MALT1
-
Official Full Name
mucosa associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation gene 1 -
Overview
MALT-1 was independently identified as a member of the human paracaspase family and an interacting partner of B cell lymphoma. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms (a and b) have been described for the MALT-1 gene. Human MALT isoform a is an amino acid protein of 824 amino acids, and human MALT-2 isoform b is an amino acid protein of 813 amino acids. MALT-1 is thought to play a role in NFkappaB signaling by enchancing NF kappaB activation through interaction with BCL-10. Interaction between MALT-1 and BCL-10 mediates IKK activation in vitro through facilitating the ubiquitination of NEMO by the ubiquitin conjugating enzyme UBC13. -
Synonyms
MALT1;mucosa associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation gene 1;MLT;mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein 1;paracaspase;caspase-like protein;MALT associated translocation;MALT lymphoma-associated translocation;MALT-lymphoma associated translocation;MLT1;DKFZp434L132
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- GST
- DDK
- Myc
- His
- Trx
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is MALT1 Protein?
MALT1 gene (MALT1 paracaspase) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 18 at locus 18q21. MALT1 is a protein that performs an important function in the human body. It was originally discovered in lymphocytes as a human paracaspase protein that acts as a signal transduction adapter downstream of protein kinase C. MALT1 is involved in the formation of semaphone complexes that, together with caspase recruitment domain family member 11 (CARD11 or CARMA1) and B-cell CLL/ lymphoma 10 (BCL10), activate the IκB kinase (IKK) complex and nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) -induced gene transcription, Leads to the activation and proliferation of immune cells. The MALT1 protein is consisted of 824 amino acids and MALT1 molecular weight is approximately 92.3 kDa.
What is the Function of MALT1 Protein?
The MALT1 protein has a dual function: on the one hand as a scaffold protein to promote the activation of NF-κB transcription factor, and on the other hand as a protease to regulate signal transduction and immune activation by cutting different substrates. It acts primarily as a component of CARD11-BCL10-MALT1 (CBM) signaling complex and is essential for T cell receptor (TCR) and B cell receptor (BCR) mediated NF-κB activation. Abnormal activity of the MALT1 protein has been linked to a variety of diseases, including some types of cancer. In addition, MALT1 promotes the survival, proliferation, and metastasis of certain solid tumors and has an extracellular role in tumor development by maintaining the immunosuppressive function of regulatory T cells (TREGs) in the tumor microenvironment. Overall, the MALT1 protein plays an important role in immune signaling, inflammatory response, and pathogenesis of a variety of diseases, and is an important target for current biomedical research and drug development.
MALT1 Related Signaling Pathway
