIF4E3,HNRNPH1,RBMS3,VPRBP,RBM33,SFPQ,HNRNPAB |
| Processing of Capped Intron-Containing Pre-mRNA | HNRNPA0A,CSTF3,SF3B2,HNRNPA2B1,SF3A1,HNRNPUL1,SF3B4,PTBP1,HNRNPF,PTBP1B |
Protein Function
Mettl3 has several biochemical functions, for example, RNA binding,RNA methyltransferase activity,mRNA (2-O-methyladenosine-N6-)-methyltransferase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Mettl3 itself. We selected most functions Mettl3 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Mettl3. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| RNA methyltransferase activity | TRMT10B,TRMT2A,METTL23,METTL7B,MEPCE,PRDM12,PRMT8B,RNMTL1A,FAM86,NDUFAF5 |
| mRNA (2-O-methyladenosine-N6-)-methyltransferase activity | METTL14 |
| RNA binding | SRSF1,EIF1AXA,DOM3Z,Aff2,EYA1,RBFOX1,RPL11,EIF4B,RPL18,THOC3 |
Interacting Protein
Mettl3 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Mettl3 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Mettl3.
MYC;ACTR2;MPP1;WTAP;RBM15B;PPHLN1;METTL14;ROBO2;SEL1L
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Geula, S; Moshitch-Moshkovitz, S; et al. m(6)A mRNA methylation facilitates resolution of naive pluripotency toward differentiation. SCIENCE 347:1002-1006(2015).
- Yang, Y; Sun, BF; et al. Dynamic m(6)A modification and its emerging regulatory role in mRNA splicing. SCIENCE BULLETIN 60:21-32(2015).