MALT1, as part of the CARD11-BCL10-MALT1 (CBM) signaling complex, plays a critical role in T cell receptor (TCR) and B cell receptor (BCR) mediated NF-κB activation. Through its protease activity, MALT1 promotes the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway, thereby regulating the activation, proliferation and differentiation of immune cells. MALT1 is involved in signaling that controls fungal infections. MALT1 also plays a role in inflammatory responses, for example by regulating T cell activation and cytokine production. MALT1 is necessary for the development of natural Treg cells and affects the number and function of Treg cells. MALT1 is involved in the activation of NF-κB and MAPK by regulating ITAM-coupled NK cell receptors, thereby selectively controlling cytokine production.
MALT1 Related Diseases
MALT1 plays a key role in regulating the NF-κB signaling pathway, and its abnormal expression is closely associated with the development of lymphoma, especially MALT lymphoma. The proteolytic activity of MALT1 can be modulated pharmacologically, making it a potential therapeutic target. In addition to blood tumors, MALT1 abnormalities are also associated with the occurrence and development of some solid tumors. Abnormal expression of MALT1 has also been associated with autoimmune diseases, such as those associated with non-gastric MALT lymphoma. Abnormalities in MALT1 may also be associated with other diseases, including cardiovascular disease
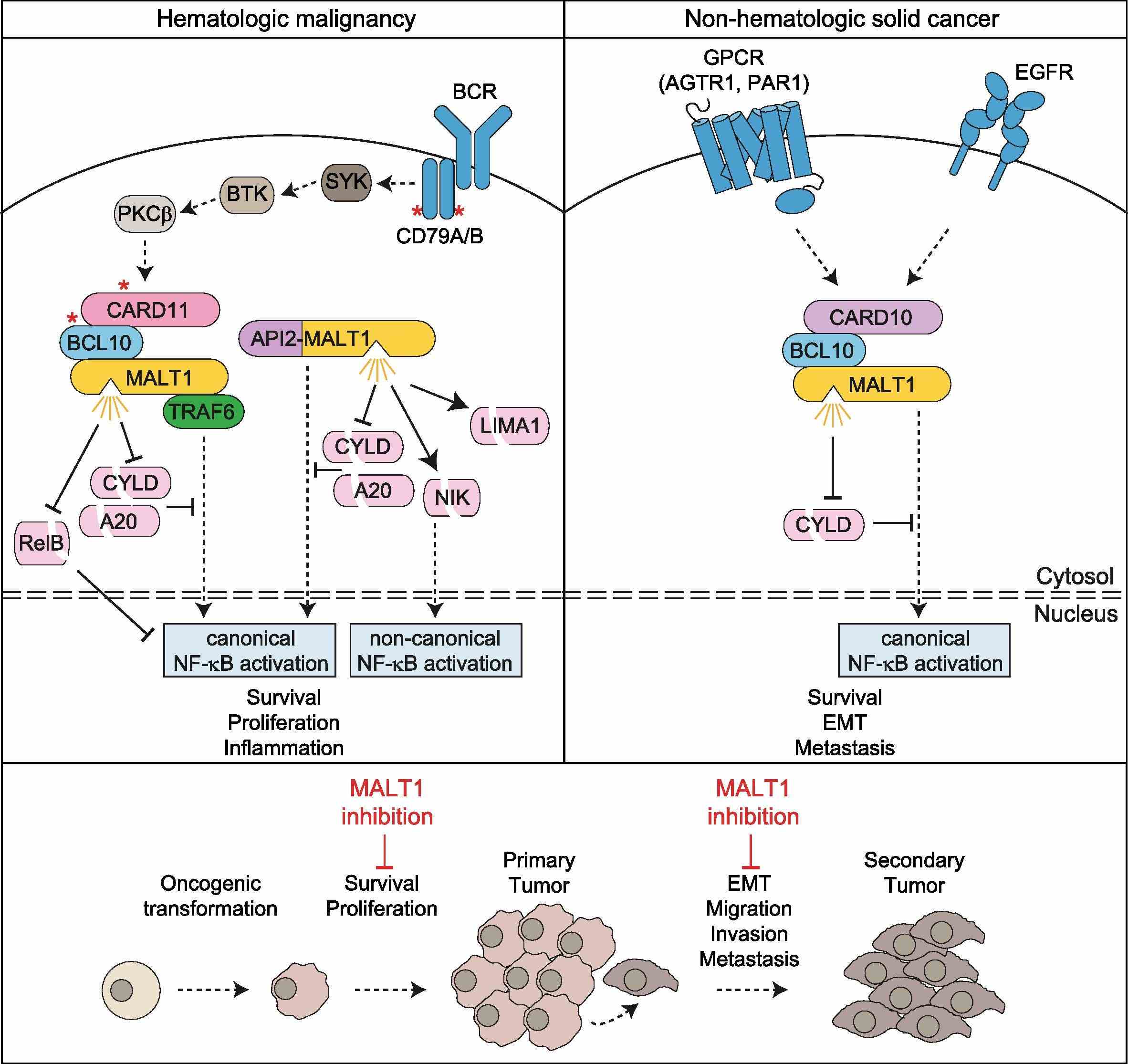
Fig1. Cancer cell-intrinsic effects of MALT1 protease activity and inhibition in hematologic and non-hematologic malignancies. (Thomas J O'Neill, 2023)
Bioapplications of MALT1
Studies of MALT1 inhibitors are being explored, including allosteric MALT1 protease inhibitors and specific covalent inhibitors, which provide new perspectives and approaches for the treatment of MALt1-related diseases. By blocking NF-κB signaling, MALT1 inhibitors may be effective in treating patients who do not respond to or have developed resistance to the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib. Malt1-directed PROTAC compounds can induce ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of MALT1, providing new possibilities for the treatment of activated B-cell type diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (ABC-DLBCL). The expression level of MALT1 can be used as a biomarker for tumor diagnosis and also play a role in evaluating the therapeutic effect of anti-tumor drugs.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Clément Maghe, 2024
Glioblastoma stem-like cells (GSCs) compose a tumor-initiating and -propagating population remarkably vulnerable to variation in the stability and integrity of the lysosomal compartment. Previous work has shown that the expression and activity of the paracaspase MALT1 control GSC viability via lysosome abundance. However, the underlying mechanisms remain elusive. By combining RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) with proteome-wide label-free quantification, researchers now report that MALT1 repression in patient-derived GSCs alters the homeostasis of cholesterol, which accumulates in late endosomes (LEs)-lysosomes. This failure in cholesterol supply culminates in cell death and autophagy defects, which can be partially reverted by providing exogenous membrane-permeable cholesterol to GSCs. From a molecular standpoint, a targeted lysosome proteome analysis unraveled that Niemann-Pick type C (NPC) lysosomal cholesterol transporters are diluted when MALT1 is impaired.
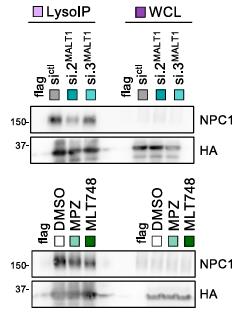
Fig1. WesternblotanalysisofNPC1fromFLAG-lysoandHA-lysoGSC#9LysoIPandWCLs..

Fig2. Confocal analysis of filipin-III and TMEM192-3xHA (HA) staining in HA-lyso GSC#9.
Case Study 2: Kathryn A Jacobs, 2020
Glioblastoma represents an exceedingly aggressive form of cancer in adults, typically allowing for a median survival time of approximately 15 months. A promising therapeutic approach is to target glioblastoma stem-like cells (GSCs), which are self-sustaining and capable of driving tumor initiation, persistence, and regrowth. This study revealed that an inverse relationship between the expression of the paracaspase enzyme MALT1—implicated in NF-κB activation by antigen receptors and in the survival of B-cell lymphomas—and the likelihood of patient survival. Silencing MALT1 resulted in a significant hindrance to the proliferation of stem-like cells derived from patients in vitro, an effect that could also be achieved using pharmacological agents both in vitro and in vivo. Inhibiting the activity of the MALT1 protease led to an increase in endo-lysosomal volume, a disruption in the autophagic process, and ultimately to cell death mediated by the lysosome. This was accompanied by the inactivation of mTOR and its detachment from the endo-lysosomal structure.
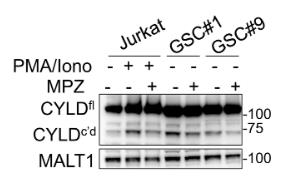
Fig3. Jurkat T cells, GSC#1, and GSC#9 were treated with vehicle (DMSO) and mepazine (MPZ, 20 μM) for 4 h.
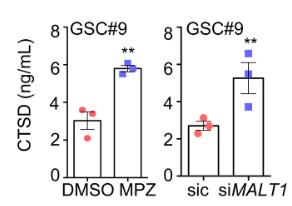
Fig4. CTSD ELISA was performed on culture media from GSC#9 treated for 8 h with vehicle (DMSO) or MPZ (20 μM).
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (MALT1-2551H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (MALT1-234H)
Involved Pathway
MALT1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways MALT1 participated on our site, such as Activation of NF-kappaB in B cells,Adaptive Immune System,B cell receptor signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with MALT1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| BCR signaling pathway | NETO2,PAG1,MAP4K1,CSK,IBTK,CSNK2A1,POU2F2,DOK1 |
| Activation of NF-kappaB in B cells | CHUK |
| Adaptive Immune System | MAPKAP1,Mill2,NCR3LG1,LILRA2,CD226,KIF3A,MKRN1,ASB2,SIGLEC5,KLHL20 |
| CLEC7A (Dectin-1) signaling | IL1B2,CASP8L1,UBE2V1,TAB1,AHCYL1 |
| CLEC7A/inflammasome pathway | IL1B2,CASP8L1 |
| Canonical NF-kappaB pathway | CYLD |
| C-type lectin receptors (CLRs) | CLEC6A,CLEC4D,ITPR2,CLEC4A,TAB1,IL1B2,CREBBP,AHCYL1,CASP8L1,UBE2V1 |
| B Cell Receptor Signaling Pathway | TTC6,PIK3R2,PILRB,PPP3R2,IGHM,NFKBIA,CD72,PLEKHA2,CRKL,PPP3CB |
Protein Function
MALT1 has several biochemical functions, for example, cysteine-type endopeptidase activity,contributes_to kinase activator activity,peptidase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by MALT1 itself. We selected most functions MALT1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with MALT1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein self-association | ZNF496,AGTR1A,PCSK9,NKX3-1,PTH1R,SHANK3,RYR2,PABPN1,EPB49,RSAD2 |
| protein binding | FSD2,MGP,MEIS1B,DYSFIP1,TBC1D17,CCND1,PDIA3,HIST1H4H,RTN4A,MAPK1 |
| cysteine-type endopeptidase activity | USP12A,CTSSB.2,CASP3A,CASP8L1,USP45,CTSL1B,CASP2,CTSO,USP19,USP2 |
| protease binding | LDLR,CSTA,Cstb,FURIN,CD70,FAP,SERPINA1,CRADD,RNF139,CAST |
| peptidase activity | ELANE,LGMN,PSMB9B,NPSN,FAP,NAALADL1,TMPRSS5,MASP1,PCSK5,MCPT9 |
| contributes_to kinase activator activity | BCL10 |
| ubiquitin-protein transferase activity | NEDD4L,FANCL,RNF130,UBE2D3,TRIM68,BTR22,TRAF4,FBXO25,TOPORS,UHRF1 |
| signal transducer activity | PLCD3A,STAT1A,FKBP1A,FPR-RS6,BAI2,TAAR15,COPS2,OLFR510,EMR4,TAAR14J |
Interacting Protein
MALT1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with MALT1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of MALT1.
BCL10;UBC;SQSTM1;IKBKG
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Zhao, XQ; Zhu, LL; et al. C-type Lectin Receptor Dectin-3 Mediates Trehalose 6,6 '-Dimycolate (TDM)-induced Mincle Expression through CARD9/Bcl10/MALT1-dependent Nuclear Factor (NF)-kappa B Activation. JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY 289:30052-30062(2014).
- Chinen, J; Notarangelo, LD; et al. Advances in basic and clinical immunology in 2013. JOURNAL OF ALLERGY AND CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY 133:967-976(2014).



